Types of Rivets: Quality Rivet Selection Guide
 Jul 17,2023
Jul 17,2023

Types of Rivets: Quality Rivet Selection Guide. Introduction: In engineering industry joining materials is critical task for Structural integrity, Joints, Strength during life span, Connection with metallic body and Ease of assembly operation. Riveting is important aspect of joining metallic materials for equivalent strength securing without fusion, bolting, adhesive bonding and material damage. But type and selection of riveting is important for material assembly, strength and cyclic stresses joining with load class of job. Thus knowledge its selection is important for correct design, fabrication and load testing.
Quick View of Article Content
Why Choose Tuofa Custom Quality Rivets
Define Rivets
It connects metallic and non-metallic material by pin type connection which holds both sides with compressive force. This connection does not involve fusion of material and threading inside surface. Thus it is easy, cheap and machining free tool to hold two sheets together. It can work in shear force environment with good result for thin sheet. But thick sheets are not good option for this kind of joint. Because deformation of thick sheet with mini force on closing end is not possible and it leads to make loose joint having no use.
Rivets Material
Material for this kind of joint can be Steel, Brass, Copper, Aluminum and Plastic. Material selection for it depends upon force requirement and equivalent stresses of rivet pin to hold two sheets together. This selection has also role in deformation of clamping sheets. Corrosion and environment chemistry dictates about use of metallic or non-metallic material for complete
life span. Metallic rivets can bear large equivalent stresses during job application but corrosive environment can make oxidation in it.
Rivet Head Styles
Head styles depend upon type of tooling and assembly process in fabrication and joining of sheets together. Rivet heads decide the end shape of mandrel and stress surface area available for holding pieces together. Rivet head styles guide the application force on mandrel edge, because mismatch between mandrel surface and rivet head can create non uniform clamping force. Different types of rivets heads are:
1. Flush Countersunk.
2. Universal Pen Shape.
3. Flat shape.
4. Button Shape.
5. Truss shape.
Figure.No.1 shows graphical description of different types of rivets head styles.
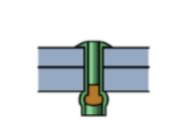
Figure.No.1 Graphical Representation of Rivet
How do Rivets Work?
It works by pressing heads on the surface of flat sheet and clamping them together during complete life time of job. First its pin goes inside hole of job and then deformation of edges make it to hold both sheets together. This joint can bear reaction tension forces and shear phenomenon during job application in particular forces frame. Thread mechanism can also make combination with rivets for better joint strength and reaction against fatigue crack. Because rivet joint working is always sensitive to cyclic stresses and crack starting point even at room temperature.
How are Rivets Installed?
Its installation depends upon type, kinds of rivets, material, thickness of sheet metal rivets and available tool for rivet clamping. Thus following steps are the description of rivet installation:
1. Make drill hole in sheet metal.
2. Select proper shank diameter to clamp the job.
3. Use mandrel to put force on head surface area of rivet.
4. At end any type of stress relieving technique is best option.
Rivet Sizes and Dimensions
It is important to select the drill size of rivet in job, rivet shank diameter and allowance value during joining process. Because these parameters can decide that structural integrity of joining sheet metals and guide about fits present between rivet diameter and drill hole in job. These parameters have also description in the form of mathematical equation as:
Shank Diameter (minimum) = 3 times of joining sheet metal thickness and Allowance = 1.5 times of shank diameter.
And length of shank is approximately summation of shank diameter and allowance of sheet metal. Example of rivet size is present in Table.No.1
|
Sheet Metal Thickness 4 mm |
|
|
Shank Diameter |
12 mm |
|
Allowance |
18 mm |
Table.No.1 Rivet Size and Dimensions
Charts and Tables are also present for finding rivet size and dimensions.
Different Type of Rivets
It has different types with respect to application type, construction, head and tails and all these factors contribute in final determination and way of application. Different types of rivets have description as per following details:
Solid Rivets
These rivets contributes maximum in joining metal industry due to simple design and ease of assembly. It has application from crude product of toolbox to aerospace industry without changing parameters.
Description
It has two main components to hold metal sheet together, one is its head (in countersunk or button shape) and another is tail (usually in flat shape). Hammering force comes from head direction and deform the tail on another direction to cold bond the tail and sheet metal. Figure.No.2 describes solid rivet.

Figure.No.2 Solid Rivet.
Features:
It can rivet the metallic sheets without any extensive use of equipment and expertise. Because only hammering on countersunk / button shape head is main requirement while remaining process is easy to make.
Common Applications:
It has large application in aerospace industry because countersunk shape standard rivets are compatible for turbulent free surface air movement. And it can even have application in low cost product due to ease of manufacturing technology and less use of complex machines.
Pop Rivets
These are special types of rivets having application in low space assembly or jobs with importance of volume ratio. Because they offer facility to worker for working from one side of sheet metal plate. That is why second nomenclature for this kind of rivet is Blind Rivet.
Description:
It has similar kind of head but different configuration on tail side for deformation without any use force mechanism. It has ease during installation but repair work becomes impossible due to inaccessible surface restraint. Figure.No.3 describes Pop rivet.

