Stainless Steel Medical Screws - Authoritative Machining Process
 Nov 19,2022
Nov 19,2022

Due to the advancement of CNC machining technology in the past 10 years, CNC machining services are increasingly used in the medical industry.
Tuofa CNC machining takes stainless steel medical screws as an example, conducts in-depth analysis on the problems of insufficient plasticity of parts and high cost of small batch processing, and uses CNC machining to make up for the shortage of special machine tools for cold extrusion processing of threads; The CNC macro program is used to improve the thread processing method, solve the problems of poor rigidity of medical screws and excessive cutting force when turning threads, and provide a reference plan for the production of small batches of special material screws.
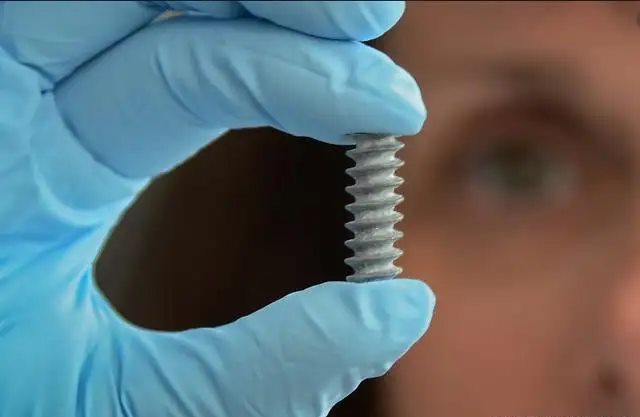

Comparison of medical screws and ordinary screws
Ordinary wood screws are widely used in the furniture manufacturing industry. Most wood screws are made of Q235A and are formed by cold extrusion, which has the advantages of low cost, high efficiency, and large output. Although the screw used in the human body is similar in structure to ordinary wood screws, it must have a certain strength and corrosion resistance. Medical screws made of 1Cr18Ni9Ti stainless steel are basically unable to be cold-extruded by special machine tools due to factors such as material, small batch production, and the need to make special tools.
The difficulties of medical screws' processing
For the production of small batches of medical screws, CNC machining can be used to make up for the lack of special machine tools. The diameter of medical screws is small, the pitch is relatively large relative to the diameter, and the rigidity is poor. In ordinary lathes, forming tools are used to process threads, and the cutting resistance gradually increases as the cutting depth of the tool increases. Due to the small diameter and long length of the medical screw, even if there is a support method in the process to offset most of the cutting resistance, it is easy to cause the screw to deform and cannot be cut, so it is difficult to use an ordinary lathe to process. CNC machining has the advantages of high efficiency and strong adaptability. Using macro programs to turn threads, the contact area between the tool and the workpiece is basically constant, and the cutting resistance will not increase with the increase of the cutting depth of the tool. Medical screws are also prone to deformation and bending. Tuofa CNC machining has carried out in-depth research on the processing of medical stainless steel screws and solved the problem that stainless steel is not easy to cut through reasonable process settings on the CNC lathe. The problem of insufficient rigidity in thread machining is solved by designing supporting fixtures and compiling macro programs for layered turning.
|
Try Tuofa Now! Tuofa Engineer Support Team - Real human quotes are more accurate than software quotes |
Get a free quote |
The principle of CNC machining of medical screws
According to the geometric characteristics of the medical screw, making a reasonable plan for the trajectory of the machining tool is the key to machining qualified parts. CNC machine tools use carbide-coated inserts to process threads. Only by calculating the reasonable spindle speed for turning medical screws can the reasonable service life of the tool be calculated according to the tolerance linear speed v of the insert. The calculation formula is
v=πDn/1000
In the formula, v is the linear speed (m/min); D is the rotation diameter (mm); n is the spindle speed (r/min).
According to the analysis of the force of the tool in the thread processing of medical screws, the main cutting force consumption accounts for more than 90% of the total power of the machine tool, and the feed resistance consumption accounts for more than 5% of the total machine power. As the cutting depth of the tool increases, the contact area between the tool and the workpiece becomes larger, and the cutting resistance gradually increases, which is easy to cause vibration, deformation, and bending of the parts and cannot be processed by CNC turning.
It can be seen that the traditional forming tools cannot meet the processing requirements of medical screws. For this purpose, the machining method is improved, using a CNC 35° profiling turning tool to control the trajectory of the tool nose to move according to the shape of the thread profile by programming a macro program. It is basically constant, and the cutting force of the tool in turning is basically constant and small, which overcomes the disadvantage of the increasing cutting resistance of traditional thread-forming tools.
Realization of CNC machining of medical screws
1. Selection of tool materials
Medical screws are mainly used for the connection between artificial joints and human bones. They need certain strength and corrosion resistance. Therefore, 1Cr18Ni9Ti stainless steel material with acid resistance, alkali resistance, corrosion resistance, and certain strength is selected. This kind of stainless steel has the characteristics of high strength, large plasticity, and serious hardening during processing. During cutting, the cutting resistance of the tool is large, which is easy to cause serious deformation of the medical screw, and the tool is subjected to high cutting temperature, which is easy to form cutting tumors. Because medical screws are prone to work hardening, making them difficult to process, you should choose blades that are not easy to bond, and have good heat resistance, wear resistance, and thermal conductivity. At the same time, they should be fully cooled during processing, and good heat dissipation should be selected, Water-based cutting fluid is more reasonable.
