Dry Machining: Coolant-Free Manufacturing Parts
 Mar 26,2025
Mar 26,2025

Dry machining is a machining process that does not use cutting fluids or coolants. It has many advantage like reduced waste and potential cost-saving. Other important features of dry machining such as how it works and important consideration regarding material, are discussed in detail in this article.
What is Dry Machining?
It is also called dry cutting in which no cutting fluid is used during the operation. Instead of traditional liquid coolant, dry machining uses mist cooling systems or minimal quantity lubrication (MQL). in MQL, a small amount of air spray is used and cool down the workpiece and tool.
How does Dry Machining Work?
The majority of heat produced during cutting is due to friction between workpiece and tool. To carry out the dry machining process, compressed air and MQL is used to lubricate the cutting zone
What is the Purpose of Dry Machining?
The key purpose of dry machining process is to reduce cost, better safety and to reduce the environmental impact by deleting the coolant requirements and its disposal
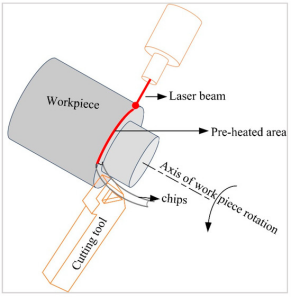
Differences Between Dry Machining and Traditional Wet Machining
As it is obvious, the major difference is no use of cutting fluid in dry machining. It is famous for its minimal environmental impact and cost-effectiveness. Traditional machining uses coolants and lubrication but it provides smoother surface and prevent deformation of workpiece
Why Do Some Materials Have to Be Machined Dry?
Certain material like magnesium, titanium or aluminum and non-metals like plastic and wood must be dry machined. It is because they could react with water or coolant during machining and also do not produce that much heat that require coolant. But heat-resistance alloy must not dry machined
Near Dry Machining (NDM)
It is also called Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL). It is a sustainable cutting process and uses very small amount of lubricant such as mist cooling system to cool down the cutting zone. It is also environmentally friendly and better than traditional coolant systems
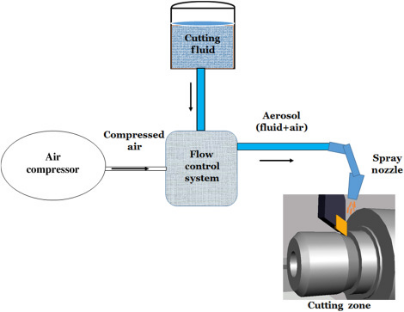
Difference between dry machining and NDM
Dry machining is without the coolant and lubrication during the operation. While Near dry machining uses a controlled amount of lubricant in the form of mist or mist cooling system
Benefits of Dry Machining
There are many advantages associated with dry machining process which are written below:
Cost Advantages
It eliminates the cost of coolant reduces all the expenses regarding purchase, storage and disposing fluid.
Health and Environmental Benefits
It reduces the risks of exposure to hazardous material in coolant, minimizing health issues and risks. It also minimizes waste and pollution reducing negative environmental impact.
Enhanced Process Efficiency
Tool life is increases specially cutting for hard material like stainless steel which faster the machining process and improves chip management solutions
Less Maintenance
This overall requires less maintenance as compared to wet machining due to better tool life and processing
Table of Dry Machining Advantages
|
Features |
Advantages |
|
Cost |
Low operational cost due to no requirements of coolant |
|
Environment |
Low negative impact due to no use of chemical |
|
Maintenance |
Less machine and tool maintenance |
|
Finishing |
No need of post machining cleaning and degrease |
Disadvantages of Dry Machining
There are also some drawback associated with dry machining which are as:
Heat Generation and Thermal Stress
It can high temperature between the workpiece and tool due to friction and can generate thermal stress and affecting dimensional stability and accuracy.
Limitations on Materials
It is not suitable for all kind of material specially those which are vulnerable to temperature-related issues or require precise heat control
Chip Control
The chip management solutions can become difficult and can result in ribbon-like chips or chips jamming
Table of Dry Machining Disadvantages
|
Catagories |
Disadvantges |
|
Heat Generation |
High heat generation and thermal stresses |
|
Chip control |
Difficult chip control or chip management solutions |
|
Limited material |
Not suitable for every kind of materials |
Dry Machining vs Wet Machining
The key differences between dry and wet machining are explained in the comparison table below:
|
Feature |
Dry Machining |
Wet Machining |
|
Environmental effect |
Low waste due to no coolant disposal |
High due to doolant disposal |
|
Cost |
Cost-effective due to low opertaion cost |
High coolant costs |
|
Tool Life |
shorter tool life due to high heat-resistant generation |
Longer tool life due to heat resistant tools |
|
Surface Finish |
Low surface quality due to high heat |
smoother surface finish |
|
Heat production |
Higher heat at the cutting zone |
Lower heat |
|
Health and safety |
Safe and no exposure to hazardous substances |
Potential health risks |
Tools and Coatings for Dry Machining
To get the most efficient result, it is important to select right tools and coating
Choosing the Right Tools
Some carbide grades and coated carbide cutting tools are used in dry machining. Cermets. Alumina, silicon nitride, and polycrystalline diamonds are best for high temperature, hardness and wear resistant material.
