Laser Etching Compared: Engraving, Marking, CNC Machining
 Apr 08,2025
Apr 08,2025

If we explain laser etching in simple terms, it is a method of marking materials. This process is used in many important industries such as aerospace, automotive, surgical and electronics. In this article, three other relevant processes to laser etching are also discussed, including engraving, marking, and CCN machining. We will discuss how these processes are different from laser etching in this article.
What is Laser Etching?
When we talk about laser etching, we often compare it with other methods. Let's start with “What is Laser Etching?”.
A Simple Explanation of Laser Etching
You see engraved logos, etc., on wood, plastic, and steel products; these permanent logos are engraved on the material's surface through laser etching. Laser etching makes these marks by melting or vaporizing, or changing the surface.
How Does Laser Etching Work?
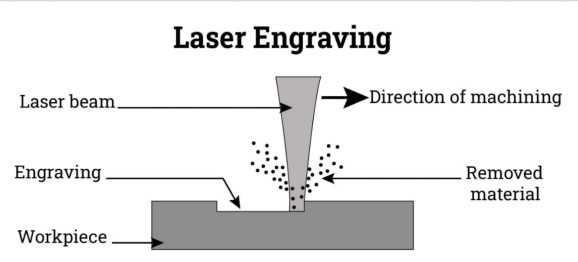
In the following figure, a focused high-power laser beam falls on the workpiece. It increases the material temperature beyond its boiling point, vaporises the material into fumes to engrave permanent, deep marks. It is the process of melting and deforming the material. A very small amount of material is removed from the surface to leave permanent marks.
When Was Laser Etching First Used? -History Intro
In the 1960s, laser etching emerged as a technology to make permanent marks on the workpiece. Now, it is an advanced process of engraving the material with high precision.
|
Year |
Milestone |
|
1960 |
First working laser invented (ruby laser) |
|
1965 |
Early laser marking experiments begin |
|
1970s-80s |
Industrial adoption of part labeling |
|
1990s-Present |
High-speed fiber lasers revolutionize precision etching |
Laser Etching vs Laser Engraving: What's the Difference?
Both processes or methods serve the same purpose, which is making logos or engraving any design, etc., on the workpiece. The following are some points on which these processes differ from each other.
Depth Comparison: Etching vs Engraving
Laser Etching
In laser etching, the marks are not deep but high contrast as compared to the other surface. The depth of the marks remains up to 0.001" or less.
Laser Engraving
In laser engraving, the marks are more like grooves on the surface because of the vaporizing of the material. The depth of the marks remains in the range of 0.001" to 0.005" or more.
- Laser engraving makes deeper cuts on products.
Appearance and Visual Differences
The following table shows the important points in terms of appearance and visual differences.
|
Feature |
Laser Etching |
Laser Engraving |
|
Depth |
Shallow (surface-level) |
Deep (tactile groove) |
|
Durability |
Good for indoor use |
Highly wear-resistant |
|
Contrast |
High (ideal for dark metals) |
Depends on material & settings |
|
Speed |
Faster (less material removal) |
Slower (deeper cuts required) |
For better understanding, you can see the following figures.

Choosing Between Laser Etching and Engraving for Your Project
If you know the speicalities of both processes, you can decide easily which method to use for your project.
Laser Engraving
If the material of your project is thick, for instance, wood and needs deeper cuts, choose laser engraving. Its cuts are long-lasting.
Laser Etching
For fast, high-contrast marks, laser etching is preferable. It is suitable for thin, heat sensitive materials, for instance plastics, etc.
How Deep Does Laser Etching Go?
Laser etching is the process which makes less deep, high-contrast marks on the surfaces. The structural integrity is not affected by laser etching. 0.0005" to 0.001" is a range of laser etching marks, which means a very small amount of material is removed.
Factors Affecting Laser Etching Depth
The following are the points which affect laser etching depth:
- Laser Power: Intensity of the laser
- Material Type & Hardness: Easy deep marks on soft materials such as Al
- Speed: If the speed of the laser is slow, cuts will be deeper
- Pulse Frequency: More pulses per area = deeper etching
Can Laser Etching Depth Be Precisely Controlled?
By controlling the points which affect laser etching depth, you can precisely control the depth of cuts. Now, due to advancements in laser etching like CO₂ lasers can make micron-level marks due to the following parameters:
- Power modulation
- Focus control
- Multiple passes
Laser Etching Depth vs Engraving Depth:
In the following table, we have provided real-life examples of the difference of depths in laser etching and laser engraving.
|
Application |
Etching Depth |
Engraving Depth |
Why It Matters |
|
Metal Tool Tags |
0.001" |
0.005"–0.020" |
Etching preserves tool strength; engraving withstands abrasion. |
|
Jewelry Logos |
0.0003"–0.001" |
0.003"–0.010" |
Etching for subtle branding; engraving for bold designs. |
We can see that laser etching makes fewer deep cuts on the workpieces.
