Types, Properties, and Applications of PP Copolymer: A Comprehensive Guide
 May 29,2024
May 29,2024

The carbon polymer chain having hexane, ethylene, and butene substitutional groups is called polypropylene which is a thermoplastic polymer. Polypropylene copolymer is an industrial plastic used in a wide range of applications. Commodity plastics copolymer and homopolymer both have different properties and are used for different applications. Homopolymers are rigid due to additional comonomers' presence while copolymers are flexible in general. In this article, you will understand polypropylene copolymers in detail and see the difference between their types and their applications.
What is Polypropylene Copolymer?
Polypropylene thermoplastic copolymer due to its versatility and cost-effectiveness is used as industrial plastic. Polypropylene copolymers are fabricated by the addiction of comonomers one or more during polymerization with polypropylene. Polypropylene copolymer also works as commodity plastic due to its excellent stress crack resistance and is a very safe material for a wide range of applications. Polypropylene thermoplastic copolymer has chemical structures with long polymer chains. This polymer chain has two types of polypropylene copolymer which are a random copolymer or block copolymer.
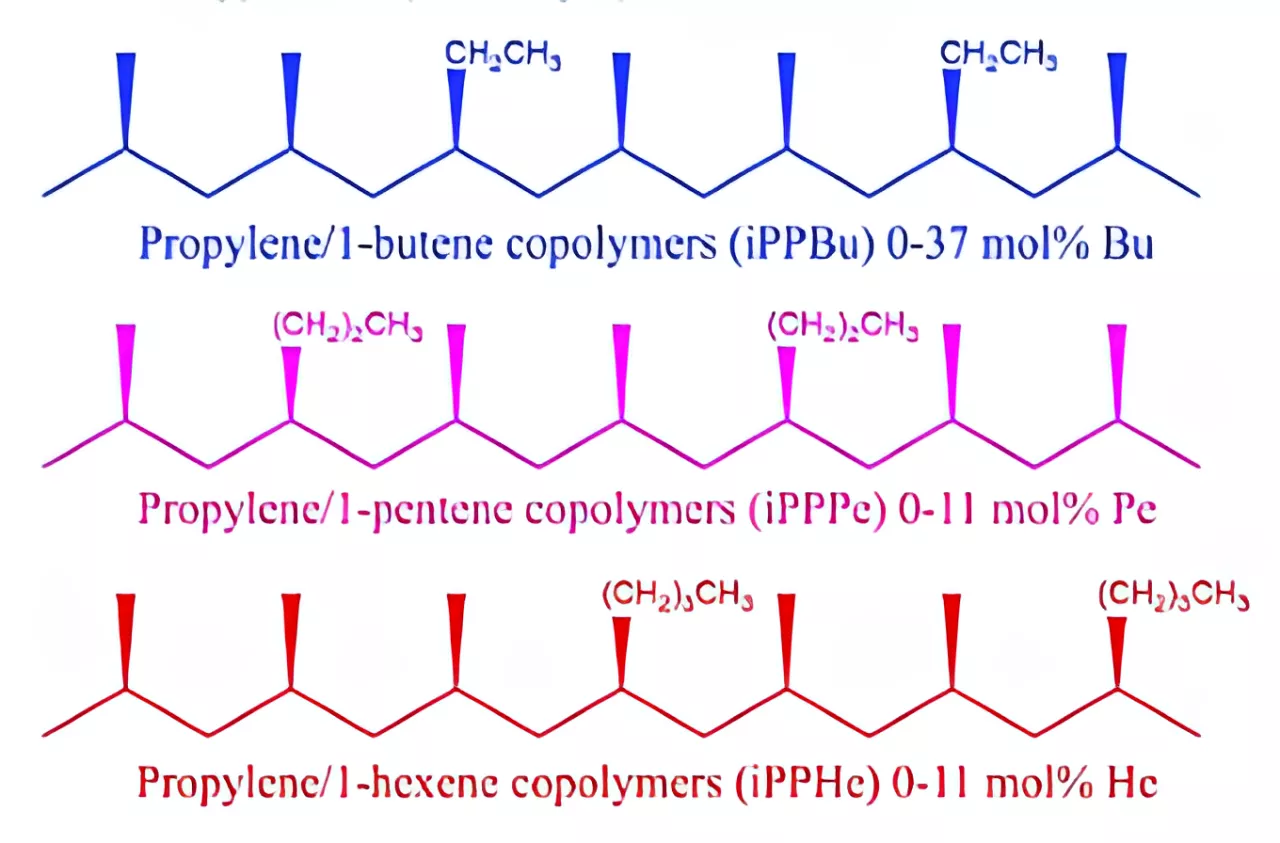
Structures of different polypropylene fabricated by incorporation of different comonomers.
