Grooving Machining: Techniques, Tools, and Applications
 Jan 07,2025
Jan 07,2025

Grooving is used in manufacturing processes to form precise and accurate grooves or recesses in metals normally. It enables a precise fit for parts like seals and O-rings. Grooving operations can create different geometries of varying sizes. The main parameters of this process are tool selection, material impact or selection, feed rate, speed and cutting depth. It serves as a foundation in modern manufacturing processes by adding precision, versatility and efficiency to the final product.
What is Grooving in Machining?
It is a machining operation that forms narrow channels in a workpiece. It is normally carried out on CNC machines with specialised cutting tool selection. it allows pathways for threads and precise fit for O-rings and seals
The Grooving Process
Grooving is a CNC turning process to create a long and narrow indentation in the workpiece. It allows other parts of geometry to move inside the groove such as canal cut into metals. The cutting size depends on the width of a cutting tool. Multiple tool channels are required to create wider grooves.
Purpose of Grooving
Grooving allows you to join parts or create parts for assembly. For example, a grooving pipe can easily be attached with sprinkler coupling and ensures pipes are connected properly disregarding the water pressure inside them. CNC machines are used in grooving with specialized tools.
Grooving vs. Turning
Grooving and turning are different operations. Grooving creates narrow cut in a material with ta cutting depth same as that of cutting tool. CNC Turning removes material from a rotating material to create cylindrical shapes.
Common Applications
Grooving is a commonly used process in manufacturing to make rings, sealing and retaining grooves. It is also a main component in fire protection systems and groove flanges are sued in HVAC system for pipe connections. Other applications include in water treatment systems and to lock sheet metal seams used in sir ducts, bucket and many more.
Grooving Machines Overview
The principle of grooving machines is straightforward. A set of rotary cutting tools shaped groove in the workpiece. metal sheet. Grooving angles and cut depth are controlled and enhances precision of sharp angles. A CNC (Computer Numerical Control) system allows for the automation of the grooving operations. It allows high precision with high-speed cutting tool selection.
Grooving Lathe Tool Features
The features of grooving lathe tool differ with its type.
Types of Grooving Tools
There are different types of grooving tools.
Face Grooving Tool
A face grooving tool moves along the material’s face in CNC lathe. Short cutting depth is preferred to get higher stability. High precision cutting fluids are used in fac grooving to improve chip control and its removal.
Internal Grooving Tool
It moves along the internal part of the workpiece. Cutting fluids are applied to allow high flow rate, material removal and chip control. The operation starts from the rear part of the hole to the front to allow chip removal.
External Grooving Tool
The tool moves in radial motion along the side of the material. material removal is along the cutting point in this grooving operation.
Parting Tool vs. Grooving Tool
The parting tools and grooving tools are different from each other. Parting tools separate material in two parts by cutting a narrow slot in workpiece. However, grooving is to create channels in the face of the workpiece.
Grooving Inserts
Grooving inserts create deep small holes with a long overhang. It is used when chatter and deflection are expected.
Carbide Inserts
It is best suited for abrasive and corrosive materials like steel or cast iron. It creates imperfect holes in material such as shaft for semi-interrupted cutting conditions.
Tungaloy Inserts
These are strong inserts used for rough facing operations. These are like forging, castings and rough-sawed blanks.
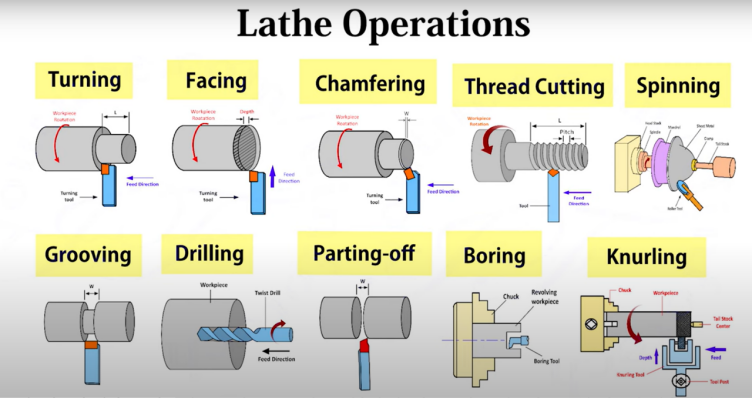
Cutting Edge Tools and Tool Wear
Normally used cutting edge tools in grooving are handheld router, router table, circular saw, track saw, router plane, cross out chisel, table saw blade and many more. Tool wear is a failure of cutting tool due to high temperature, inappropriate machining parameters or machining operations.