Figure.No.3 Pop Rivet
Features:
It requires less time and manpower due to one surface working and pulling tool involvement. Due to involvement of mechanism and standard shape it needs less force on accessible surface side. Common Applications:
Usually electronic components need less space and make assembly in less dimensions. Thus upon assembly quality rivets are pop rivets due to unavailability of access from electronic component side.
Types of Pop Rivets
They have different types depending upon tail deformation from inaccessible surface. Types are as follow:
Pull Mandrel Rivets
Load have application on tail side to pull it toward head until the tension mandrel becomes break after deforming tail. All the operation have working area from one side without need of any second man. Figure.No.4 describes Pull Mandrel Rivet.
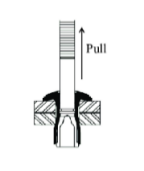
Figure.No.4 Pull Mandrel Rivet.
Threaded Stem
It has same configuration but instead of pulling mandrel in outward direction it can allow thread mechanism to do same job. Thread mechanism can pull tail side towards head side to deform the tail and make cold bond on it. Figure.No.5 describes threaded stem rivet.
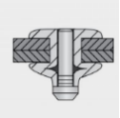
Figure.No.5. Threaded Stem Rivet.
Drive Pin
Instead of pulling compression on pin makes tail; side to deform in preform die with old bonding with far side sheet metal. It is very useful technique in place where there is need of hammering instead of hammering mechanism. Figure.No.6 describes Drive Pin rivet.
Figure.No.6 Drive Pin Rivet.
Tubular Rivets
It has hollow section like tube in middle to deform rivet shape easily on less application force and punching hit. It can work in low strength and ductile material easily without any rupture or crack causing. Figure.No.7 describes tubular rivets.

Figure.No.7 Tubular Rivet.
Description:
These types of rivets can join low strength metals in good manner because it can create bon at low striking force and less strain in material. Two types of tubular rivets are usually available in market for cold joining purpose,
A. Full Tubular Rivets.
B. Semi Tubular Rivets.
Features:
It can bond even nonmetallic and composite type plastic due to less force exertion and small drill hole diameter requirement. Thus surface of original material receives less deformation and impression.
Common Applications:
They have application in nonmetallic sheet bonding, aerospace industry and wood piece joining due to less need of stress concentration on surface area of job.
4.Drive Rivets:
These rivets have one side hammer action to protrude the other far side of tail and expands on metallic sheet without making sharp edge. Figure.No.8 describes drive rivet.

Figure.No.8 Drive Rivet.
Description:
It can work to bond one side accessible job with compression of pin and make tail to deform on far side of striking direction. Narrow space components are perfect example of the types of drive rivets.
Features:
It needs uniaxial force without insertion of mandrel and thread mechanism in any case. They have special property of uniform distribution of force. It can work in narrow space jobs without any need of back hammering.
Applications:
Aerospace industry needs these rivets due to close environment and inaccessible surfaces on electronic side of jobs. Thus drive rivets can easily join close electronics circuit boxes without any need of cutting operation.
5. Peel Rivets:
It has preform type of small strip which comes to tail side in particular direction so that petal type strips hold job together. It can even perform in plastic, leather and other nonmetallic material without causing damage to surface and material. Figurer.No.9 describes Peel Rivet.