PP copolymer has excellent flexibility, stress crack resistance, transparency, and chemical resistance. PP copolymers have low density and melting point compared to other commodity plastics.

Polypropylene Copolymer
YouTube video explaining polypropylene copolymers.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HrKJgsNVISE&pp=ygUdcG9seXByb3B5bGVuZSBjb3BvbHltZXIgdHlwZXM%3D
Types of PP Copolymer
The presence of the ethylene group in the PP copolymer distinguishes the different types of copolymers. The amount of ethylene and the way ethylene is incorporated into the PP copolymer cause variations in the characteristics of PP copolymer types. Three basic types of PP copolymer include impact, block, and random copolymer. Impact and random copolymer are discussed below.
Impact Copolymer
Impact copolymers are fabricated with exceptional mechanical properties like excellent stress crack resistance and impact resistance making them desirable industrial plastic, especially for automotive applications and auto electrical systems. These applications require material to withstand high mechanical stresses and vibrations, so an impact copolymer is the best choice. Impact copolymer provides shock and vibration resistance to electrical components for their efficient working and is a reliable material for auto electrical systems. Impact copolymers are also used in applications like fuse boxes, wiring harness components, battery housings, and electrical connectors.
Impact copolymer sheets.
Random Copolymer
In a random copolymer, the random distribution of ethylene monomers along the polypropylene polymer chain is seen. Random polymers have high clarity and transparency in contrast with homopolymer PP. The random copolymer has a low melting point and high flexibility. In comparison with homopolymer PP the Random copolymers have low stiffness. Random copolymers are used in applications like food containers and packaging, storage bins, kitchen utensils, diapers and sanitary napkins, blister packs, medical trays, etc.
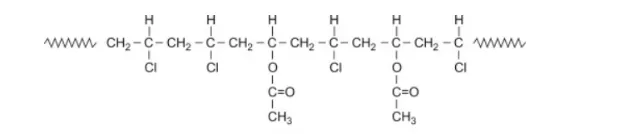
Chemical structure of random copolymer.
YouTube video explaining random copolymers and their applications.
Homopolymer Polypropylene vs Copolymer Polypropylene
Homopolymer only includes propylene monomer units while copolymer polypropylene consists of different monomer units incorporated with propylene monomer units. The key differences between them are listed below.
|
feature |
Homopolymer Polypropylene (PP-H) |
Copolymer Polypropylene (PP-C) |
|
Composition |
Only propylene monomer units |
Propylene incorporated with other monomer units like ethylene |
|
Types |
Single type |
Random Copolymer Block Copolymer (Impact Copolymer) |
|
Crystallinity |
Higher crystallinity |
Lower crystallinity |
|
Stiffness |
Higher stiffness |
Lower stiffness |
|
Impact Resistance |
Lower impact resistance |
Higher impact resistance |
|
Flexibility |
Lower flexibility |
Higher flexibility |
|
Transparency |
Lower clarity |
Higher clarity especially in random copolymer |
|
Chemical Resistance |
Excellent chemical resistance |
Slightly less chemical resistance in contrast with homopolymer |
|
Melting Point |
Higher melting point range from ~160-165°C |
Slightly lower melting point range from ~135-159°C |
|
Density |
0.904-0.908 g/cm³ |
· 0.898-0.900 g/cm³ Impact Copolymer · 0.904-0.908 g/cm³ Random Copolymer |
|
Applications |
· automotive parts · pipes · fittings |
· Flexible packaging · medical devices · automotive components · consumer goods |
|
Cost |
lower cost |
added comonomers and processing make costs higher |
|
Thermal Expansion |
Lower coefficient of thermal expansion |
Higher coefficient of thermal expansion |
|
Processing |
higher rigidity allows smooth processing |
Has to manage impact and flexibility during processing. |
|
Stress Crack Resistance |
Lower stress crack resistance |
Higher stress crack resistance |
|
Typical Use Case Examples |
· Pipes · rigid containers · household goods |
· Packaging films · medical applications · automotive parts |
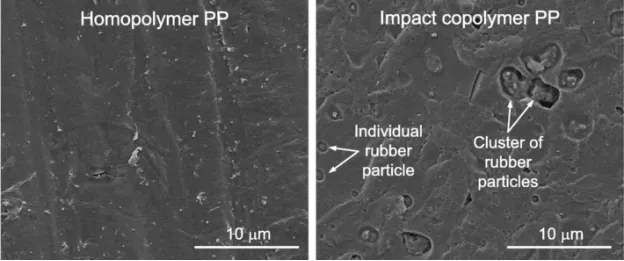
Microstructure shows a clear difference between homopolymer and impact copolymer.