Material Impact on Grooving
Depending on the type of material like soft or hard, grooving gives different results
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is hard and has high work hardening. This creates tool wear, and the grooving operations require slow cutting speed.
Aluminum
Aluminum is malleable and can easily be bent. Grooving on aluminum is done when design structure is special and normally manufacturing methods cannot meet the expectation
Brass
Brass is malleable and has high machinability. It allows high cutting speeds and gives better surface finish.
Titanium
Ti has difficult machinability. It has low stress/strain ratio and low elasticity.Deformation can occur during grooving. But using texture tools can reduce friction and increase machinability.
ABS Plastic
ABS plastic is brittle and has low heat resistance. for good grooving results, a router triangular plate chamfering triangular board can be used. It is also suitable for many woodworking equipment and can be used for grooving, and etc.
PC
PC is non-toxic and an impact-resistant plastic. It can be grooved by cutting plotter milling, roll grooving machine and laser cutting.
POM
POM is widely used where high tolerances, machining, and deformation resistance are required. It is a versatile engineering plastic and grooves increase its adhesion to other materials
PTFE
Grooving on PTFE is the same as that for rubber, especially O-rings. The only difference is it has less width and less pressure is applied due to relative material stiffness.
Material Hardness and Groove Quality
Groove quality has significant effect on material hardness, depending on its type and the welding process. For example, V-grooves increase the hardness of weld zone by 33%. And smaller weld grove can increase the toughness and hardness of welds. Similarly, if high heat input and slow cooling rate reduce hardness.
Electropolishing for Surface Finish
Electropolishing can be done on the surface with multiple grooves. It improves the surface finish of a part by up to 50% without disturbing its dimension tolerance. But other factors like dimensional tolerance or material removal rate also influence final surface finish.
Precision Grooving Techniques
Common practice in precision grooving includes many factors. Such as:
Managing Cutting Forces & Vibration
Workpiece fixing and proper placement can reduce vibration issues during grooving. Other things to manage are cutting speed and low feed rate helps to improve surface finish and groove quality. Shallow cutting depth can reduce vibration and cutting forces.
Radial Depth of Cut
It measures how much a tool can engage the material perpendicular to its axis. It is also called cutting width. Groove quality highly dep ends on the feed rate, cutting speed, and radial depth of cut.
Maximizing Tool Efficiency
To maximize tool efficiency, the most important thing is to select the right grooving tools and grooving inserts. The right insert selects according to material, groove geometry, and to the machining parameters.
Improving Groove Surface Finish
Better groove surface finish can be attained by selecting the right tool, coolant, cutting speed and feed rates, tool geometry, wiper technology, and avoiding thin and large cutting tools.
Grooving Operations on CNC Lathes
Grooving operations on lathe has some steps
Setting Up CNC Lathe for Grooving
It starts with securing tightly the workpiece and marking out the positions.
Adjusting Lathe Parameters for Quality
Select the grooving tools and calibrate it. Set up the CNC lathe machine and adjust the RPM setting. Enter and run the program and after a successful grooving operation clean up the setup and tools.
External vs. Internal Grooving
External and internal grooving are different in terms of groove location and tool used. External grooving cuts channel outside the workpiece. It moves along the outer diameter of the workpiece. Internal grooving creates cuts inside the workpiece and creates deep holes and cavities
Deep Grooves: Challenges & Solutions
Deep grooves have multiple challenges like chip evacuation, difficult cutting fluids access, tool wear, and incorrect machine setup can lead to tool deflection and poor surface finish. Solution to overcomes these issues are to use flywheel to reduce vibration, properly designed cutting tool, lubrication, proper alignment and replacing bearing regularly.
Preventing Tool Wear in CNC Operations
To prevent tool wear in CNC operations, use right cutting parameters, cutting fluids, selecting wear resistant tool material, and monitor tool wear regularly.
Troubleshooting Grooving Issues
Here are some common issues to check while grooving
Chip Control Solutions
Chips control can be done by using high flow cutting fluids, nonlinear tool path, side tuning, speed packing, use small bar, narrow inserts, clamping, thicker blade, and use large diameter tools to fit the groove.
Managing Tool Vibrations
The best way to reduce tool vibration is by using dual-contact spindle and tool holding systems. It also improves accuracy in grooves.
Surface Finish Adjustments
To adjust good surface finish in grooves, use high-speed cutting tools, proper evacuation, correct tool noise radius, wiper insert, eliminate dwell and pause and high cutter lead angle.