Laser Etching vs Laser Marking: How Do They Compare?
As we mentioned earlier, laser etching and laser marking are used for the same purpose, which is to make logos, QR codes, etc. Earlier, we mentioned some factors, such as makrs depth, etc. discussed to understand the difference between laser etching and laser engraving. Here is an extended explanation.
Understanding Laser Marking and Its Purpose
First, we need to know what laser marking is. It is a broader field which includes annealing, etching, engraving and foaming. The purpose of laser marking is to alter the material's surface without significant material removal.
When to Use Laser Marking Instead of Etching
Laser Marking
- For heat-sensitive material like coated materials, choose laser marking due to low heat. Laser etching can melt it.
- For surface change only, Laser marking is best because laser etching involves slight surface ablation.
- For dark, high-contrast marks on stainless steel, use laser marking.
- For high-speed industrial coding, laser marking is good.
Which Method Lasts Longer: Laser Marking or Etching?
According to the following table, laser marking lasts longer.
|
Factor |
Laser Marking |
Laser Etching |
|
Durability |
High (chemical/oxidation bond) |
Moderate (surface melt) |
|
Wear resistance |
Excellent (embedded mark) |
Good (but can wear off under abrasion) |
|
UV/chemical exposure |
Resistant |
May fade over time |
Common Materials for Laser Etching
Laser etching is suitable for various materials. A few of them are discussed below:
Laser Etching on Metal
Metals like Al or stainless steel are laser etched using fiber lasers or high-power CO₂ lasers. The laser melts the surface to create a permanent, high-contrast mark on the surface of the workpiece.
- Use low-power laser for fine marks on the surface
- Use a dry lubricant to avoid oxidation during the etching process
- Use multiple low-power passes for deeper cuts
Laser Etching Glass
The best laser technique for making marks on the glass is the CO₂ laser. This laser creates a frosted look by micro-fracturing the surface. Laser etching is used for drinkware, lab equipment, etc.
For smooth, even frosting, use low speed and high frequency.
For better results,
- Pre-mask the glass
- Avoid deep etching
Laser Etching Wood
There are different types of wood, like hardwood (oak) and softwood (pine). For hardwoods, CO₂ lasers are best. This laser vaporizes the surface and creates light or dark burns on the surface.
Use medium-power lasers for clean marks on the wood.
For better results,
- Sand the surface first
- Use vector mode
Laser Etching Plastics
CO₂ lasers can precisely make marks on ABS, Acrylic, polycarbonate and PET plastics.
- Use low-power (5-15W) lasers
- White plastics result in the best contrast
- Avoid PVC because it releases chlorine fumes
Can Leather and Textiles Be Laser Etched?
Yes, low-power lasers are available for etching leather and textiles. CO₂ lasers are often used for etching leather and textiles.
- For best results,
- Low power + high speed
- Ventilate the area well during laser etching on leather and textiles
Step-by-Step Guide: The Laser Etching Process Explained
By practicing the following ways, you can be a master in laser etching. So, let's discuss these factors:
Preparing Your Design Files
Designing files is the first step in laser etching. For designing files, different software and formats are used. For instance,
Formats
- Vector Files (SVG, AI, DXF)
- Raster Files
Software
- Adobe Illustrator
- RD works
Machine Setup and Calibration Tips
In the machining setup, you should check the following parameters:
- Lense Cleaning:To avoid blurry marks
- Focus Calibration
- Air Assist:To reduce burning
- Test Run:Test a little section to check the working
Calibration Tips
Do material-specific calibration
For metals, use a high-power laser (20-50W)
For plastics, use low-power lasers (15-40W)
Executing the Etching Process
The following table shows some optimum values to execute laser etching precisely:
|
Material |
Speed |
Power |
Focus (Z-Height) |
|
Stainless Steel |
800 mm/s |
70% |
Slightly defocused (~0.5mm below surface) |
|
Anodized Aluminum |
1200 mm/s |
30% |
Sharp focus |
|
Acrylic |
500 mm/s |
40% |
Sharp focus |
|
Wood |
300 mm/s |
60% |
Sharp focus |
|
Leather |
1000 mm/s |
15% |
Slightly raised (~1mm above surface) |
Post-Etching Cleaning and Finishing Steps
Post-etching cleaning is important to make the appearance of the product aesthetic.
The following are some final steps:
- Remove Residue using acetone or compressed air for metals and plastics, respectively
- Apply blackening compound on metals or rub the area of plastic with toothpaste to get high contrasts
- Apply a protective coating
- Inspect the quality using bright light or a magnifying glass
Laser Etching Vs CNC Machining: Precision Methods
CNC machines are also used for engraving logos or QR codes on the workpiece. If you know the strengths of these technologies in terms of cost, precision, quality, etc. You can choose one of them easily depending on your requirements.