Pros and Cons of PP Copolymer
PP copolymer is an engineering material due to its unique properties used in different applications that's why also called industrial plastic. The pros and cons of PP copolymer are discussed below which would help you in choosing the best application for PP copolymer.
Pros
- Improved impact resistance
- Improved flexibility allows ease of forming and processing.
- Transparency and clarity
- Properties can be changed by adjusting comonomer ratios.
- Good impact resistance and stress cracking resistance.
- Cost-effectiveness.
- Water-repellent plastic which helps them to work well in humid environments and water.
- Excellent resistance against steam sterilization[8].
Cons
- Low stiffness causes a lack of rigidity.
- Randon copolymer and block copolymer thermoplastics become embrittle at low temperatures below -20 °C.
- Degrade in the presence of UV rays.
- Limit to work at high temperature of 90-120°C above this it would start deteriorating.
- Don’t show good resistance in aromatic and chlorine solvents so becomes swell and loses its properties.
- The crystallinity effect causes a change in dimension in post-molding.
- Don’t allow paint to adhere[9].
Chemical Properties
- Polypropylenes are considered safe in making containers of cleaning solution due to their ability to show good resistance to diluted acids and bases.
- Poor chemical resistance to halogenated solvents of polypropylene thermoplastic polymer makes them swell and deteriorate their properties so are not considered safe to use in halogenated solvents.
- Polypropylene doesn’t absorb water and is hydrophobic so is considered safe in water.
- Show good resistance to acids and alkalis but does get damaged in some oxidizing agents.
- Show good resistance to bleaches in general but hydrocarbons of chlorine cause swelling of Polypropylene copolymer and dissolve at high temperatures. So are not considered safe to use in chlorinated hydrocarbon environments.
- Polypropylene copolymers show poor resistance to UV rays, so we add UV stabilizers during polypropylene fabrication which provide then resistance to UV rays[10].

Polypropylene cleaning solution containers.
Molecular structure – tacticity
The arrangement of the pendant groups concerning backbone polymer chains refers to the tacticity of molecular structure. The physical properties of these industrial plastics depend upon the tacticity of molecular structure. There are three types of tacticity isotactic, atactic, and syndiotactic. The isotactic presence of substituent groups on carbon polymer chains is on the same side. These isotactic arrangements provide crystallization and efficient packing to the polymer chain. Syndiotactic polymer arrangement has substituent groups on opposite sides of the carbon polymer chain. This syndiotactic polymer arrangement also allows crystallinity. Atactic polymers don’t have any specific arrangement of the substitution groups along carbon polymer chains. These atactic arrangements result in an amorphous irregular structure [11].
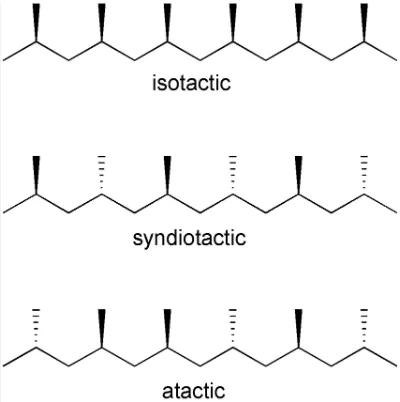
Three types of Molecular structure – tacticity.