2. Structure and size of medical screw parts
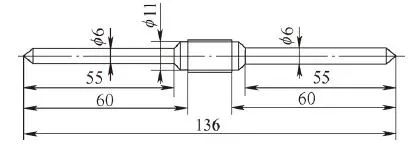
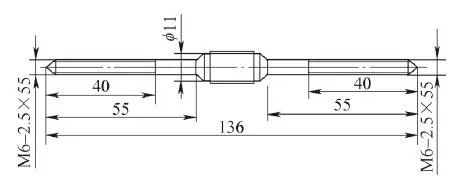
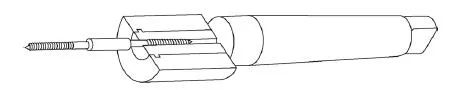
The size of the medical screw shown in Figure 1 is M6-2.5mm×55mm, the outer diameter is 6mm, the pitch is 2.5mm, the width of the bottom groove is 0.4mm, the width of the top groove is 0.05mm, the tooth angle is 60°, the length is 55mm, and the right end Maximum diameter 11mm. Due to the poor rigidity of the parts and the relatively large thread pitch relative to the diameter, there are certain difficulties in how to enhance the rigidity of workpiece clamping and the reasonable preparation of CNC machining macro programs.
Figure 1: Medical Screws
 a) 3D map
a) 3D map
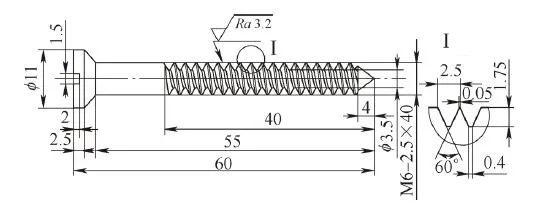 b) Structure and size
b) Structure and size
3. Processing technology
Medical screws are produced in small batches. If the general one-clamp-one-top method is used to turn threads, due to the poor rigidity of the workpiece, it cannot withstand the cutting force, and bending deformation will occur in the middle of the workpiece. Therefore, the workpiece must be supported during thread turning to ensure that the workpiece is in The support fixture is stable and reliable, preventing the workpiece from being deformed and unable to be processed. It is necessary to design a special turning thread full support fixture to assist in supporting the screw.
The thread pitch of the part is relatively large. In order to reduce the cutting resistance when cutting the thread and prevent the deformation of the part, a 35° profiling turning tool with a carbide titanium carbide coating is selected, and the macro program is used to compile the macro program layered cutting thread by the trajectory synthesis method, which can greatly reduce the turning thread. The cutting resistance at the same time remains basically constant.
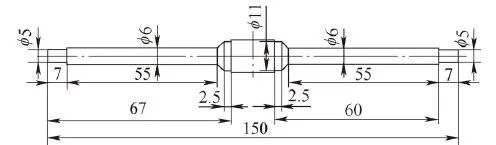
The medical screw processing process is shown in Figure 2. The specific steps are:
① The two parts are connected together for processing, leaving an extra 15mm in the middle to facilitate the clamping of the self-centering chuck, and the extra 7mm at each end is used as a process head for drilling the center hole.
② One clamp and one top turn the outer circle of 6mm in diameter and 11mm in diameter.
③ Clamp the 6mm outer circle to remove the process head so that the center hole is also removed, and the two ends of the part can be turned into a complete taper.
④ Clamp the 11mm outer circle, use the support fixture to support the 6mm outer circle of the medical screw, and use the macro program to turn the thread.
⑤ Cut off the screws connecting the two pieces together to ensure the size of 60mm.
⑥ Clamp with a vertical rotary table on a horizontal milling machine, and mill a 1.5mm wide slot with a saw blade cutter.