Figure.No.9 Peel Rivet.
Description:
It acts as blind to job because of one side working and introduce four numbers of leg towards tail bearing surface. Thus it can hold metallic and nonmetallic material without any use of hammering and clamping on tail side.
Features:
Brittle and softer materials have risk of breakage on bearing surface but it can reduce this risk with introduction of four petals with minimum force of contact.
Common Applications:
Insulation and wood material are the perfect example of soft and brittle material but these types of rivets can join them with minimum clamping force and bearing surface area.
Blind Rivets Vs Solid Rivets
Using rivets of these two types are always need in engineering industry but rivet comparison is necessary for application in particular environment and job. Table.No.2 describes difference between these two sheet metal rivets.
|
Can hold sheet metal with quality rivets. |
Can hold sheet metal with quality rivets. |
|
Need working from head and tail side. |
Tail side access is enough to work. |
|
No use in closed container design. |
Work in space with limitation. |
|
Need more time for installation. |
Need less time for installation. |
Table.No.2 Difference between Solid and Blind Rivets.
Types of Rivets PDF
Standards rivets, rivets with holes, rivet head styles describes different classification. Kinds of rivets and its types have best description in following list,
1. Solid Rivets.
2. Pop Rivets.
3. Tubular Rivets.
4. Drive Rivets.
5. Peel Rivets.
6. Plastic Rivets.
Types of Metal Rivets
Its classification ca be in two types, one is its physical or mechanical appearance like rivets with holes, rivet heads and rivet working process. Second is its material grade which are also important due to effect on final cold bonding of job. Its different metal type classification is as follow,
Aluminum Rivets
It is soft, ductile and malleable material with large deformation and anti- corrosion property, hence small riveting force can produce large deformation on tail side. Briles rivets need large deformation on job surface so that better sealing characteristics are present on leakage area. Thus aluminum is best material for it. Light weight aerospace industry also need low weight aluminum rivet instead of heavy stainless steel bolting mechanism. Bifurcated rivet also need lightweight and large deformation rivet to hold job together, thus aluminum is good option for it.
Brass Rivets
It is high conductive, malleable and corrosion resistant material which has well anti friction properties. Thus if structure is of brass or copper then lightweight aluminum can introduce galvanic corrosion in it. And structure lose it corrosion properties. Only brass rivet can make joint integrity in this case without disturbing electrical properties of main structure.
Stainless Steel Rivets
It is good strength carbon alloy which can resist deformation on application of force. Thus if job bonding need high force for clamping and fit then brass, copper and aluminum rivets cannot do work for it. It need some high strength material which can deform material up to that value which need to counter with same magnitude on unbounding process. These have common application in stainless steel sheet metal work.
Rivet Applications
Rivets have application in every field of assembly and join industry because it provides bonding of material without expensive equipment and large fastening space as of bolt. Following applications describe rivet importance in many fields:
Types of Rivets for Leather
Leather has low scratching strength, thus it needs low strength rivet with less bearing surface area on binding side. Thus Blind flower rivet petals is best option among available types of rivets in common practice of engineering industry. It can make bond between soft leather and hard aluminum with flower petals and produce less scratches at soft leather. Otherwise leather bonding becomes too difficult and fragile in clothes and jacket. Figure.No.10 describes aluminum blind flower rivet petals.

Figure.No.10 Rivets for Leather.
Types of Aircraft Rivets
Aircraft needs joining of sheet metal in various compartments and height strength of joint to bear aerodynamic forces during flight. It needs lightweight structure to make fuel consumption economical and aerodynamic balance in moderate place. Otherwise welding of thin sheet metal work can produce defects in plate which can cause rupture on aerodynamic forces application. Solid and blind types of rivets have application in aircraft sheet bonding with different rivet heads. These types of joints can have sealing properties when briles rivets are introduce in joining process. Quality rivets are the important criteria for these types of application.
Rivets for Sheet Metal
Thin sheets have only application of rivets for bonding because bolts take much space and welding can destroy thin sheet integrity. Thus quality rivets can provide good strength bonding without any space occupation and damaging thin thickness by burning, as in case of welding. Solid and blind rivets take part to cold bond sheet metal without any rupture and defects in structure.
Rivets for Plastic
It is difficult to bond plastic sheet with thermal welding, adhesive and bolting due to limitation of chemistry, low strength and space issue. Thus riveting is good option for this kind of joint due to optimum joint efficiency. Nylon is good material for this joint. Because it has enough strength to hold shear and tension forces without any break. Figure.No.11 shows plastic rivet.

Figure.No.11. Plastic Rivet.
Rivet Alternatives
Any joint method other than this lies in scope of alternative technique of bonding. It is designer who can decide on drawing that which types of rivets are best solution for cold bonding of material. Alternatives are present in Table.No.3.
|
Adhesive Bonding |
Act as an alternative but cannot bear large forces in structure |
|
Bolting |
It can take too much space and weight |
|
Welding |
Does not work on thin sheet metal and aluminum foils |
|
Clamping |
Takes too much space |
Table.No.3. Alternatives of Riveting.
Why Choose Tuofa Custom Quality Rivets
Custom rivets is need for specific design and job with extra parameters, which requires analysis before execution of job. Thus expertise in riveting is the first step for these types of custom designs. Tuofa, China can suggest, design and execute any type of custom quality rivet. Tuofa has ISO 9001 certification with team of experts for CNC machining, Riveting and Job finishing. Tuofacan suggest Rivet drill hole by machining, Type of Rivets and can execute quality rivets for clients.
For more information please visit toufa-cncmachining.com.
FAQs about Quality Rivets
What are Types of Rivets in Engineering Drawing?
Symbols are the representation of it on engineering drawing and can describe Types of rivets, Joint detail of sheet metal and Size of hole. Figure. No. 12 describes the symbol representation of Rivets on engineering drawing:
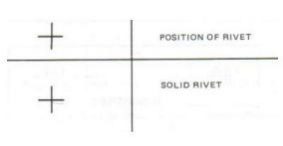
Figure.No.12 Rivets on Engineering Drawing.
What are Rivets Made of?
They are made metallic and nonmetallic material, with cutting and forming operation. Metallic materials need for their construction are Steel, Aluminum, Copper and Brass. But steel is common material for construction. Nylon is major material in category of nonmetallic material.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 Fabrication vs Manufacturing: Understanding the Differences
Fabrication vs Manufacturing: Understanding the Differences 