YouTube video explaining the tacticity of polypropylene.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bFSZTJIdilU&pp=ygUhcG9seXByb3B5bGVuZSBjb3BvbHltZXIgaXNvdGFjdGlj
Crystal structure of polypropylene
There are three types of crystal structures of polypropylene given below:
Alpha (α) Phase
Alpha isotactic polypropylene is crystalline and is a more stable form. Alpha isotactic polypropylene has the structure of the monoclinic unit cell. In general, Alpha isotactic polypropylene has good tensile strength and stiffness. iPP is formed when the melted form is cooled at moderate rate.
Beta phase
The beta phase occurs very rarely it has a pseudo hexagonal unit cell structure with high toughness and impact resistance compared to the alpha state. The stiffness of the beta phase is less in contrast with the alpha phase. The beta phase fabrication is difficult because the cooling rate of the melt is controlled by adding specific nucleation agents.
Gamma phase
The gamma phase also occurs very rarely and has a triclinic unit cell structure found in copolymers and blends. The gamma phase of polypropylene copolymer is as much studied as the other two are that’s why you would not find much research on this. This Gamma phase is achieved by high-pressure crystallization and due to the presence of a specific comonomer.
Isotactic polypropylene (iPP)
The isotactic copolymer is industrial plastic with a high degree of crystallinity which is 30 to 60%. Isotactic polypropylene has substitutional groups attached to one side of the carbon polymer chain. Its more dominating phase is the alpha phase with a density of 0.936-0.946 g/cm³ and a melting point of 185-220°C. The isotactic arrangement led to high rigidity, stiffness, and creep resistance. Thermoplastic resins also have high crystalline isotactic structure arrangement.
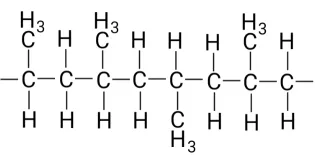
Isotactic Polypropylene.
Syndiotactic polypropylene (sPP)
syndiotactic polypropylene is a commodity plastic with a low melting point of 161-186°C. The melting point depends upon the tacticity degree. In sPP, the substitutional groups are arranged on opposite sides of the polymer chain. The fabrication of sPP can be prepared by metallocene catalysts [14].
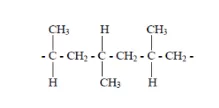
Syndiotactic polypropylene
Atactic polypropylene (APP)
Atactic polypropylene is an amorphous and irregular structure with random orientation of methyl groups along the carbon polymer chain. It lacks a crystalline structure.

Degradation
Polypropylene is considered non-degradable, but research has been conducted to focus on the degradation of polypropylene copolymer and found 3 methods of degradation discussed below.
Thermal degradation
The breaking of carbon bound at high temperatures causes the degradation of polypropylene copolymers. They degrade at a temperature range of 345°C to 493°C.
Microbial degradation
Fungus and bacteria are used to degrade polypropylene copolymer. Engyodontium album and Aspergillus terreus are used to degrade polypropylene copolymers.
Advanced oxidation process and chemical treatments
UV radiation and Fenton's reagent are used for the pre-degradation of polypropylene which is then microbially degraded. Potassium persulfates generate sulfate radicals which are also very useful for the degradation of polypropylene copolymer.
Optical properties
Optical properties like transparency, haze, gloss, light transparency, and clarity of different types of PP copolymer are given below in table.
|
Optical Property |
Homopolymer Polypropylene (PP-H) |
Random Copolymer Polypropylene (PPRC) |
Impact Copolymer Polypropylene (PPBC) |
|
Clarity |
Moderate |
High |
Moderate |
|
Transparency |
Low to Moderate |
High |
Moderate |
|
Haze |
Higher |
Lower |
Moderate |
|
Gloss |
Moderate |
High |
Moderate |
|
Light Transmission |
Moderate |
High |
Moderate |
Biaxially oriented polypropylene (BOPP)
Stretched polypropylene film from a transverse direction and machine direction are called biaxially oriented polypropylene. The biaxial orientation process enhances the film's mechanical and physical properties. The BOPP film has high gloss, clarity, and excellent moisture repellent used for packaging purposes.

