What Is Zirconium Metal: Properties & Uses
 Mar 27,2025
Mar 27,2025

Zirconium metal is one of the most important and irreplaceable metals across the periodic table. The chemical and physical properties that it exhibits are unique. As a result Zirconium metal and its alloys and compounds are an integral part of industries like nuclear power, bio medical and high temperature materials etc.
Is Zirconium a Metal?
Yes, Zirconium is metal. Metals usually exhibit properties like high electrical and thermal conductivities, ductility, malleability and a lustrous appearance. Zirconium being a metal fulfill these properties criteria. Further, it is located in the 'transition metals' group in the periodic table.
What Is Zirconium Metal?
Zirconium metal has an atomic number of 40 in the periodic table. It has a silver-gray color in pure form, while Zirconium alloys have variations in colors. It has an extremely low neutron absorption making it ideal for nuclear applications. It has a high melting point and high resistant to corrosion leading it to be used in a variety of industries.
Common Myths About Zirconium Metal
Due to a lack of knowledge and some misconceptions, people have associated certain myths with Zirconium metal. Let's clarify 4 myths here:
- Myth 1: Zirconium is the Same as Zircon
People often confuse the word 'Zirconium' with 'Zircon', however both are very different. Zircon refers to a non-metallic compound group of zirconium which finds it applications in jewelry and thermal barrier coatings. Contrary to that more than 90% of the Zirconium metal is used in nuclear industry alone with no connection to the applications of Zircon. Both Zircon and Zirconium look different to each other. Zircon is inexpensive while pure Zirconium can cost around USD 30000 per metric ton.
- Myth 2: Zirconium is a Rare Element
Zirconium is the 15th most abundant element in the earth's crust. It is not at all rare. Probably, due to Zirconium metal uses in advanced and high-tech industry, common people are not much familiar with it.
- Myth 3: Zirconium is as Strong as Steel
Steel is way stronger than Zirconium. In common structural application steel would be seen everywhere but Zirconium would not be. It is only the exceptional properties not strength of Zirconium metal that makes it suitable for structural applications like cladding of nuclear fuel pellets.
- Myth 4: Zirconium: Metal Or Ceramic?
Zirconium is a metal and zirconia a ceramic. Maybe to the a similarity in the words people confuse the two.
Zirconium Properties: Physical and Chemical
The below table highlights some of the key Zirconium Metal Properties:
|
Property |
Value |
|
Appearance |
Silvery-gray, lustrous |
|
Density |
6.52 g/cm³ |
|
Melting Point |
1855°C |
|
Boiling Point |
4409°C |
|
Tensile Strength |
330–680 MPa |
|
Electrical Conductivity |
2.4 × 10⁶ S/m |
|
Thermal Conductivity |
22.7 W/m·K |
|
Corrosion Resistance |
Excellent |
|
Malleability |
High |
Key Physical Properties:
Strength:
Zirconium metal has a moderately good strength for certain structural applications like nuclear fuel claddings or bio medical implants. Certain alloying elements can tremendously enhance strength.
Density:
Zirconium metal has a density of 6.52 g/cm³ which is lower than steel but way higher than Titanium and Aluminum.
Melting Point
A melting point of 1855 o C is higher than most of the metals and it make Zircconium suitable for high temperature applications.
Chemical Properties:
Reactivity
Zirconium metal is highly resistant to oxidation but reacts with strong acids and halogens at high temperatures. High temperature reaction with steam has caused hydrogen explosions at nuclear sites making it an area of concern.
Corrosion Resistance
Zirconium metal is corrosion resistant in acidic, alkaline and sea water environments.
Stability
It is highly stable in high temperature and harsh chemical environments making it a unique choice for certain applications.
How Zirconium Compares to Other Metals
Comparatively, Zirconium doesn't appears to be superior from the strength or density point of view from common metals like Titanium, steels or aluminum. However, Zirconium Metal Properties like corrosion resistance, neutron absorption, chemical and thermal stability and bio compatibility makes it ideal for certain applications.
Is Zirconia Similar To Titanium? -Titanium Vs Zirconia
There are few commonalities between Zirconium and Titanium like bio-compatibility, corrosion resistance and HCP crystal structure. However, the application of both metals are radically different.
Comparison of Zirconium and Steel
Zirconium and steel are very different from each other. Both metals have a very different set of applications. For example the neutron absorption of steel if manifolds higher than that of Zirconium. Zirconium alloys are biocompatible while steel is not.
The Production of Zirconium Metal
Different grades of Zirconium metal is produced depending on the applications. For example, the commercial grades require a lesser purity than the nuclear grades. There are different methods and steps for different grades.

How Is Zirconium Extracted?
Commercially, Zirconium metal is extracted using Kroll Process. The Zircon (ZrSiO4) ore is reacted at 1000oC with Chlorine gas:
ZrSiO4 + 2Cl2+ 2C → ZrCl4 + SiO2+ 2CO
It forms Zirconium tetrachloride (ZrCl4). The Zirconium tetrachloride is then reacted with Magnesium metal at high temperature to produce Zirconium metal:
ZrCl4 + 2Mg → Zr + 2MgCl2
Zirconium Refining Process
 Liquid-liquid solvent extraction method is used to preferentially dissolve Zirconium metal leaving behind Hafnium which is undesirable in nuclear applications. Methyl isobutyl ketone (MIBK) or tributyl phosphate (TBP) are used as solvents for this dissolution.
