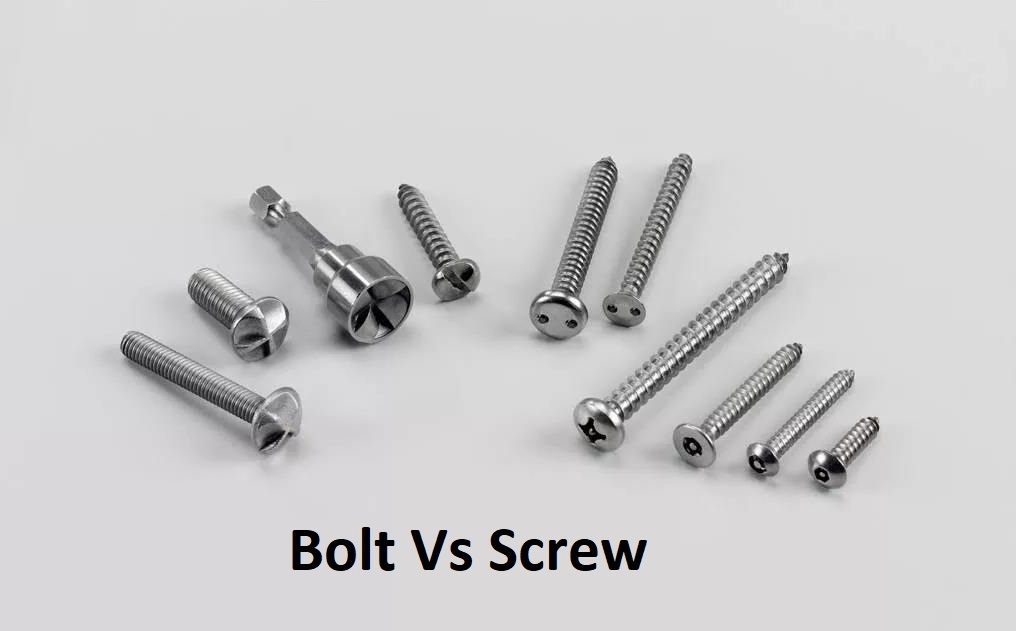
Bolt Vs Screw: What is the Difference Between?
 Aug 06,2023
Aug 06,2023

Bolt Vs Screw: What is the Difference Between? Both fasteners have application in structural part of machines due to ease of joining process, disassembly option, equivalent strength to weld and provision of clamping force. But they have different types with different classification parameters, thus it is essential to learn key differences and selection criteria of both items. Otherwise wrong selection of bolt vs screw can reduce the joint efficiency, clamping force and shear resistance of structure joint, thus it is disaster for every structure which has wrong fastener in it. This article will explain mechanics selection of mechanical screw and mechanical bolt with thread, head, clamping and loading.

What is a Bolt
It is fastener which have two elements to provide clamping force, shear strength, load carrying capacity and holding force, thus provide machine elements with good kind of structural integrity. This fastener can replace welding and riveting in engineering drawing due to equivalent strength of metallic material and good structural design. Different types of threading, head styles, shank length and thread pitch options are available for installation of same in steel joints. Nut is another essential part of it which can provide compression on counter side of structure so that tension load value from stresses can diffuse in it.
What does a Look Like?
Bolt looks like fastener having threads on its shank and can easily receive operation from tightening tool to transfer clamping force on nut and itself without yielding. Anatomy of bolt have description in Figure.No.1. Same figure clearly shows that head, length, diameter and thread pitch is everything which reflect the bolt description and its capacity of handling. Different types of tools and thread mechanism decide that which bolt is going to take part in structural mechanism. Its look also decide the material corrosion condition because mark of pitting then it cannot hold the need of fatigue resistance against load.
Figure.No.1 describes bolt.
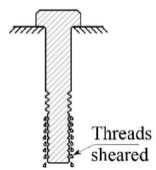
Figure.No.1. Bolt.
Types of Bolt
Different types of it are present in market which tell about its nature, presence of head tool compatibility, clamping force and interference with structural components. Following is the list of types of it:
Hexagonal Bolt
Anchor Bolt
Eye bolt
Socket Head Bolt
U-Bolt
Shoulder Bolt
T-Head Bolt
These types have selection criteria which depends that which structure and material have connection for it. For example if lifting have relevance with structure then of course eye bolt have its place to support the same.