Biaxially oriented polypropylene film.
Mechanical Properties
The mechanical properties of impact copolymer, random copolymer and homopolymer are compared below in the table.
|
Property |
Homopolymer |
Random Copolymer |
Impact Copolymer |
|
Density (g/cm³) |
0.904-0.908 |
0.904-0.908 |
0.898-0.900 |
|
Young's Modulus (MPa) |
1300-1800 |
1100-1600 |
900-1400 |
|
Yield Strength (MPa) |
30-40 |
25-35 |
20-30 |
|
Fatigue Resistance |
High |
Moderate |
High |
Thermal properties
The contract between thermal properties of random copolymer, impact copolymer and homopolymer are shown numerically below in table.
|
Property |
Homopolymer |
Random Copolymer |
Impact Copolymer |
|
Melting Point (°C) |
160-165 |
130-140 |
140-150 |
|
Crystallinity (%) |
50-70 |
30-50 |
25-40 |
|
Thermal Expansion (10^-5/°C) |
6-8 |
8-10 |
9-11 |
Electrical Properties
Electrical properties like dielectric constant, volume resistivity, dissipation factor, and dielectric strength of impact copolymer, random copolymer and homopolymer are numerically given below.
|
Property |
Homopolymer |
Random Copolymer |
Impact Copolymer |
|
Dielectric Constant (εr) |
2.2-2.6 |
2.2-2.6 |
2.2-2.6 |
|
Dielectric Strength (kV/mm) |
20-40 |
20-40 |
20-40 |
|
Volume Resistivity (Ω·cm) |
10¹⁶ |
10¹⁶ |
10¹⁶ |
|
Dissipation Factor (tan δ) |
0.0002-0.0005 |
0.0002-0.0005 |
0.0002-0.0005 |
Applications of PP Copolymer
PP copolymers can be used in the following applications:
- Auto Electrical Systems
- Bumpers and Exterior Parts
- Interior Components
- Housing for Appliances
- Electrical Components
- Pipes and Fittings
- Furniture
- Battery Cases
- Tool Housings

PP copolymer car bumpers.
Why Polypropylene Plastic is Commonly Used in CNC Machining Services
Polypropylene thermoplastic polymer is lightweight and has exceptional stress crack resistance making it suitable for different applications. Although polypropylene can melt and gall, that’s why CNC machining of polypropylene is difficult. CNC machining makes its surface slicky which makes it desirable for mechanical applications like gear. Thin features on the surface are developed very easily like living hinges by CNC machining.
Polypropylene thermoplastic polymer living hinges by CNC machining.
Conclusion
It is concluded that polypropylene copolymer which is also commodity plastic is used in vast applications due to its engineering characteristics and diverse types also called industrial plastic. Alpha, gamma, and beta phases are the crystal structure of polypropylene. Monoclinic unit cell structure is present in the Alpha phase. A Pseudo hexagonal unit cell structure is present in the beta phase and a triclinic unit cell is present in the gamma phase. The three-tacticity molecular structure decides the crystallinity of the polypropylene. Isotactic and syndiotactic polypropylene are crystalline while atactic is amorphous. The two major types of polypropylenes are random copolymer and block copolymer. Random polypropylenes have randomly oriented polymer chains that's why are flexible. While block polymer is rigid and has high impact and stress crack resistance.
FAQ
Is Polypropylene used as an alternative to polyvinyl chloride (PVC)?
Yes! Polypropylene and PVC both are thermoplastic polymers so can be altered in some applications but not in applications like medicine and construction because have different mechanical properties.
What role does the methyl group play in the properties of polypropylene?
Yes! In determining the polypropylene applications methyl group is very important. The presence of methyl group influences polypropylene characteristics like thermal properties, tacticity, crystallinity, stiffness, and strength.
How does PP copolymer perform in terms of chemical resistance compared to other plastics?
PP copolymer chemical resistance is far better than other plastics in general. Show good resistance to diluted acids, diluted bases, and fats in contrast to plastics. PP has poor chemical resistance in contrast to PVC but is better than polyethylene. Show excellent resistance to humidity but are microbial attack sensitive.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 What is the Melting Point of Titanium?
What is the Melting Point of Titanium? 







