Melting Point of Aluminum: A Complete Guide
 Oct 11,2024
Oct 11,2024

Aluminum (Al) is a versatile element. It is famous for its high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion properties and superior conductivity. However, one crucial feature which has impact on processing techniques and applications is the melting of aluminum. Melting point is an important parameter for metal transition from solid to liquid phase. Engineers and metallurgist always consider it a key element in any industrial process for high temperature applications. The importance of melting point of aluminum and its effect in multiple properties are discussed in this article.
What is the Melting Point of Aluminum?
Melting point is the temperature at which any solid converts to liquid state. The melting point of pure aluminum 99.99% is 660,37 ° C. There could be a slight difference in melting temperature with the difference in purity. For example, the melting point of 99.5% Al is 657 ° C and for 99.0 % Al is 643 ° C
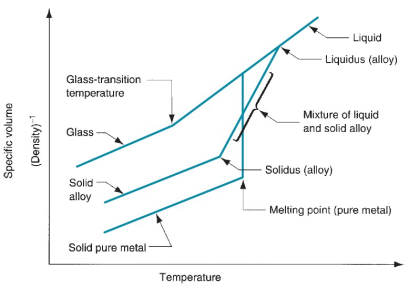
Understanding melting points
Melting Point of Aluminum in Kelvin
Melting point of Al in Kelvin is 933.5K.
Why is Melting Point Important?
Importance of melting point must be acknowledged because there is industrial, or high temperatures applications are involved. The aluminum casting temperature or aluminum welding temperature are important to be known. Insufficient or incorrect melting temperature can result in structural defects and weakness, poor production performance and errors in heat treatments, welding or any other methods. This can eventually lead to higher-end cost.
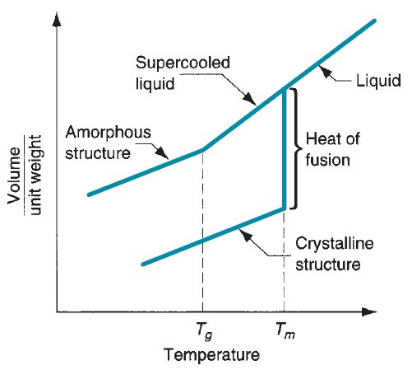
Change in volume for a pure metal (a crystalline structure) and glass (noncrystalline structure)
Boiling Point of Aluminum
The boiling point of Al is 2,470 °C. Higher boiling point means ions are packed closely together. This increases their bond strength and eventually the boiling pint.
Melting points of common aluminum grades
The melting temperatures of aluminum grades are significantly different than pure aluminum. This is because of their compositions, structure, forms of aluminum and the percentage of alloying elements.
- Aluminum Alloy 6061: melts at 580 – 650°C
- Aluminum 6061 T6: melts at 582 - 652°C
- Aluminum 7075: melts at 475 – 635°C
- Aluminum 2024: melts at 500 – 635°C
Aluminum Oxide Melting Temperature
Aluminum oxide has higher melting point than pure aluminum which is 2,072 °C. it is because aluminum oxide has ionic compound along with some covalent character. It has much stronger bond than pure Al which requires higher energy to break the bond while melting. This eventually results in higher melting temperature to get liquid phase.
The relationship between melting point and other physical properties of aluminum
Physical like thermal properties are directly related to the melting temperature of any metal. these properties are heat capacity, thermal conductivity and thermal expansion have an impact on how Al respond under different temperatures. Al I ductile or has ductile fracture behavior under all kind of temperature. But the lower temperatures or cryogenic temperatures change the materials properties. these changes can affect the toughness, durability, ductility and strength of aluminum.
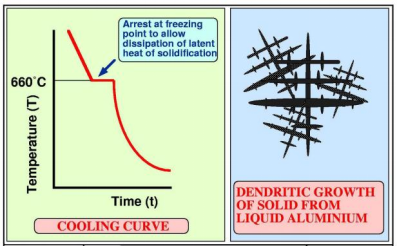
Solidification of Aluminum
Factors Affecting Aluminum's Melting Point
There are several factors that can affect the melting point of Al.
Purity and Alloying Elements
Purity of metal has a great influence on melting temperatures. If the amount of alloying element is higher, the melting temperature would be different than pure Al. if silicon and iron are added the melting point will be lower. But their addition has a great effect on properties like tensile and compressive strength.
The Role of Impurities in Lowering the Melting Point of Aluminum
Common impurities like copper, silicon or iron are added during extraction and processing of Al. The melting point decreases, and mechanical properties are increased with these additions. It initially affects the phase transition and stability of metal which then alters the melting points.
