Bad Welding: How to Detect, Prevent & Repair?
 Apr 21,2025
Apr 21,2025

Welding defects are flaws that appeared during different types of welding procedures. Welding processes are utilized in manufacturing for joining materials for bridges, buildings, automobiles, pipes, aircraft and many more. However, these defect affect its applications and demands. This article will explore the reasons why these defects occur and how they affect internally and externally the materials.
What Is Welding?
It is fabrication method to join the metals by melting and fusing them with each other with a filler metal. A bond permanent bond is created called weldment by using heat and pressure to fuse the metal. It has become a fundamental method in manufacturing, construction and repairing material in different industries.
10 Types of Welding
Welding are categorized based on arc welding (SMAW, GMAW, GTAW, FCAW, SAW), oxyacetylene welding and other different methods.
|
Welding types |
Description |
|
1.Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) |
A coated electrode provides shielding to create a weld |
|
2.Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW/MIG) |
A continuous electrode wire is used and a shielding gas used to create a weld |
|
3.Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW/TIG) |
a non-consumable tungsten electrode and a shielding gas are used to create preciseweld |
|
4.Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW) |
similar to MIG but electrode is a flux-coated wire. |
|
5.Submerged Arc Welding (SAW) |
Submerged electrode in a granular flux is used to protect the weld pool |
|
6.Oxy-Acetylene Welding |
a flame to heat and fuse the metal and creates a weld pool |
|
7.Plasma Arc Welding (PAW) |
similar to TIG process with more constricted arc and produce precise welds |
|
8.Resistance Spot Welding |
creates small pot welds by using electrical resistance to heat the metal. |
|
9.Laser Beam Welding (LBW) |
A laser beam is used to melt the metal and create welds |
|
10.Electron Beam Welding (EBW) |
An electron beam with high velocity creates deep and high-quality welds. |
Bad Welding vs. Good Welding: A Life-or-Death Comparison
Bad weld examples are cracks, porosity, penetration which weaken the structure. It eventually leads to material failure under stress or loading conditions. In critical applications, it can cause accidents, collapses or even loss of life. Whereas a good weld has smooth surface, consistent quality and full penetration.
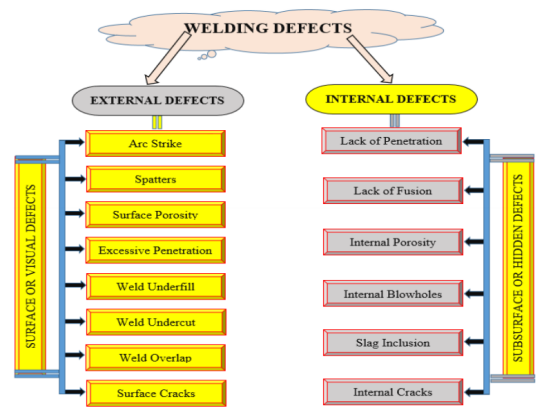
1. Visual Appearance
Bad weld appears as incomplete fusion and penetrations, cracks, excess slag, porosity, and spatters. A good weld has a uniform, smooth surface with no cracks or holes or undercut.
2. Structural Integrity
Bad welds has weak joint which comprises the structural integrity and can lead to potential failures. Perfect welds structures has high strength and durability and proper welding ensures reliable joints.
3. Causes of Defects
Bad welds are caused by improper welding parameters, poor techniques and environmental condition. These all has a drastic effect on structural integrity and strength of material and cause failures.
4. Real-World Impact
The real-world bad weld examples are:
- Bridges: weak bridge could collapse and cause fatalities and injuries.
- Pressure vessels: bad welded pressure vessesl can vurst and cause explosion
- Airplane: bad welds in airplane parts can cause structural failures and catastrophic crash
A good welds examples are:
- Bridges construction: perfect welds can connect steel beams, girders to form a strong bridge framework
- Manufacturing:in automotive and aerospace industries, good welds ensures durable and safe vehicles for passengers.
- Pipelines: welding connects pipes to transport, oil, gas and water to prevent leaks and spill
How Can You Tell If a Weld Is Bad? -Tips For Detect
Bad welds can be identified by visual inspection and non-destructive testing. If cracks, porosity, or incomplete fusion are visible, it indicated bad weld
What Should a Perfect Weld Look Like? Visual Indicators
A perfect weld is clean, smooth, uniform, flat bead and consistent profile. It is free of holes, cracks or an flaws.
