Getting Started with CAD: Tools, Types, and Tips
 Dec 20,2024
Dec 20,2024

Computer-Aided Design or CAD has revolutionized the designing process for engineers, architects, manufacturers, product developers and even fashion designers since its inception, and it still continues to do so as it advances and evolves. Let’s get a quick overview of how it impacts the whole designing process.
What is CAD?
As the name indicates Computer-Aided Design or CAD facilitates the designing process in a whole lot of industries with the use of computers and CAD software tools. It helps designers to use modern digital design solutions to design, visualize, analyse and optimize their designs effectively that would not have been easy or even possible in their hand drawn technical drawings.
Computer-Aided Design Examples
There are a whole lot of applications of CAD in various industries that include but are not limited to engineering, architecture, aerospace, manufacturing, fashion design, electronics, process design, medical technology etc.
What is the CAD System in Medical Terms?
Doctors and bio-technologists value the CAD systems for their benefits in the research and product development of critical medical support equipment and implants. As examples, high end products like stents for cardiac patients or hip and knee implants for orthopedic patients have brought wonders to the medical sciences. CAD has been quite instrumental to its design.
Types of CAD Software
CAD software come in a few types, each type specializing in some form of designing process. Some type of CAD tools facilitates architects in making blueprints, some assist product developers to visualize the design even before its created and some helps engineers to optimize designs with high precision.
|
Type |
Description |
Use Cases |
|
2D CAD |
Focuses on 2D drafting |
Architecture, schematics |
|
3D CAD |
Creates 3D models |
Product design, prototyping |
|
Parametric CAD |
Models with adjustable dimensions |
Mechanical design, engineering |
|
Direct Modeling CAD |
Flexible geometry editing |
Conceptual design, fast iterations |
|
Surface Modeling CAD |
Builds complex surfaces |
Automotive, aerospace design |
|
Solid Modeling CAD |
Models solid parts |
Mechanical components, assemblies |
|
Cloud-Based CAD |
Online, collaborative design |
Remote work, team projects |
|
CAM-Integrated CAD |
Combines CAD with manufacturing tools |
CNC machining, manufacturing |
2D CAD
2D CAD is the most suitable for drafting in two dimensions for applications like architectural blueprints. It comprises of lines, curves and arcs basically.
3D CAD
3D CAD is suitable for 3D modelling of products. It facilitates to draw, design, analyse and optimize a product design even before it is created.
Freeform CAD
Free form CAD is used designing intricate and complex shapes like a shirt worn by a human body.
Parametric and Non-Parametric CAD
In a parametric model, the geometry is mainly controlled by non-geometric features called parameters which can be defined by dimensional, geometric, or algebraic constraints while hthe converse is true for non-parametric CAD.
What is AutoCAD used for

AutoCAD is one of the most widely used CAD software developed by AutoDesk for 2D and 3D modelling. Because of its popularity it is used in very diverse fields architects, project managers, engineers, graphic designers, city planners etc.
2D Drafting and Technical Drawing
CAD software like AutoCAD can be effectively used for 2D drafting and technical drawing. It is especially relevant in preparing architectural blueprints and technical drawings for manufacturing. 2D technical drawings can be made for 3D engineering designs to view top view, side view, front view and isometric view separately with visible dimensions.
3D Modeling and Visualization
3D modelling allows product developers and engineering designers to conceptualize the designs even before they are created. It brings a lot of ease and savings in R&D. Near to actual objects can be visualized and photo-realistic rendering can be done. It saves from the pain of unnecessary adjustments and wastage in manufacturing, as it facilitates in a precise design before actual product development.
Figure 2: Photorealistic rendering of a skyscraper on AutoCAD
Assembly Design and Simulation
Multiple 3D models can be joined in the assembly module. Simulations can be made in various possible environments and conditions to test the product.
Additive Manufacturing and CAM Integration
Various CAM modules in machines like CNC allow for the CAD design to be imported. This gives the design a very high precision as human errors are avoided. It is also useful in 3D printing.