Tool Coatings for Heat Control
Consider tool coating like Aluminum Titanium Nitride, Titanium Aluminum Nitride and Aluminum Chromium Nitride are used to provide high temperature resistance, hardness, and longer tool life
Cutting Parameters
Use optimized cutting parameter like low cutting speed, high feed rate to have high surface finish and low rate for low material removal rate and large depth of cut for high material removal rate can give better cutting results.
Applications of Coolant Free machining
Coolant free machining has become famous in many industries. Its common applications are as:
Dry Machining Aluminum
Aluminum is one of the most commonly used material in industries like aerospace, automotive, construction, manufacturing, packaging and so on. Dry machining aluminum offers multiple benefits like low costs, environmental benefits and better accuracy by CNC dry machining.
Dry Machining Steel and Titanium
Steel and alloys and Titanium is a very demanding material aerospace and automobile. Dry machining titanium offers sustainability, cost-effective, low risk of corrosion and less chip removal.
Dry machining for screws: Why this process works well
Dry machining is very effective for hard material like screws because coolant can cause thermal stress. Screws like ball screws, gear screws and extrude screws give better performance with dry machining
Prototyping and custom part manufacturing
Dry CNC machining can be a best option for prototype and low-volume production for testing and validation of functional prototypes. It provide tight tolerance and intricate detail in parts and can be used for aerospace, energy, food processing and automotive industries.
Near Dry Machining (NDM) and Minimal Quantity Lubrication (MQL)
Near dry machining or MQL uses mist cooling system during operation. Major differences between dry machining and near dry machining are written below:
Differences Between NDM and fully dry machining
Key differences between the two processes are as:
|
Features |
Dry Machining |
Near-Dry (MQL) Machining |
|
Lubricant |
None |
Minimal, controlled amount |
|
Cooling |
air cooled |
Air cooling with lubricant |
|
Applications |
Limited to specific materials and operations |
For variety of materials and operations |
|
Environmental Impact |
Low |
low |
Benefits of Near Dry Machining
There are number of advantages associated with near dry machining process such as:
- No water, earth and atmospheric pollution
- No occupational risk to health
- Significant reduction in cost
- Less thermal shocks as compared to dry machining due to use of coolant
Practical Applications of NDM
NDM is suitable for all the CNC operations. Some applications of NDM are as:
- Versatility in machining
It can be used in different machining operation like milling, drilling, band sawing, circular sawing, tapping and turning
- Machine
It can be with machine like lathe, drill presses and Swiss-type lathe
Materials
It can employed with cast iron, steels, aluminum and even difficult-to-cut aircraft alloys
- Lubricant
It can be used with many lubricant like synthetic esters, fatty alcohols or with water
- Coatings
Advances in tool coatings, like TiN, TiCN, and TiAlN, have improved the feasibility of near-dry machining,
Materials for Dry Machining
High-temperature resistant and wear resistant materials are the most suitable for dry machining
Best Materials for Dry Machining
Dry machining reduces heat fluctuation in materials like hardened steel, high temperature alloys like aluminum, cast iron, stainless steel, ceramics, cermets and carbides, Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN), Polycrystalline Diamond (PCD), TiAlN heat-resistant coating, Brass and Bronze, carbon steel, polycarbonate, Acetal, PEEK and PVC.
Materials That Require Coolant
Dry machining titanium and super alloys and some stainless steel require coolant to machine because of their hardness these are difficult to machine and require precise surface finish which cannot be achieved form dry machining
Heat Management in Dry Machining
Heat management is carried out by tools that can control heat and coatings
Tools That Control Heat
Tools made with high carbide grade can control heat with their density and high heat-resistant tools such as Ultrafine Micrograin Carbide (YG-1 X-Power) or Nanograin Carbide (YG-1 X5070)
Tool Coatings and Lubricants
Tool standard coatings like TIAlN or TiCN coating would not be sufficient therefore heat resistant tools and heat resistant coatings like hardened steel with special Y1200 blue coating are used due to high heat resistance up to 1200°C.
Factors to Consider for Dry Machining
There are some factors essential to consider during dry machining
Machine Requirement
To get efficient results of machining, machine must have features like robust chip management solution, high-spindle speed, cooling system, optimized tool geometry and material compatibility.
Cutting Conditions
Optimum cutting conditions are high feed rate, high tool nose radius, low cutting speed to maintain tool life and better surface finish
Process Selection: Dry vs Wet
Dry machining requires less coolant and energy, cost-effective and is faster. Wet process are better for material that are hard, difficult-to-machine are are prone to deformation.
Turnkey CNC Machining Solutions with Tuofa China
Tuofa CNC one of the leading CNC precision machining service offer low cost, on-demand and on-time delivery services. Custom-parts, prototypes and high-volume production options with cost-effective solutions for your manufacturing needs. Tuofa is good choice based on years of experience, professional expertise, advanced machines and setup to meet your production requirements
FAQs About Dry Machining
What is dry run in CNC machining?
Dry run is a simulation of machine program without any actual cutting or material removal process. It is to determine the potentials issues and errors in operation.
How is lubricant applied in near dry machining?
Lubricant is applied to cutting zone as aerosol with control compressed air mist with oil
Can all materials be machined dry?
No, it is not suitable for heat resistance and hard materials
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 Inconel Machining Solutions: Tips & Tools For Tough Alloys
Inconel Machining Solutions: Tips & Tools For Tough Alloys 







