What is the Melting Point of Titanium?
 May 31,2024
May 31,2024

By understanding them, you will see why people prefer titanium. Industries such as aerospace, medical, and manufacturing use it. Its melting point impacts its use in many industries. It has a high melting point. This, combined with its other unique properties, makes it invaluable. It's crucial in fields where performance under extreme conditions is key. This post will provide detailed information. It will help you see the critical role titanium plays in modern engineering and design.
What is Titanium?
Titanium is a lightweight, high-strength metal known for its excellent corrosion resistance. Companies use titanium in aerospace, medical devices, and chemicals. This material's unique strength-to-weight ratio makes it perfect for planes.
Chemical Properties
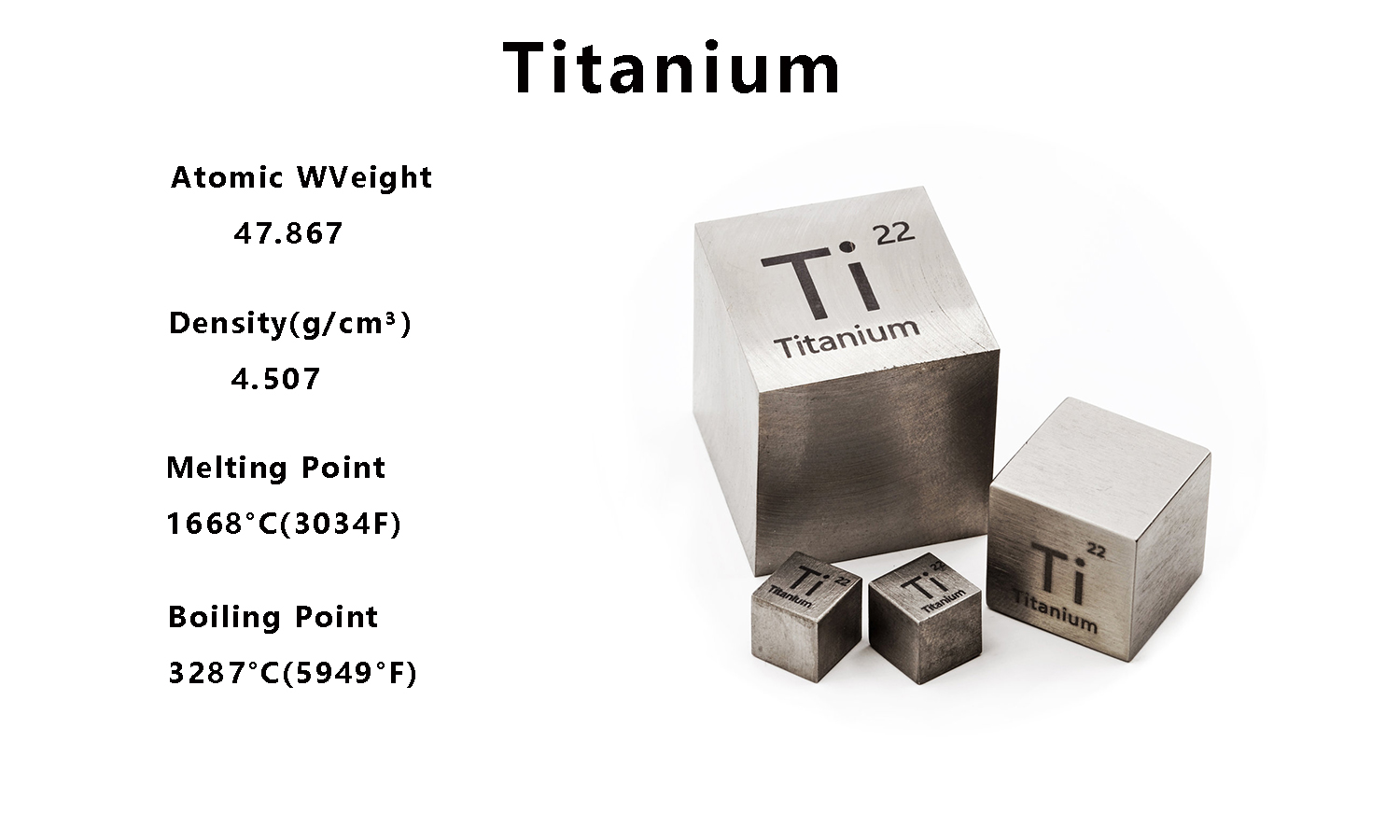
Titanium has the atomic number 22 and symbol Ti. It is a lustrous transition metal known for its silver look. It occurs in various minerals such as rutile and ilmenite. Titanium has five common isotopes. It's the most abundant, making up about 73.8% of natural titanium.
Physical Properties
Titanium's impressive combination of physical properties has a renowned reputation. It has a density of 4.506 g/cm³. This is much lower than steel, but with comparable strength. Its hardness ranges between 6 and 6.5 on the Mohs scale, and it boasts a tensile strength of around 434 MPa. Additionally, titanium exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance, especially against seawater and chlorine.
Melting Point of Titanium
The melting point is the temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid. This happens at atmospheric pressure. It's a key physical property. It shows how stable a material is to heat.We measure melting points using techniques like DSC. We use a high-temperature furnace with precise temperature controls. It also allows for observation. Titanium has a melting point of 1668°C (3034°F). High-temperature environments need materials with a high melting point. This material fits the bill due to its key characteristic. Titanium's melting point is much higher. Aluminum's melting point is 660°C.However, it is lower than that of refractory metals like tungsten, which melts at 3422°C. This makes titanium ideal for applications. They need a balance of weight, strength, and temperature resistance.