The impact of microstructures on the melting behavior of aluminum
If the grain size is smaller in microstructure, the melting point moves towards the lower point and decreases the heat of fusion. Coating on aluminum parts increases the melting point.
Pressure
Pressure also has a significant effect on the melting behavior of metal.
Effect of Pressure on Melting Point
If the pressure is high, melting point would be increase for aluminum. This implies when high pressure is applied, more heat is required to melt the metal. But only ice or water has a rare exception in this case. It melts when pressure applies.
Heating Rate
Melting behaviors also changes with the rate of heating.
Rapid Heating vs. Slow Heating
If the heating rate is slow, it allows more gradual and controlled changes in the structure. It results in an accurate determination of the melting temperature. Higher heating rate results in hemispherical temperature and lead to elevated melting temperature. This phenomenon is known as hysteresis of melting temperature.
Applications of Aluminum's Melting Point
Melting points can affect the casting, weldability, and heat treatment of aluminum.
Aluminum Casting
Aluminum casting temperature must be medium. Low melting temperature results in defects like shrinkage due to low fluidity. Higher temperatures can cause hot cracks and porosity in the final part.
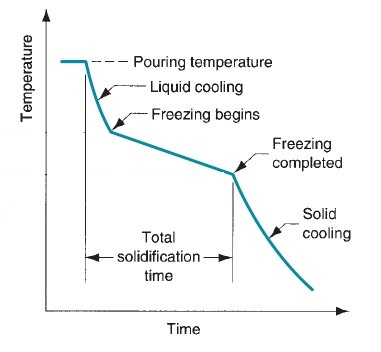
Cooling curve of Al casting
Aluminum Welding
Aluminum welding temperature must be appropriate to get welding results. Lower melting temperature can cause cold cracking. Temperature difference is directly related to rate of heat loss.
Fusion Welding Processes
The incorrect aluminum welding temperature can result in less fusion of weld metal into base metal. incorrect heat settings, or melting point can cause lack of penetration which can cause welding cracks.
Solid-State Welding Processes
Higher or lower aluminum welding temperature can weaken the welds. Lower temperature causes less penetration and cause weak weld spots. Higher temperatures weaken the aluminum parts due to excessive heat supply.
Measuring and Controlling Aluminum's Melting Point
Appropriate melting point and to ensure the correctly achieving the melting point is checked by measurement tools and by controlling parameters.
Temperature Measurement Tools
There are many temperature measurement tools like thermocouples, thermometers, temperature labels, pyrometers, thermistors, and smart sensors. Common tools are discussed below:
Thermocouples
It is a temperature measuring sensors. It consists of two different metal wires which connected by one end to the instrument. This can accept the input from thermocouple and measures the readings.
Pyrometers
This device measures relatively higher temperatures such in for furnaces. Most of them work by measuring radiation from the body of furnace. This has an additional advantage of safety to avoid contact with the hot furnace.
Melting Point Determination Methods
Melting point can be determined by many methods. The common ones are capillary method, differential scanning and hot stage microscopy.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
It is a thermal analysis apparatus. This measures the change of physical properties with the temperature and time. The temperature and heat flow related with the material’s behaviors with respect to time and temperature can be measured by DSC.
Hot Stage Microscopy
It is combination of thermal analysis and microscopy. This helps in studying the material’s behavior with respect to time and temperature.
Comparison of Aluminum's Melting Point to Other Metals
What Melts Faster, Aluminum or Steel?
Aluminum melts faster because it has melting of 660°C, and steel has 1370°C melting temperature.
Aluminum vs. Copper Melting Point
Al has lower melting point. Al melts at 660°C, while copper melts at 1084°C
Aluminum vs. Iron Melting Point
Al has lower melting point. Al melts at 660°C, while iron melts at 1510°C
Melting Point of Brass vs Aluminum
Al has lower melting point. Al melts at 660°C, while brass melts at 930°C
FAQ
What is the Easiest Metal to Melt?
Mercury has the lowest melting point which is -39 °C
Can a Gas Stove Melt Aluminum?
No, gas stove cannot melt aluminum because they do not have high-enough temperature that could melt aluminum.
Temperature and Heat Source
Temperature is equal to constant source of heat supply. If the temperature is high, the more heated the object would be.
What Metal has the Highest Melting Point
Tungsten has extremely high melting point metal which is 3,399°C.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 What is the Density of Copper? Calculation and Uses
What is the Density of Copper? Calculation and Uses 