Laser Etching vs CNC Machining:
The important factors, such as precision, speed, cost, etc., are discussed below in this table:
|
Factor |
Laser Etching |
CNC Machining |
|
Precision |
±0.01mm (10µm) |
±0.025mm (25µm) |
|
Speed |
Faster (seconds for marking) |
Slower (minutes-hours for cutting) |
|
Material Removal |
Minimal (surface-level) |
Significant (3D shaping) |
|
Cost (Per Part) |
Lower (no tool wear) |
Higher (tooling + setup) |
|
Best For |
Logos, serial numbers, fine details |
Structural parts, deep engravings, 3D contours |
Laser etching can make micro-level marks on the workpiece more efficiently and cost-effectively.
What Is the Difference Between CNC And Laser Etching?
The difference related to precision, speed, cost, etc., is discussed above. The further difference is that CNC machining is better than laser etching. For instance, a CNC machine is suitable:
- For structural modifications
- For thick materials
- For ultra-smooth surface
- High-force applications
Combining CNC and Laser Etching
In many applications, CNC machining and laser etching are used in combination for cost and time savings, enhanced durability. Such as in the case of:
- Functional + Aesthetic parts
- Hybrid Manufacturing
- Prototyping
Laser Etching Vs Traditional Methods
There are various traditional methods other than laser etching for engraving on the workpiece. These methods include chemical etching, mechanical etching, etc. In this section, we will see how laser etching is different from these traditional methods.
Laser Etching vs Chemical Etching:
Advantages
|
Laser Etching |
Chemical Etching |
|
No chemicals needed |
Uniform Depth |
|
High Precision |
No heat damage |
|
Fast Speed |
|
|
Versatile for various materials |
|
Limitations
|
Laser Etching |
Chemical Etching |
|
Limited depth; surface level |
Toxic waste |
|
Can't be used for reflective materials |
Slower process |
Laser Etching vs Mechanical Etching
Mechanical etching is often used for heavy-duty industrial parts such as steel stamps etc., while laser etching is used for delicate materials, i.e. glass
|
Factor |
Laser Etching |
Mechanical Etching (Diamond Drag/CNC) |
|
Precision |
Extremely High |
Moderate (tool wear affects consistency) |
|
Speed |
Very Fast |
Slower (physical contact required) |
|
Material Stress |
None (non-contact) |
Deform soft materials |
|
Maintenance |
Low (no moving parts) |
High (burr removal, tool replacement) |
Choosing the Right Method
The selection engraving method depends on purpose, material and the complexity of the design. For instance, for plastic material, laser etching is best because chemical etching will destroy the material's integrity. If you need deeper cuts, use mechanical or chemical etching.
Applications for Laser Etching Across Industries
In this section, we will explore some common industries where laser etching is being used or can be used.
Industrial & Manufacturing Uses
Laser etching is commonly used for industrial & manufacturing uses. For instance, it is used in microelectronics, automotive parts, tool and die marking, etc.
- Pros
- Permanent Marks
- High Precision
- No physical damage
- Fast & Automated
- Cons
- Not suitable for reflective materials
- Marks depth is limited
Branding and Logo Etching for Businesses
Laser etching is also used in branding and logo etching for businesses. Its common applications include jewelry, promotional products like metal cards, etc. and electronics.
- Pros
- High-quality finish
- Customizable
- No ink or chemical
- Cons
- Not suitable for all materials, i.e. plastics
- Expensive for small-scale production
Security, Identification, and Traceability
You see different hidden marks on the ID cards or passports, these marks are engraved using laser etching. Its other applications include military equipment and pharmaceutical packaging.
- Pros
- Tamper-proof
- Micro-text & barcode
- UV/Convert Marks
- Cons
- High initial costs due to specialized tools requirement
Medical Devices and Healthcare Applications
The applications of Laser etching in medical devices and healthcare are given below:
Surgical Tools
Lab Equipment
Medical Implants
- Pros
- Biocompatible
- Sterilization-resistant
- Meets Medical Standards
- Cons
- Higher Regulatory Requirements
Conclusion
We conclude that Laser Etching is a versatile engraving method which uses a focused beam to make permanent marks on the workpiece. It is not suitable for reflective and low melting point plastics. It is used in various industries, including medical and healthcare, security departments, etc.
FAQs
How Long Does Laser Etching Last?
It depends on the material. For metals, it remains permanent. For plastics, it lasts for at least ten years.
Does Laser Etching Wear Off Over Time?
In the case of metals, laser etching does not wave off easily, but in plastics, yes, It can wave off.
How Fast Is the Laser Etching Process?
It depends on the complexity of the required design. For a simple text, it only takes 2-10 seconds.
Is Laser Etching Safe for All Materials?
No, it is not safe for all materials because it can reduce the structural integrity of some coatings and PVC.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 Spline Shaft Guide: Types, Standards, & Materials
Spline Shaft Guide: Types, Standards, & Materials 