Advantages of Using CAD Software
CAD brings a lot of ease and cost savings for its user in many industries. For example, it saves times for the 2D drafters who would otherwise have to use many sheets and man hours to make a simple design with hand drawings. CAD take only a fraction of the time! It also saves money, for instance for the fashion designers, who would otherwise need to print a lot of designs and color variations to select the best one. With CAD all these combinations can be tested quickly without the need to print every time.
Popular CAD Software Tools
Nowadays there are a lot of CAD software tools in market, but the most common are AutoCAD, SolidWorks, Creo and FreeCAD. Each of these has its own set of features that make it popular among a certain industry. The below table highlights the prominent features of these software.
|
Feature |
AutoCAD |
SolidWorks |
Creo |
FreeCAD |
|
Developer |
Autodesk |
Dassault Systèmes |
PTC |
Open-source Community |
|
Type |
2D & 3D CAD |
3D CAD |
3D CAD |
3D CAD |
|
Use Case |
Architecture, Engineering |
Mechanical Design |
Engineering, Manufacturing |
General Design |
|
Platforms |
Win, macOS |
Windows |
Win, macOS |
Win, macOS, Linux |
|
Cost |
Subscription |
Paid |
Paid |
Free |
|
Learning Curve |
Moderate |
Moderate to Steep |
Steep |
Moderate |
|
2D Drafting |
Strong |
Limited |
Limited |
Basic |
|
3D Modeling |
Good |
Excellent |
Excellent |
Good |
|
Parametric Design |
Limited |
Strong |
Strong |
Strong |
|
Simulation Tools |
Basic |
Integrated |
Integrated |
Limited |
|
File Support |
DWG, DXF |