Factors Affecting the Melting Point of Titanium
Changing the diffusion mobility of atoms in titanium can alter its melting point by up to 450 °C . This is why some titanium alloys have higher melting points.
Alloying Elements
Titanium alloys, like Ti-6Al-4V, have aluminum and vanadium. These elements enhance their mechanical properties. These alloys have a lower melting point than pure titanium. This is because they contain alloying elements that disrupt the metal's lattice. For example, the Ti-6Al-4V alloy melts at 1604-1660°C. This range is a bit below pure titanium's. But it's still good for high heat. Manufacturers use this alloy in aerospace and medical implants.
Purity of Titanium
The presence of impurities can affect the melting point of titanium. Industrial-grade titanium has more impurities. It generally has a lower melting point than high-purity titanium. High-purity titanium is often used in critical applications. It keeps its high melting point and good properties well. It does this better than its industrial counterpart. This difference is crucial. It matters in fields like aerospace and medical. These fields need materials that perform well.
Environmental Conditions
Pressure and the air can change the melting point of titanium. These are external conditions. High pressure can increase the melting point. In a vacuum or inert atmosphere, it stays at standard values.Measurements taken in labs may differ from those in the real world. This is due to these factors. Understanding these variations is vital for practical applications. Titanium components must perform well under varying conditions.
Importance of Titanium's Melting Point in Industries
Titanium's high melting point, low weight, and strength make it ideal for specific uses. It is used in airplanes, missiles, and rockets. Durability and heat resistance are crucial for these applications.
Aerospace
Titanium is extensively used in aerospace for manufacturing jet engine components and airframes. Its high melting point ensures it can withstand the extreme temperatures of flight.Titanium has a high melting point. This helps it last a long time in aerospace. It cuts the need for frequent maintenance and replacements.
Medical
Applications in Prosthetics and Implants.Titanium is perfect for medical implants and prosthetics. It's biocompatible and has a high melting point. High temperatures sterilize titanium without degrading it. This ensures the safety and longevity of medical devices. Titanium can endure high sterilization temperatures without losing strength. This makes it a preferred material in the medical field. It enhances the lifespan and reliability of implants.
Manufacturing and Engineering
In manufacturing, titanium has a high melting point. This allows for precise CNC machining and fabrication. At Tuofa, we use advanced techniques to handle titanium well. We use them to make high-quality parts for many industries. At Tuofa, we specialize in machining titanium. We use top equipment and experienced professionals to deliver great products. Our products meet strict industry standards.

Titanium Melting Point vs. Other Metals
Titanium melts at 3135°F (1725°C), about 400°F higher than steel and 2000°F above aluminum. It is lightweight, strong, corrosion-resistant, and abundant in nature.
Titanium vs. Steel
Titanium has a higher melting point: 1725°C. This is above the 1370-1510°C of steel. Also, titanium has a better strength-to-weight ratio. These properties make it great for critical applications. They matter for weight and heat.
Titanium vs. Aluminum
Aluminum melts at 660°C, much lower than titanium. But, titanium is strong and corrosion resistant. This justifies its use in tough environments, despite the higher cost.
Titanium vs. Nickel-based Alloys
Nickel-based alloys, such as Inconel, have high melting points (up to 1390°C-1425°C). They also resist oxidation well. But, titanium has lower density and a good melting point. These balance its downsides for aerospace and medical uses.
Performance in High-Temperature Environments
Materials designed for high-temperature environments must withstand extreme heat without losing strength or integrity. This capability is crucial for applications in aerospace, automotive, and industrial sectors.
Strength Retention
Titanium maintains its strength at high temperatures better than most other metals. This makes it suitable for high-stress applications like turbine blades and engine parts.
Oxidation Resistance
Its great oxidation resistance at high temperatures. This quality also makes titanium a good fit for high-temperature applications. It cuts the risk of failure from oxidation.
Innovations in Titanium Processing
Recent innovations have improved titanium processing. These enhancements have increased efficiency and quality. Costs have been reduced. This has expanded titanium's use in aerospace, medical, and automotive industries.
Electron Beam Melting
EBM is an advanced technique used to process titanium. It allows for precise control over melting and solidification. This results in better material properties.
Plasma Arc Melting
PAM is another new method to refine titanium. It produces high-purity titanium by removing impurities with high-temperature plasma.
Common Myths and Facts
One common myth is that titanium is difficult to machine due to its high melting point. In reality, with the right techniques and equipment, titanium can be machined effectively.Studies confirm that titanium's high melting point is a big advantage. It offers durability and performance that surpass many other materials. This is true for many applications.
Conclusion
In short, titanium has a high melting point. It is also strong, resists corrosion, and is biocompatible. These properties make it essential in aerospace, medical, and manufacturing. Understanding the factors that affect its melting point is key. Knowing the latest processing innovations can help you make smart material choices. We've invite you to explore Tuofa's titanium machining services. You can find them at Tuofa (https://www.tuofa-cncmachining.com). Our expertise and advanced capabilities ensure that we can meet your needs. We provide high-quality titanium components. They excel in performance and durability. It's contact us today to learn more about how we can assist you with your next project.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 Exploring Ultem 1000: A Comprehensive Guide
Exploring Ultem 1000: A Comprehensive Guide 







