Polypropylene vs Polyethylene: Choosing the Right Material
 Apr 02,2024
Apr 02,2024

Polypropylene and polyethylene have many features in common. The chemical structures of both polymers are very similar. However, they both are different materials so obviously possess some differences. Polypropylene can survive elevated temperatures during working. It is a food safe material and has high resistance to moisture. While polyethylene is a common packaging plastic and a good electrical insulator. But these features are not enough to draw any conclusion of which is the best material for specific application. This article will explore the key differences and similarities with the pros and cons of each plastic. Furthermore, it will highlight the applications and other important features of both materials.
Introduction to Polypropylene (PP) and Polyethylene (PE)
PP and PE plastics are thermoplastic. Both are lightweight and have chemical resistance. These plastics can be melted and reproduced multiple times.
Definition and Overview of Polypropylene (PP)
PP is a thermoplastic and a polyolefin. This means it is composed of repeating propylene units. It can be manufactured by different processes. Common procedures are injection molding and extrusion.

Definition and Overview of Polyethylene (PE)
PE is made of different monomers still being a polyolefin. The most common monomer in PE is ethylene. PE products are made of a variety of methods. Same as the PP which is injection molding and extrusion. PE has high chemical resistance and electrical resistance. Common grades of PE are low-density polyethylene (LDPE) and high-density polyethylene (HDPE). LDPE is flexible and a food safe material. HDPE is a hard and strong material and has common applications of food containers, pipes and bottles.

Polyethylene and polypropylene are both types of what material?
PP and PE plastics belong to the thermoplastic family. They both are polyolefin. They both have the capability to be melted and reproduced multiple times.
Polypropylene vs Polyethylene: Pros and Cons
PP and PE plastic both have some pros and cons. These are discussed in detail below:
Polypropylene Pros and Cons
Polypropylene has many advantages. These are:
- PP has high chemical resistance. It cannot easily react with acid and therefore it is a food safe material.
- PP has high resistance to corrosion. It is a safe material to be used in chemical tanks and containers. The melting point is also suitable for many climate-based applications. It cannot freeze and can be used in making pipes.
- PP converts to liquid when reached to it melting point. It means it can be reshaped several times without degradation. The good heat response makes it suitable for injection molding applications.
- PP is a good high electrical insulator. The good insulation makes it ideal for electrical components applications like cable or wires.
- PP has high resistance to moisture. It is considered aa a good option for waterproofing applications.
- PP is soft and flexible. It means it can bend to any shape without breaking.
- PP has high impact resistance. it can survive heavy loads up to 4800psi.
- PP is a lightweight material. This makes its manufacturing very easy.
The disadvantages of PP are as:
- PP can be affected by UV-degradation. It is not a suitable choice for high UV penetration applications.
- At high temperatures, its chains can be degraded. This leads to oxidization and cracking of polymer chains.
- PP has poor bonding features.
- PP is a flammable material.
Polyethylene Pros and Cons
PE has many advantages. And these are as follows:
- PE is soft and flexible plastic but has good impact resistance. It will stretch without breaking, which is uncommon in polymers.
- PE has high resistance to water. It has high durability in moist areas as compared to other plastics.
- PE is a good electrical insulator. This makes it electrostatically charged polymer, therefore has applications as antistatic agent.
- PE is transparent to opaque. This low-density clarity makes it a good option for a food safe and packaging material.
- High-density PE is a cost-effective polymer because it is recyclable. This can be used in manufacturing new plastics from old material.
- The melting point of PE is from 120-180℃. High resistance to heat makes it very demanding in many high temperature applications.
The disadvantages of PE are as follows:
The degradation of PE takes longer than other polymers. It takes decades to degrade at landfill site which results in running out of space.
- Disposal of PE is harmful in the form of incineration. It releases harmful gases.
- Common extraction of PE is from natural gas or petroleum. This is a limited amount of extraction.
- High production of PE takes heavy amount of energy and releases CO2 emissions.
Recycling PE is possible but can be a complex and costly project.
What is the Difference Between Polyethylene and Polypropylene?
PP and PE plastics can be differentiated with density. PP is a lightweight polymer and has high resistance to elevated temperatures. it also has high chemical resistance and is harder than PE. PP has resistance to breakage. While PE is a soft and flexible polymer. It has the advantage of easy coloring and can mold to any shape.
Chemical Properties
Chemical resistance: The chemical resistance of PE is higher than PP. PE is non-polar in nature and has high chemical resistance. It is non-reactive to many acidic and basic medias. At higher temperatures, the chemical resistance is exceptional.