Figure 2: Medical screw processing process
 a) Drill a center hole at both ends of the blank
a) Drill a center hole at both ends of the blank
b) Turning the outer circle and leaving the process head
 c) Turning taper after cutting off the craft head
c) Turning taper after cutting off the craft head
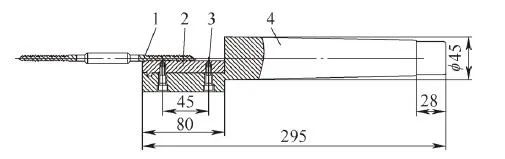
 d) Support for turning threads with fixtures
d) Support for turning threads with fixtures
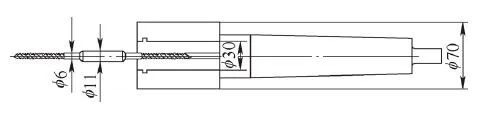
 e) Flat length after cutting, grooving on the milling machine
e) Flat length after cutting, grooving on the milling machine
4. Working principle of thread turning support fixture
The thread-turning support fixture is shown in Figure 3. During processing, the two pieces of medical screws are clamped together to facilitate the realization of small batch production in different processes; the support sleeve is made of HT200 gray cast iron, which has the characteristics of a low friction coefficient. The boss on the support sleeve plays the role of axial positioning; the function of the two screws on the clamp is to connect and fasten the support sleeve and the clamp body; the left end of the clamp body plays the role of positioning the support sleeve, and the right end is a standard Morse 5 No. taper. The fixture is installed in the tailstock of the CNC machine tool, and the tailstock is moved when processing the thread so that the support sleeve in the fixture supports the external turning of the screw. The CNC turning thread is shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4 CNC turning thread
 a) Partial sectional view
a) Partial sectional view
1—Medical screw 2—Support sleeve 3—Screw 4—Clamp body
 b) Front view
b) Front view
 c) 3D map
c) 3D map
Figure 3 Thread turning support fixture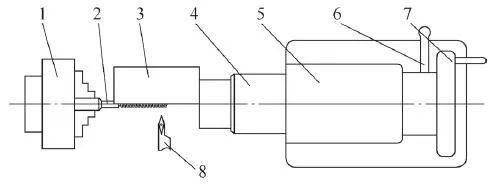
1—Self-centering chuck 2—Medical screw 3—Support fixture 4—Machine tool tailstock sleeve
5—machine tool tailstock 6—tailstock locking handle 7—tailstock handwheel 8—35° CNC copy tool
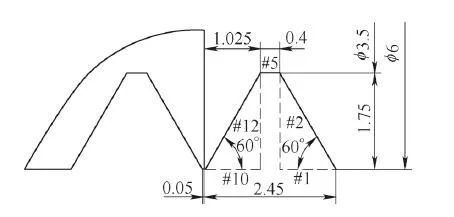 Figure 5 Macro program relationship
Figure 5 Macro program relationship
5. Macro Programming
Among the various elements of parts processing, macro programming is the key. The following is the macro programming for the thread processing for the CNC turning of the FANUC0i system. The principle of macro programming: the tool determines a point in the thread profile shape and moves a pitch each time; the tool returns to the starting point and moves a point along the thread profile shape, and then moves a pitch; until the entire profile is turned. After the shape, the layered feed turning is realized through the coordinate system offset, and the complete tooth shape is finally turned. Figure 5 shows the macro program relationship, and the second-level nested program is as follows.
T0101;
M03S800;
#8=1.75;
N10G52X#8Z0;
G00X6Z2.45;
#1=0;
N20#2=#1*TAN[60];
#3=6-2*#1;
#4=2.45-#2;
G0X#3Z#4;
G32X#3Z-55F2.5;
G00X7;
G00Z2.45;
#1=#1+0.1;
IF[#1LE1.025]GOTO20
#5=0;
N30#6=1.425-#5;
#7=3.5;
G00X#7Z#6;
G32X#7Z-55F2.5;
G0X7Z1.425;
G0Z1.425;
#5=#5+0.1;
IF[#5LE0.4]GOTO30;
#10=0;
N40#12=#10*TAN[60];
#13=3.5+2*#12;
#14=1.025-#10;
G0X#13Z#14;
G32X#13Z-55F2.5;
G00X7;
G00Z1.025;
#10=#10+0.1;
IF[#10LE1.025]GOTO40;
G52X0Z0;
#8=#8-0.5;
IF[#8GE0]GOTO40;
G00X100Z10;
M30;
6. Processing precautions and quality inspection
During the processing of medical screws, the error of the outer diameter of 6mm should be controlled to be about 0.04mm. If the error of the outer diameter is large, it will cause a poor fit between the 6mm diameter semicircular hole in the support fixture and the outer circle of the screw. , the supporting effect of the fixture will be weakened, and vibration or workpiece deformation will occur during turning. At the same time, when turning the thread, the blade must be kept sharp, and the tool cannot be changed in the middle, otherwise, the thread will be easily buckled.
Use a micrometer to measure the outer circle size of the medical screw with a diameter of 6 mm, use a caliper to measure the pitch of the thread, and use a surface roughness comparator to measure whether the surface roughness value Ra3.2μm of the thread meets the standard. After testing, the CNC parts fully meet the size requirements and can meet the requirements of use.
| Let's Start A New Project Today |
| Get a Free Quote |
Conclusions from Tuofa CNC machining
Tuofa CNC machining has completed the design and macro programming of medical screw support fixtures through the analysis of the medical screw CNC machining principle, realized the CNC machining of medical screws and made up for many shortcomings of cold extrusion ordinary screws. The small batch processing of medical screws is completed at a lower cost. This method of processing medical screws using CNC machine tools provides a reference for the processing of similar screws with special materials.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 State-of-the-art skills in machining thin-walled shell-and-tube hardening hardware
State-of-the-art skills in machining thin-walled shell-and-tube hardening hardware 