Challenges and Innovations in Zirconium Production
Zirconium metal production faces challenges like costly Hafnium separation, high energy usage, and environmental concerns. Innovations in electrochemical reduction, novel purification methods and recycling would improve efficiency.
Zirconium Alloys: Varieties and Their Applications
Certain alloying elements are added to Zirconium metal melt to make a solid solution to enhance certain physical or mechanical properties. For instance, the strength of pure Zirconium may not be desirable for cladding application, but an addition of Niobium would improve the strength.
What Are Zirconium Alloys?
Addition of certain chemical element(s) in the crystal lattice of Zirconium metal would be termed as Zirconium alloys. Some of the common alloys are shown in the table below:
|
Alloy |
Density (g/cm³) |
Tensile Strength (MPa) |
Corrosion Resistance |
Applications |
|
Ti Grade 17 (UNS R58640) |
4.64 |
1100–1200 |
Excellent in high temp environments |
Aerospace, gas turbines, marine |
|
Ti Grade 19 (UNS R58240) |
4.75 |
1150–1250 |
Good corrosion and wear resistance |
Aerospace, biomedical, structural |
|
Zr-2.5Nb |
6.55 |
400–600 |
Excellent in acids and high-temp |
Nuclear reactors, heat exchangers |
|
Zircaloy (Zr-4, Zr-2) |
6.56 |
500–750 |
Outstanding in nuclear environments |
Nuclear fuel cladding, reactors |
Other Metal Alloys Containing Zirconium
- Titanium Grade 17 (Ti-5Al-2Sn-2Zr-4Mo-4Cr) AlloyUNS R58640
Titanium Grade 17 is a high-strength, corrosion-resistant alloy used in aerospace, gas turbines, and marine applications.
- Titanium Grade 19 (Ti 3Al 8V 6Cr 4Mo 4Zr) AlloyUNS R58240
Similar to Grade 17, this grade 19 is also a high strength grade used in aerospace, biomedical, and structural applications.
The Role Of Zr Element In Other Alloys
Addition of Zr in Titanium can enhance the corrosion resistance, creep resistance and overall strength of the alloys.
Common Zirconium Alloys And Their Properties
- Zirconium-2.5% Niobium (Zr-2.5Nb):
It is a grade used for nuclear applications. Niobium stabilizes high temperature performance by enhancing the microstructure. It improves strength, corrosion resistance, and creep resistance.
- Zircaloy (Zr-4 and Zr-2)
Nickel improves corrosion resistance, strength, and thermal stability. Zr-2, is a nickel containing grade. It is suitable for boiling water reactors. While in Zr-4, nickel is removed to improve performance in pressurized water reactors.
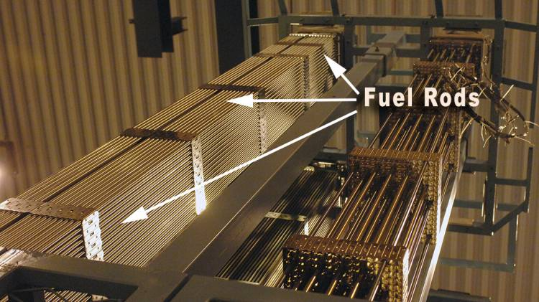
Applications of Zirconium Alloys in High-Performance Industries
Zirconium alloys exhibit unique properties which make them suitable for high performance industries. Low neutron absorption makes it ideal for cladding material of nuclear fuel pellets. Biocompatibility make Zirconium alloys suitable for medical implant. High creep resistance and a high melting point allows Zirconium alloys to be used in aerospace and propulsion systems.
Environmental and Safety Considerations for Zirconium
Although Zirconium extraction is considered as a by product of Titanium extraction from heavy sands, there are still environmental and safety consideration particularly linked with Zirconium extraction. At large Zirconium metal does not pose any major risks. Only a few precautions should be kept in mind.
Safety of Zirconium in Manufacturing and Handling
Zirconium metal is non-toxic and biocompatible; thus, it does not pose risk to human health and safety. However, Zirconium fine can cause respiratory issue is inhaled. These fines can also cause sparks. Hence, Zirconium fines should be disposed off properly.
Environmental Impact of Zirconium Mining and Recycling
Zirconium mining and extraction can cause land degradation, energy wastage and carbon emissions. Recycling can be done only at a fraction of environmental and financial cost. Hence maximum effort should be put to conserve our resources by recycling.
Conclusion:
Zirconium metal possesses properties that are unique to it. For instance, its neutron absorption behavior is unmatched with most of the commercial metals and alloys. The high temperature performance of Zirconium alloys is also exceptional. As a result, Zirconium is irreplaceable in nuclear industry and in some of the high temperature applications.
FAQs
How is zirconium alloy used in medical applications?
Zirconium alloys can be used in medical and dental implants due to high corrosion resistance and biocompatibility.
How does zirconium compare to titanium?
Titanium is somewhat comparable to Zirconium in a few applications. However, some of the properties of Zirconium are way more superior to Titanium.
Is zirconium metal safe to handle?
Yes at large due to non-toxicity and biocompatibility. However, Zirconium fines can catch fire.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 Monel vs Inconel: Which Nickel Alloy Better?
Monel vs Inconel: Which Nickel Alloy Better? 