SLDDRW, STEP, IGES |
STEP, IGES, DWG |
STEP, IGES, STL |
|
Customizability |
AutoLISP, APIs |
Add-ins, APIs |
Add-ins, APIs |
Python scripting |
|
Cloud Support |
Web App |
3DEXPERIENCE |
Creo+ |
Minimal |
|
Popularity |
Very High |
High |
High |
Moderate |
|
Best For |
Architects, Engineers |
Product Designers |
Advanced Engineers |
Hobbyists |
AutoCAD: A Versatile Tool for Various Industries
It is the most popular CAD software. Due to its excellence in 2D drafting and 3D modelling, it is exceptionally popular among architect and engineers.
SOLIDWORKS: Parametric 3D Design Excellence
Products developers value SolidWorks for its facilitation in parametric 3D design.
Creo: Advanced Design and Simulation Solutions
Manufacturers give due credit to Creo for its performance in advanced design and simulation studies.
FreeCAD: Open-Source Accessibility for Designers
This open for all and free software is particularly popular among general population and academics.
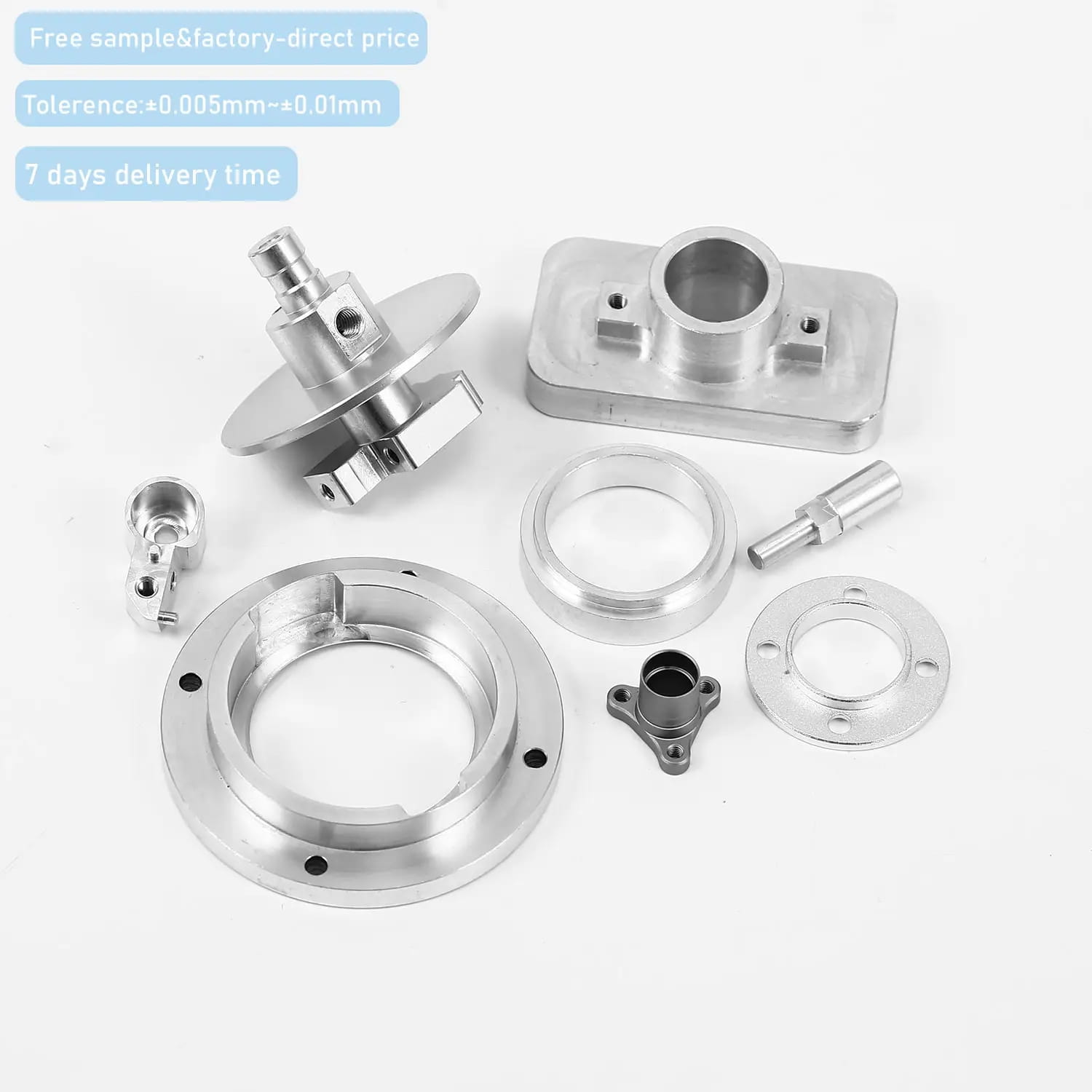

Applications of CAD Across Industries
As discussed above CAD facilitates designing of various products with the ease that is unimaginable without it. Take modern automobiles as an example. CAD facilitates at every step from conceptualizing to simulation and rendering. It is a complete solution. It is used in almost every industry where designing is involved. Most relevant are the manufacturing of medical equipment, sports goods, toys, automobiles, phones, complex engineering goods, surgical goods, aerospace parts, industrial plants and many others.