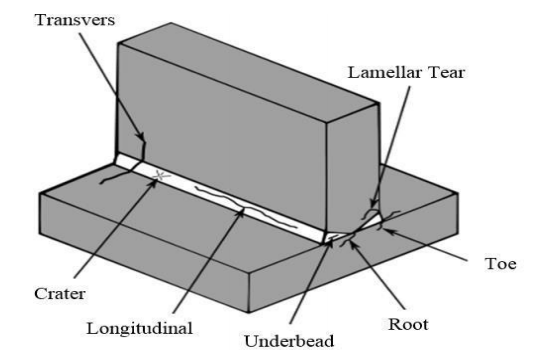
What Makes a Weld Structurally Sound? -Integrity Checks
A structurally sound weld has consistent bead formation, no cracks or holes and has proper fusion and penetration and finished product has no structural distortion.
What Are The Industry Standards of Welding?
Welding standards like BS EN ISO-15614 outlines the requirements of qualifying welding procedures. BS-EN-ISO-9606 and AWS-D1.1 specify the process and qualification to perform welding tasks.
What Are The Common Bad Welds In Different Welding Methods
Different welding methods show different bad weld which are discussed below:
MIG Welding: Burn-Through & Poor Gas Coverage
Burn-through occurs due to excessive heat melts by base metal. Poor gas coverage in MIG leads to defects due to environmental conditions
TIG Welding: Tungsten Contamination Issues
TIG welding result in tungsten inclusion which weaken the weld and cause cracks. Contamination also be caused by the improper shielding gas flow.
Stick Welding: Slag Inclusion & Arc Strikes
Bad stick welds are Slag inclusion occurs by entrapping of non-metallic by product in the weld and arc strikes occurs when arc is struck on metal outside of intended welded area during stick welding.
Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW) Pitfalls
FCAW has man pitfalls like high consumable costs, more fumes and smoke,slag buildup and welding defects like porosity or undercuts,
Dissimilar Metal Welding: High-Risk Scenarios & Solutions
High-risks scenario in welding dissimilar metals welding are materials with different strength, composition and thermal coefficient. Solutions are proper preheating and material selection and specialized welding methods and filler metal use.
Key Challenges of Dissimilar Metal Welding
One of major challenging in dissimilar metal welding are different melting points, risk of galvanic corrosion, and different properties and thermal expansion. This results in structural distortion, weak joints and crack. Common examples are welding aluminum to steel, copper to aluminum, nickle alloys to steel and mild steel to stainless steel.
How To Better Weld Dissimilar Metals?
It involves using careful material selection, process control to mitigate welding defects, and proper filler metal choice. Transition material like coating or interlayers can connect compatibility gaps and improves weld quality
How To Fix Bad Welds: Salvage or Scrap?
Salvage is removing defected weld or re-welding the area but it depends on weld type, application and level of damage. Scraping is removing the defected area b grinding or gouging. Salvage is more cost-effective than scrap.
Grinding vs. Re-Welding Strategies
Grinding mainly focuses on shaping, smoothing and removing defects like spatter. Re-welding is adding a new weld metal to reinforce or repair the flaws like improper penetration or undercut
Cost Analysis: Repair vs. Replacement
Repairing is more cost-effective than replacement but frequent repairing can be costly than replacement. Factors like material accessibility, cost of downtime and type of defects, all are depend on fixing bad weld strategies
How To Prevent Bad Welds?
Bald welds can be prevented b focusing on preparation, process control, proper preheating and post-weld treatments, and skilled execution.
Machine Settings for Common Metals
A general rule of thumb is used of 1amp for every 0.001inch of material thickness, for example 1/8ich thick steel require 125 amp
Electrode Selection Guide
Electrode are classified with AWS classification which outline the material composition, welding positions and coating
Environmental Factors
These are like release of fumes, gasses and consumption of material and energy. Air pollution and climate change like wind or temperature can cause improper welding results.
Conclusion
Bad welding a re welding defects that can be identified by visual inspection and non-destructive testing. It can be prevented by careful material selection and preparation, proper training, process control and repairing it by removing flaws and re-welding. Bad weld examples are holes, porosity, undercut, lack of fusion and penetration.
FAQs:
Can a Bad Weld Be Fixed?
Yes, bad weld can be fixed by repairing the weld area or replacing it with a new weld depending on weld defect and applications
How Long Does a Bad Weld Last?
A bad weld can last up to several years or decades depending on factors like type of metal or severity of defects.
Is Bad Welding Illegal?
No, its not illegal itself but failure compliance with OSHA/ASME standards in industries can lead to violations and legal consequences
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 CNC Machining Espresso Machine Parts List: Process & Surface Finish
CNC Machining Espresso Machine Parts List: Process & Surface Finish 