Reducing Tool Chatter & Wear
To reduce tool chatter and wear, use tight tools and tool holders, short tool overhangs, less cutting forces and depth, using antivibration bars and allow machine to strike arcs.
5 Grooving Techniques for Precision
Deep Face Grooving
Deep face grooving is normally up to 20-25mm. It focuses on creating grooves that are aligned axially to the workpiece. It is done when creating grooves on the end face of a part.
Achieving Smooth External Grooves
External grooves are done for shafts and tubes in manufacturing. To get smooth external grooves, consider good surface finish to fit the compartment and make multiple passes if groove is wider.
Optimizing Groove Geometry
To get optimized groove geometry, the following characteristics are considered.
|
Groove geometry |
Parameters |
|
Groove position |
0.2–0.5 Cax |
|
Groove width |
0.2–0.4 Cax |
|
Groove inclination angle |
60ᵒ |
Multi-Edge Grooving Inserts
Multi-edge grooving inserts are naturally suitable for many grooving operations. These are like CNC turning, grooving, threading, profiling, and parting-off.
Custom Grooving Tool Configurations
If there are special designed requirements which cannot be done by normal tooling, custom groove tooling is done. Customization helps in cycle time, insert at special angles and simplify programming
How to Choose the Right Grooving Tool
There are some factors to consider when choosing the right Grooving Tool such as material type, groove shape, chip control, machine setup and characteristics and insert width etc.
Key Considerations
Some key considerations are:
Tool Material
Tool selection like carbide or Tungaloy depends on factors like material type, cutting conditions, tool holder compatibility, groove geometry, diameter range and most importantly the budget.
Tool Compatibility and Geometry
Tool compatibility must be aligned with material type and geometry must be adjusted with the cutting edge, rake angles, and clearance angles to get better chip removal and surface finish
Choosing Between Internal & External Tools
External and internal tools selection depend on the tool size and shapes, material impact, grooving methods, cutting fluids choice, feed rate, and chop control
Selecting Tools Based on Workpiece Material
Material impact on tools is a critical factor. Hard materials require durable and harder tools like carbides. Ductile materials can be machined easily with high-carbon steel or other less durable tools
Tools for Different Grooving Operations
There are many tool options for different grooving operations like parting tools, thread cutters, CNC turning tools, O-rings inserts, small internal grooving tools, knurling tools etc.
Improving Grooving Efficiency and Quality
There are a few factors to consider getting better grooving efficient and quality.
Optimizing Feed Rate & Cutting Speed
Good grooving results are obtained when the operation starts with low feed rate and gradually increase to higher feed rate to improve chip control and evacuation. Adjust the cutting speed with the feed rate to get longer tool service life.
Achieving Consistent Groove Dimensions
Groove dimensions can be measured by measuring tools like rulers or callipers. For larger inner diameter use an O-Sizer or Pi-Tape. There are O-rings calculators available like ERIKS or Ceetak O-Ring Calculators
Reducing Tool Wear with Proper Settings
To reduce the tool wear, optimize the cutting parameters, use cutting fluids and lubrication, less cutting speed, avoid re-cutting chips, and keep the deflection under control.
Using Cutting Fluids for Better Results
Cutting fluids decreases friction and increases the tool lifespan and precision cutting. Fluids reduce the tool wear and improve cutting accuracy
Improving Surface Finish for Grooving
High surface finish can be achieved by using insert geometry and wiper technology. The insert must be with tight tolerance and right radii and width. For mass production, insert must be with correct profile and chamfer.
Grooving Machining FAQs
What is the Difference Between a Slot and a Groove?
Slot is a straight, long hole with radius at its edges. Groove has a cylindrical shape and has cuts at external or internal diameter.
What Types of Machines Are Used to Machine Grooves into Metal?
Machines that are used to groove into metal are CNC machining centers, lathe, milling and slotter machines, and gear cutters.
How Do I Prevent Tool Chatter in Grooving Operations?
Tool chatter can be minimized by using rigid tools and tool holders and applying consistent tool pressure.
What Materials Are Best for Grooving Tools?
Carbide inserts are the best grooving materials because they have high wea resistance, temperature resistance, and are versatile and handle a variety of materials.
How Can I Improve Surface Finish on Grooves?
Better surface finish can be achieved by high cutting speed, balanced tool to get less vibration, good damping in machines, and by using chip breaker and wiper.
Is It Necessary to Coat Grooving Tools for Better Performance?
Coating increases the service life of grooving tools and also improves the cycle times and surface finishes.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 Aluminum Car Parts: Process, Materials, Benefits
Aluminum Car Parts: Process, Materials, Benefits 







