Crankshaft VS Camshaft: Understanding the Key Differences
 May 16,2023
May 16,2023

You have already seen many engines with different shapes and sizes but depends upon the crank and camshaft. Any type of Engine that runs on the combustion of fuel and air, has these two durable components common(crank and camshaft). Whether it has a Flat or V-shaped cylindrical Engine. The crankshaft performs a remarkable conversion: it changes the linear(Up/Down) motion of the piston into the rotatory motion of the axle which gives power to rotate the wheels of the Automobile. The camshaft controls the intake of the Mixture of Fuel + air and the extraction of remaining gases from the cylinder through the valve.
What is a Shaft?

The shaft is a Durable long rod and Mechanical Component mostly used to transfer power and torque to the other moveable part of the machine through different links and Gears e.g.Spindle of the Lathe Machine. Engaging the shaft with different types of gears (size and shape) will increase the Torque. Most of the Shafts have a bearing at both ends that makes it move the shaft more smoothly. It could be a Ball Bearing or a journal Bearing.
The water Pump is used to transfer power through a shaft and it is the most common example in our daily life. The motor is rotated at its high R.P.M which causes to move the impeller shaft. The impeller moves the water from the Ground to our desired place. The second most common use of a shaft is in an engine. The whole performance of the engine mainly relies on the hardness, stiffness, and material the Shaft can bear under the complex and numerous engine cycles
Types of Shaft
- Crankshaft
- Camshaft
- Axle shaft
- Spindle shaft
What is Crankshaft?
The Crankshaft is Located at the end of the engine, above the oil pan. A robust metal rod serves as a crucial link between the piston and other engine components. Its primary function is to receive power from the combustion process and transmit it to the vehicle through various gears and drive train components. The time of the engine mainly matter on the factors of hardness, stiffness, and surface finishing of the shaft to bear the Numerous cycles of Power stroke without damaging it.
What does a Crankshaft do?
The crankshaft performs a remarkable conversion: it changes the linear(Up/Down) motion of the piston into the rotatory motion of the axle which gives power to rotating the wheels of the Automobile. The connecting rod transfers this recip-rocating motion through the connecting rod into the rotatory movement of the wheels through different gears.
Types of Engine use Crankshaft
- Single Cylinder Crankshaft
- V-twin Cylinder Crankshaft
- Multi Cylinder incline Crankshaft
- V-Multi Cylinder Crankshaft
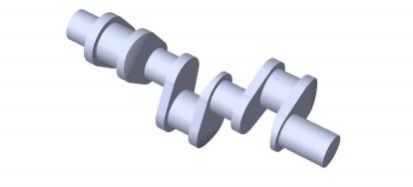
Single Cylinder Crankshaft
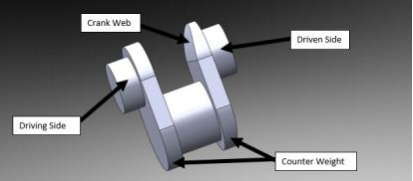
The single-cylinder crankshaft is mostly used in Bikes, Motorcycles, lawn movers, and air conditioner Compressors. Its Design is very Basic and lightweight. A slider-crank mechanism is powered by the to-and-fro motion of the piston in the Engine block or cylinder head that transfers the power through the axle to move Wheels. It contains one crank pin, two crank webs, and a journal at both ends. It can adopt the Two Stoke or a Four Stoke cycle.
The ultimate use of a lightweight shaft in an engine offers significant advan- tages, including enhanced efficiency and reduced fuel consumption compared to other crankshaft designs. The reduced weight of the shaft results in lower stress on the bearings, which contributes to improved durability and longevity of the engine components.
V-twin Cylinder crankshaft
The V-twin cylinder crankshaft is an advanced version of a single-cylinder crankshaft. V-twin Cylinder crankshaft has a difference of dual cylinders that Emerges more Power during the Engine cycle. Both pistons can give power strokes at the same time or can be adjusted to work relatively. It could be a Single or dual crank pin with two pistons and a bearing at both ends.
The V-Twin angle can be adjusted according to our requirements.
The angle is 360,180,90 and 45 degrees.
The 45 Degrees V-Twin Engine has an air-cooled effect. Many famous bike companies adopt the 45 Degrees V-Twin Engine.
The most famous company is Harley-Davidson. Most Common Examples of V-twin Cylinder crankshafts are used in Tractors, Water pumps, lawn movers, and air Compressors.
Multi Cylinder incline Crankshaft
This type of engine in the Modern Era are used in a large number of automobiles that required more power and torque. It contains Four and Six cylinders and they are all inline in the same plane. That is why it has another name that is known as an incline Engine. They all transmit power to the single crankshaft. If the crankshaft is not balanced dynamically then the engine produces a lot of internal vibration that has a negative effect on the efficiency, output, and life of the Engine. Among many other Drawbacks, one of the Common and negative drawbacks of Multi Cylinder inclines they produce a lot of vibration in a small engine.
What is the Purpose of the Crankshaft?
Helicopters: Helicopters use a Crankshaft to rotate a fan at the back and upper part of the body. The crankshaft is used to Transfer a large amount of force and power that is required to move the Fan at a full R.P.M. The Fans create enough pressure difference to lift it.
Ships and submarines: They are used in Ships, to transfer the Power Generated from the linear motion of the piston to the impeller to push the Water.
Pumps: In reciprocating pumps, the crankshaft’s role is to convert the linear motion of the piston into rotatory motion that will push the Gasses and Fluid.
Hand watch and wall Clock: They both have a mechanical component that converts the rotatory motion into the sliding motion.
Shaper Machine: A Shaper Machine machine is a Single point cutting tool that uses the Quick return mechanism and converts the rotational motion into the Sliding motion of the ram.
What is Camshaft?
A camshaft is a component of a piston engine, which is a cylindrical rod with several cams on its surface that control the opening and closing action of the valves. The mechanical design of a camshaft requires a lot of strength and support, while the cam is typically driven at a uniform speed by a shaft.
Read on to learn more about the process.
How does a Camshaft Work