For more information please visit at following YouTube videos,
Screws Characteristics
Screws are similar fastener elements which can thread and go inside the material without having presence of nut to clamp and put shank in compression. Their major property is to provide versatile solution to clamping structure so that it can accommodate the readymade fastener for assembly and disassembly purpose. Major characteristics of it are overall size, shape, head, length, material, thread type and purpose. Designer always select it depending upon its parameters and structure requirement, but the major characteristic of DIY (Do it yourself) is the final thing for its major application.
Screw Threading and Head Types
Its threading and head types tell about load bearing capacity, versatile nature, interaction with structure elements and behavior in tension / compression. Following are major types of it:
Machine Screws
Wood Screws
Drywall Screws
Sheet Metal Screws
Eye Screws
Concrete Screws
Set Screws
Flat Screws
Now comes to threading types and head nature, it is name indicating phenomenon like machine screw always have thread capacity and tension strength to counter load on it but drywall screw need only frictional force to hold hanging load on wall.
How do Bolts and Nuts Work
Both of these items make compression load on the structural element with presence of same threading pitch and type n it. While the female counterpart should have pre-drill in it so that clearance is present to go through the hole and provide place of nut for clamping mechanism. After making joint and compression they can resist shear and tension in a way that few thread can counter equivalent stresses of mechanics. And of course they give option to assemble and disassemble any time. Thus great clamping action with the provision for assembly and disassembly makes it fit for machine design.
Figure.No.2 describes bolt and nut.

Figure.No.2. Bolt and Nut.
Difference Between Bolt and Screw
Bolt vs Screw option in steel structure makes critical decision on design and analysis stage, because both can do same thing but with different cost and load carrying capacity. Therefore it is important that designer should have feasibility of both items in analysis without making compromise on safety and stability of structure. Combination of both also have application in clamping mechanism for example sex bolt can have both of them in place to clamp the member without introduction of nut on counter side.
Bolt Vs Screw Chart
Difference between both of them have description in terms of size, material, structural application, construction, clamping force, reliability, load carrying capacity and applicable standard. Table.No.1 have description of same parameters and items in it:
|
Bolt |
Screw |
|
Material canbe HSLA and stainless steel |
Material can be of stainless steel, copper, brass and even of plastic |
|
It has application for engineering structure to support critical applicationsm which have these kinds of fasteners |
Any structural, support casing, toys, decorative and protective cover parts may use them |
|
All the pre drill holes components may use them |
All components which can use threading hole in it may use them |
|
High clamping force can satisfy it |
Usually have design of low clamping force |
|
High reliability |
Low Reliability |
|
High load carrying capacity due to availability of big diameter |
Low load carrying capacity due to small diameter limitation |
|
Hexagonal Head U-Shape and allen key type are example of it |
Drywall, Round, Machine and Flat head types |
|
ASME Section II, SA-193 B7 or ISO 888 |
ISO 68-1 |
|
It is stronger |
It is weaker |
Table.No.1. Bolt Vs Screw.
Bolt Vs Nut
Difference between a nut and a bolt is the aspect which has relation with tightening of it, and shape profile structure goes to tension and compression stage. Nut basic function is to provide engagement length to the bolt on the clamping side of structure, while it can also help bolt to hold its compression torque without losing structure integrity of material. Bolt also make difference from nut in the shear mode because it goes to tension and develop the shear stress at thread portion but nut has calculation to resist shear forces and material integrity with equivalent stresses.
Fastener Vs Screw
Fastener are the clamping elements which can support, clamp, tighten and hold the two joining elements with different shapes of screws, bolts, studs and nuts. But on other hand screws are the particular class of fastener which can hold two elements without nut, counter side compression force, large diameter for big clamping force, coarse and deep thread and high torque for flange compression. For example carriage screw is also the category of fastener but off course in routine nomenclature it only depicts to hold carrying items, and fasteners have always place in joining member structure.
Nuts Vs Screw
Nut are the essential members of bolt system so that they can provide necessary counter compression on other side of structure member with bearing of shear tress on the thread engagement area. On the other hand screw fasteners does not require any type of nut except sex bolts, but they can make clamping or hanging just due to frictional contact and shear area of threads in it. Both items have clear difference in shape of them because each one has particular purpose to perform during clamping mechanism. They can be of stainless steel, low alloy steel and carbon steel with corrosion resistant coating on surface.