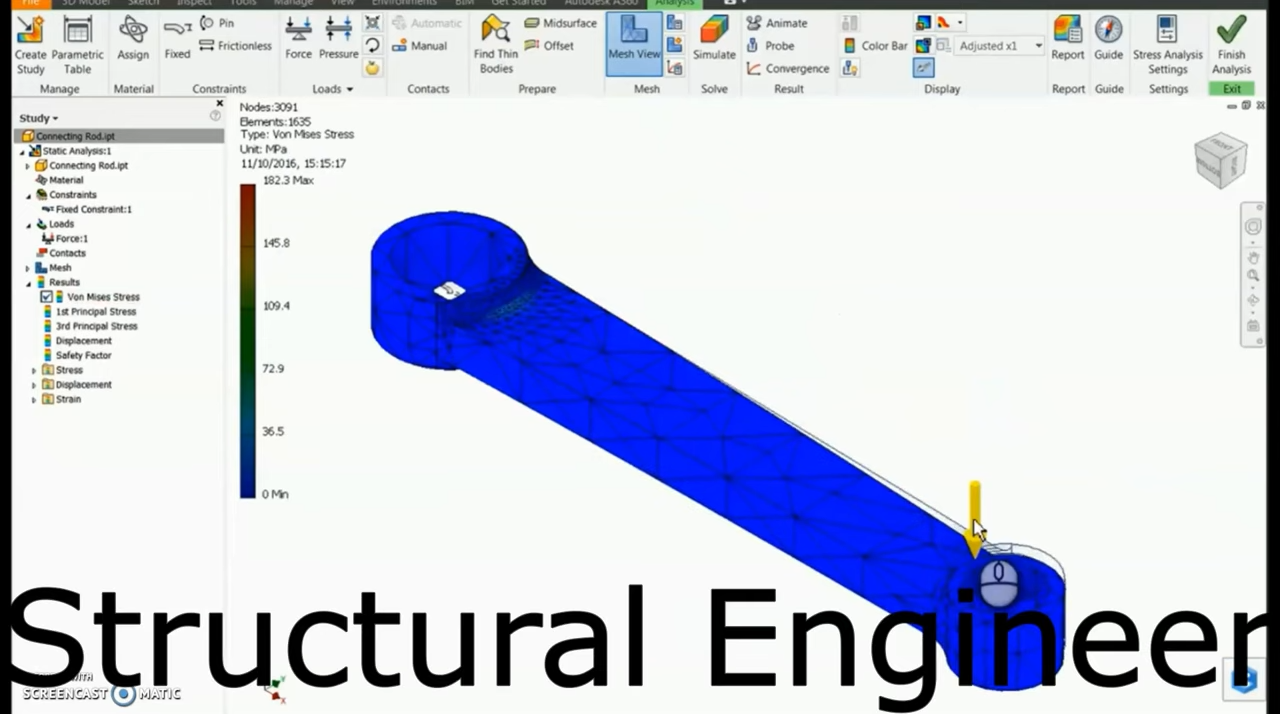
Figure 3 Three-dimensional modelling and simulation of automobiles in SolidWorks
Cloud-Based CAD Solutions
Cloud-based CAD tools let you design, collaborate, and store projects online, making work more flexible and accessible. They are great for teamwork, with real time updates. Examples include Fusion 360 and Onshape.
How to Choose the Right CAD Software
The key to choosing the right CAD software is about knowing the correct process for designing you product. For example, the most relevant for architectural CAD would be AutoCAD. Similarly, the most versatile for 3D modelling would be SolidWorks and the most advanced for 3D modelling and simulation would be Creo. The reviews of industry people about the particular software are also pertinent. Do consider them!
How to Get Started with CAD
CAD is not difficult to learn. All you need is a little attention and a bit of advice from the instructor. Almost every CAD company supplies tutorials with the CAD software. Also, there are tutorials on online sources such as YouTube. Practice matters a lot! The more you use it the more you’ll explore it.
Learning CAD: Tutorials, Courses, and Certifications
Learning CAD can be easier with tutorials, courses, and certifications. These tools teach everything from basic 2D drafting to complex 3D modeling, helping you grow skills and advance in design or engineering careers. Here is a YouTube tutorial:
Beginner-Friendly CAD Software Options
If you are new to CAD, tools like FreeCAD is a great choice. It is easy to use, with beginner friendly interface and tutorials to help you start designing quickly.
Building a Career in CAD Design
As CAD is an integral part of almost every industry where designing is important, there are a lot of career choices for the people who know about CAD.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About CAD
How does CAD improve design accuracy?
CAD improves accuracy by minimizing human error. Also, the designs can be simulated and test to make it more accurate.
Can CAD software be used for 3D printing?
CAD files can be imported into the programmer of a 3D printer. Rest of the job is upto the 3D printer.
What industries benefit most from CAD?
All industries who need to design benefit from it. The most common are industries who employ product developers, architects and engineers.
What are the types of CAD software available?
Types vary from software to software. Some are good in 2D drafting while others are good in 3D modelling and rendering. Some are licensed while others are free.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 Grooving Machining: Techniques, Tools, and Applications
Grooving Machining: Techniques, Tools, and Applications 