Intake Stoke: As the engine piston moves downward (creating an empty space above the piston). The piston is subjected to gas pressure in the cylinder for reciprocating motion, and through the connecting rod will be this motion into the camshaft rotary motion, the connecting rod is used to connect the piston and camshaft.
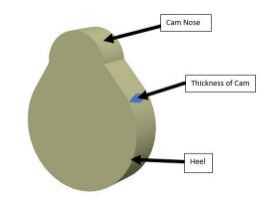
The cam nose reaches the rocker arm (spring-loaded), resulting in the opening of the inlet valve. The pressure difference between the fuel injector and the empty space above the piston allows the fuel-air mixture to fill the empty space.
Exhaust Stoke: As the engine piston moves upward (pushing the burned fumes toward the valve), the belt wheel rotates the camshaft through the timing belt or gear train.
The cam presses the rocker arm (spring-loaded), resulting in the opening of the outlet valve. The pressure difference between the piston and the exhaust manifold facilitates the removal of the remaining gasses from the upper portion of the cylinder.
Figure 3: The 3D view of Camshaft
What does a Camshaft do?
The profile and shape of the cam lobes are optimized to ensure smooth and precise valve operation, reducing the likelihood of valve train noise. If the cam is at a High jerk level the Sound pressure level will be greater that means at a high R.P.M. the noise of the Valve train will be Greater. but if we adjusted the Cam profile at the lower jerk level that means the Cam will be will continuously make contact with Follower (Spring loaded) the valve train noise will be reduced gradually. In this way, the camshaft plays a key role in controlling the noise and vibration of the valve at high R.P.M.
Impact of Variable Cam Timing on Environment
If you go back to Early Car Eras, we see that there were no good sensors. The Federal institution is making laws on the emission of Carbon dioxide (CO2). On the other hand, we need a system in which the car engine will remain in good performance and emit low Carbon dioxide (CO2) from its exhaust. There is no other way to control the Intake of Fuel in the cylinder and the Car engine is continuously producing way more Carbon dioxide (CO2) from its Exhaust Manifold.
The early approach of every Car Manufacturing Company is to control and Enhance the material used as a catalyst converter. No one is focusing on the intake of low Fuel consumption at a slow speed (R.P.M).
They designed the ECU unit which is also known as the trained Muscle of the Engine which is depending upon various other elements of the car. It is the Electronic Circuit that gets the data from the sensor of the different parts of the car and controls the intake of Fuel e.g. Engine Speed, exhaust valve time, speed of the Crankshaft, Water Flow ratio ETC.
Now, the ECU is responsible for how much time the Valve will remain open which will also control the amount of fuel. The intake of Fuel will be adjusted according to the load applied. With this technology, there is a gradual decrease in the intake and consumption of Fuel making the car more Eco-friendly.
What Material is Camshaft and Crankshaft?
The camshaft shaft is made of Forged steel. The camshaft has to bear a lot of Wear Stress because they are continuously moving. No other than steel is used in their manufacturing.
The Gears and crankshaft are made of Nodular iron or allowable forged steel. It is only possible when they pass them a number of processes so that they can resist the many power Cycles in the Engine. They both are connected to the bearing. The type of bearing that is used also depends upon the accuracy of the shaft.
The most important and common thing between them they required a lot of surface finishes, grinding, and polishing. If they do not have surface accuracy then a lot of friction will be produced between the other engine components. As a result, the life cycle of the engine will be reduced.
Differences Between Crankshaft and Camshaft
|
Crankshaft |
Camshaft |
|
|
Mechanical Properties |
The power is produced by the combination of compression and combustion stoke to rotate the crankshaft |
The intake and exhaust stroke provide the resources to generate power to move the Crankshaft in a rotary mo- tion |
|
Material Properties |
The whole performance of the engine mainly relies on the hardness, stiffness, and material the Camshaft can bear under the complex and numerous engine cycles |
The whole performance of the engine mainly relies on the hardness, stiffness, and material the Camshaft can bear under the complex and numerous engine cycles |
|
Use |
Transfer the Mechanical Energy to the rotary motion of the wheels |
Responsible for the fuel/air mixture and Exhaust system to work properly |
|
Profile |
The crankshaft has a stairs-like structure. The Gap between the structure is connected with the connecting rod, which transfers the energy and rotates the shaft |
The camshaft has the Cam mounted on it that is responsible to move the Follower(Rocker-arm) |
|
Price |
It will cost you between 500 to 1000 US Dollars |
It will cost you between 1000 to 2000 US Dollars |
Top Outsourcing Company: Beyond Your Expectations
Shenzhen Tuofa has 17 years of experience in the field of customized mechanical parts. If you need to find an external company to customize parts for projects in automotive engineering, medical, energy, or consumer goods, please contact info@tuofa-cncnmachining.com. We guarantee quality while helping you shorten the time to market for your products.
FAQs about Crankshaft and Camshaft
What is Piston?
The Piston converts the linear (Up/down) movement of the piston that is gen- erated by the combustion of the Fuel/Air and through the connecting rod it transfers into the rotatory motion of the Crankshaft. The Piston has four parts. Every part of the piston has its own function.
What is a Faster Crankshaft or Camshaft
They both work relatively close to each other. In other words, the speed of the camshaft is depend upon the speed of the crankshaft and the Working property of the camshaft produces power that rotates the crankshaft. |
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 How to Use a Micrometer: A Comprehensive Guide
How to Use a Micrometer: A Comprehensive Guide 