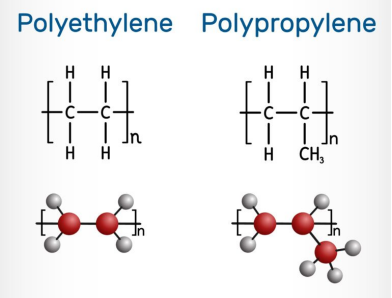
Chemical Structure
PP and PE plastics both belong to the polyolefin family. But they are both very different chemical structures. PE is made of ethylene monomers. PP is made of propylene monomers. They both impart differences in their chemical and physical properties.
Physical Properties
The physical properties of PP and PE plastics are as:
| Properties | Polypropylene | Polyethylene |
| Density | 0.91g/cm3 | 0.94g/cm3 |
| Melting range | 130-170℃ | 115-135℃ |
| Chemical resistance | Acid, strong base, solvent and organic solvent resistant | Acid, base and solvent resistant |
| Flexibility | Rigid and hard | flexible |
| Water resistance rate | 0.8% | 0.5% |
| Transparency | Transparent | Opaque |
Is polypropylene stronger than plastic
Polypropylene is typically stronger and more durable than many other common plastics, offering better resistance to wear and tear in various applications.
Tensile Strength of PP and PE
The tensile strength of polypropylene (PP) generally ranges between 30 to 35 MPa (megapascals), showcasing its capacity to withstand considerable force without breaking. In comparison, polyethylene (PE) varies more broadly in tensile strength due to its different forms: Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is around 8 to 31 MPa, while High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) can range from 20 to 33 MPa. These differences highlight the importance of material selection based on specific strength requirements in applications.
Crystalline Solid vs. Amorphous Solid in PP and PE
PP and PE both are semi-crystalline solids. PP normally appears cloudy or hazy in its natural form. The properties of PE are dependent on the relative crystalline and amorphous content.
Mechanical Properties
| Properties | Polypropylene | Polyethylene |
| Tensile strength | 5800psi |
LDPE: 2100psi HDPE: 6100psi |
| Impact resistance | Less | High |
| Flexural strength | 20MPa |
LDPE: 26MPa HDPE: 50MPa |
| Flammability | 260℃ |
DPE:343℃ HDPE:388℃ |
| Vapor transmission rate | 10b/m2/day(high) | 5g/m2/day (less) |
Thermal and UV Resistance
Thermal resistance of PP is 80℃. The strength of PP starts decreasing after reaching this temperature. PE has thermal resistance of 130℃.
PE is prone to UV degradation in a prolonged exposure. While PP performs better in UV rays and is a good option for outdoor use. But the UV resistance of both polymers can be enhanced by adding stabilizers.
Cost of PP vs. PE
There are many factors involved in calculating costs like supplier, manufacturing, application, etc. But in general PE is slightly costly than PP.
- Cost of HDPE and LDPE is $1.50/pound and $0.7/pound, respectively.
- The cost of PP is from $0.3-040/pound.
Polyethylene vs Polypropylene: In CNC Machining Service
As a metallurgical expert in materials science at Tuofa CNC Machining, let's delve into the comparison between Polyethylene (PE) and Polypropylene (PP) in the context of CNC machining services. This comparison is crucial for professionals in the manufacturing industry and mechanical designers.
According to its basic Material Characteristics
Polyethylene (PE)
- Variants: Includes LDPE and HDPE.
- Properties: Offers high ductility and impact strength but lower temperature resistance.
Polypropylene (PP)
- Properties: Higher thermal resistance, rigidity, and hardness compared to PE.
CNC Machinability
Machining Polyethylene
- Ease of Machining: Generally easier to machine due to its softer nature.
- Tooling Considerations: Requires sharp tools to prevent material build-up on the cutting edge.
Machining Polypropylene
- Challenges: Its rigidity can lead to more wear on cutting tools.
- Tooling Adaptations: Requires robust and possibly more specialized tooling.
Applications in CNC Machining
Applications of PE
- Ideal Uses: Components that need high ductility and are not exposed to high temperatures.
- Industry Examples: Low-stress applications like plastic containers or insulation parts.
Applications of PP
- Ideal Uses: Parts that require higher temperature resistance and rigidity.
- Industry Examples: Automotive parts, living hinges, and laboratory equipment.
Post-Machining Considerations
Finishing of PE Parts
- Techniques: Includes chemical smoothing or flame polishing.
- Limitations: Susceptible to deformation at high temperatures.
Finishing of PP Parts
- Techniques: Mechanical finishing methods are more effective.
- Durability: Better resistance to high temperatures during post-processing.