Pros and Cons of Bolt and Screw
Both items have pros and cons with their particular nature of job, work, structure and stress criteria, same has description in Table.No.2.
Bolts Screw Pros: -It can hold members with strength. -It is versatile in nature. -Use in heavy duty loading application. -Have application in different shapes or profiles. -Easy to disassemble. -Readily available for installation like drywall screw. -High Reliability. -Good for DIY work. Cons: -Expensive and delicate. -No application in concrete structure. -Need pre drill holes. -Can wear on high shear force. Table.No.2. Pros and Cons of Bolts and Screw.
Bolt Advantages
It has various superior properties for binding nature of job, because it can make connection with nut on the other side of member with introduction of pre force concept. It is reliable method to join two structural members because lot of engineering and design calculation have background when selection process come to an end. Disassembly process becomes so easy that only negative direction torque can make separation on same job. They are available in larger diameter that is why heavy duty structure has application of same item.
Bolt Disadvantages
They are expensive and particular profile with special coating of corrosion resistant material so that long span life is result of it. Always need pre drill holes for insertion in structure because clear hole can make facility of provision of nut on other side of surface. Special equipment need presence on site (either remote or local) for application of particular torque present on drawing of structure. These limitation have solution in self tapping bolt but off course then there is need of less clamping force requirement on the surface of structure member.
Screw Advantages
It can work in versatile nature so that easy assembly of joining members is possible without any need of special instrument, pre drill hole, access for nut and two side pre clamping mechanism. If DIY is need of job or job does hold critical members then feasible option for joining is allen screw types, because easy assembly process is always the user requirement for any job manual. It can have easy availability of item in market for common user due to application in several equipment of domestic appliances. And different head shape can have place for same size item due to similar nature of work.
Screw Disadvantages
Whenever Bolt vs Screw technical aspect come to design stage of joining members then disadvantages of screw make designer to go for bolt option due to drilling limitation, low diameter availability, unavailability of code provision, thread damage and limitation of tapping depth. Usually structure members have use in concrete hanging or bonding by fasteners, but in case of screw it is not viable that same can happen due to less penetration capability of screw thread in hard and brittle concrete.
When to Use Bolts or Screws
Both of these items use in particular application keeping in view of different design and engineering parameters for material, joint strength, clamping, force and compression value. Bolts have application for high reliability, high joint efficiency and more tightening torque value with insurance of two side compression provisions and diameter of stress calculation value. But on the other handscrew finds its use in versatile nature of job in which load bearing strength is not critical and screw can easily perform its function with just option of quick assembly and disassembly (keeping the threads intact and available for load types).
Figure.No.3 describes bolt vs screw.

Figure.No.3 Bolt Vs Screw.
Why Choose Tuofa to Custom High Quality Bolts and Screws
Question of bolts vs screws comes to an engineering design stage due to difference of reliability, cost, clamp bearing strength and shear force criteria. Thus selection of one item out of two is critical for economy and design judgement of project. These selection process should be done by company having qualification in relevant field. Tuofa has ISO certification and relevant experience in fabrication and assembly of engineering structures with bolting and screw option, so that design conditions have complete satisfaction with it.
For more information please visit https://www.tuofa-cncmachining.com/
Of course, our engineers can also provide you with more suggestions on the design of part drawings. Contact info@tuofa-cncmachining.com
FAQs about Bolts and Screws
How to identify Screws?
Identification parameters are diameter, thread pitch, shank length, bearing diameter, head type and point edge direction located at end of thread portion. Hex vs Allen screw have easy identification present on top of head which have conformance with tightening tool and for application in working place.
Cap Screw vs Bolt Screw
Both seems similar in shape but they have difference between them in term of counter clamping element i.e. nut present on other side of bolt joining structure. Cap screw can bear load in tension mode but it cannot go beyond certain diameter for handling of large clamping force with property of nut presence on other side of binding members.
Machine Screw Vs Bolt
Both have application in design of machine elements but the difference between bolt vs screw of this type is present in clamping force magnitude, bear stress threshold, tension in shank length and nut presence for extra compression on counter side of part.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 How to Cut Aluminum | 5 Cutting Ways
How to Cut Aluminum | 5 Cutting Ways 