Polyethylene and Polypropylene Products
Packaging and Storage Containers
- PP is a useful material. It is normally used in making food packaging and other things like carpet, rope, and grocery bags etc.
- PE is a versatile polymer. LDPE is a flexible material and used in making food containers and packaging materials. While HDPE is a rigid material and used in making bottles, bucket, or pipe. It is also an electrical insulator and is electrostatically charged material. It is used in making cable wires and wire insulation.
Applications and Uses in Industry
PP polymer has many applications. Some of them are:
- PP is used in making furniture due to having slippery surface.
- PP has low friction which is ideal for automotive applications. It is used in making gears in machines and cars.
- It has high chemical resistance. Therefore, it has many applications such as cleaning agent, bleach and first-aid products.
- PP is a great electrical insulator. It is used in making cables and wire and for electrical insulation, and casing for batteries.
- The medical applications of PP are for making syringes, vials, petri dish, pill box, specimen bottles. It is non-reactive with solvents. Therefore, it cannot react with any harmful liquid and is easy to clean. This feature is most suitable for medical applications.
- PE polymer also has many applications. These are as:
- HDPE is rigid and is used to make trays, bottles, pipes, buckets, and crates etc.
- LDPE is flexible and is used in making trash, plastic and grocery bags. It is a common material for making food packaging material.
- PE is used in making water and sewer pipes for housing. It has great chemical resistance.
- PE films are used in greenhouses. It is also used in walk-in tunnels and low tunnels covers.
- PE crosslinked and copolymer is used for wires and cable because of being goof electrical insulator.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
There are many factors involved in the environmental impact and sustainability of PP and PE plastics. Some highlights are as:
Eco-Friendliness and Recycling
The landfilling PP wastes have a great effect on the environment. Cadmium is released after a significant amount of time from the waste of PP. This is a toxic gas for plants and animals. But it is safer than many other plastics. It does not produce toxic waste when burned down. However, it can be melted and reshaped easily which makes recycling easy.
PE pollution disturbs the environment by changing natural habitations. PE waste reduces the oxygen level which is harmful for aquatic animals. This also disturbs the food chains and affects many species.
Impact on Daily Life
PP is considered as safe plastic to be used in our daily life. But heavy use of plastic can be a cause of cancer. Unfortunately, it is impossible to avoid plastic completely in our daily lives.
PE is elastic and has high chemical stability. It is also a non-biodegradable polymer. And conventional disposal like landfilling or incineration increases pollution.
Which is Better Polypropylene or Polyethylene
1.List of Elements: PP vs. PE
PP is made of propylene monomer while PE is made of ethylene monomer.
2.Amorphous vs. Semi-Crystalline Polymers
The major difference in amorphous and semi-crystalline material is its molecular structure. amorphous has random and entangled monomers. Semi-crystalline has an arranged structure. PP and PE plastics, both are semi-crystalline.
3.Resistance and Durability Differences
PE is a soft and flexible material. The durability of this polymer is exceptional because it can bend to any shape. PP has high resistance because it is rigid and stiff. The durability of PP is also good.
4.Transparency: Clear Bags vs. Opaque Materials
PP is a transparent material and PE is opaque, translucent material.
5.Is polypropylene better than plastic?
PP is softer and flexible than man common plastics. It is considered a safer option than many plastics.
Selecting the Right Material
For any project, the selection of right material between PP and PE plastic, you should know many factors. Depending on the factors like durability and strength, PP is a good choice. It is the best choice for medical applications, automotive, and for food packaging. PE is flexible and soft material. It is also the best for food packaging material.
For electrical insulation, PP and PE both have nearly the same electrical resistance. But PP has better temperature range from -30-110℃. It is commonly used in wall insulations for cable and wire insulation.
Conclusion
PP and PE plastics both are commonly used polymers in our daily lives. They both originate from petroleum products but have different features. Depending on the factors like manufacturing, cost, application, durability, strength and many more, both can be a suitable choice. The environmental impact of both polymers is less and are eco-friendly material. However, PP is a better choice when strength is required. Thermal resistance and chemical resistance are very good. PE is good for cost effective factor and has lesser environmental impact.
If you are new to the field and has no experience in selecting right material, then it is better to consult an expert. TUOFA CNC machining has experts with years of experience in selecting the right material. Skilled labor, advanced tools and machinery make them the best consultant globally. For contact expert in TUOFA CNC machining, please visit: https://www.tuofa-cncmachining.com/
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 91 Types of Metals and Their Engineering Applications
91 Types of Metals and Their Engineering Applications 







