420 Stainless Steel | Hardness, Composition, Properties
 Feb 21,2024
Feb 21,2024

There are many alloys that comprise great admiration in the world of metallurgy. One of them is 420 stainless steels with its vigorous composition and remarkable properties. This material stands tall in this era of modern engineering due to its importance in various advanced level applications. As we go deep into this study, numerous qualities of this material can be discovered which is well known for its reliability and sustenance.
Carbon and chromium being the main constituent elements of 420 stainless steel leads them to properties which symbolize strength as well as endurance. Furthermore, this material proves to be fundamental based on its usage in various applications whether in the field of aerospace, medical or in kitchen utensils. In addition to this, when this material is heat treated, it opens the door for the engineers to test this in numerous products that require high strength and precision rate. Not to forget that this steel offers excellent machinability to meet the criteria for applications demanding complex geometries. So, despite your profession, if you are interested in getting basics and knowing wonders of this material, this article surely uncovers all the endless probable of 420 stainless steel- leading material for advance innovation in metallurgical world.
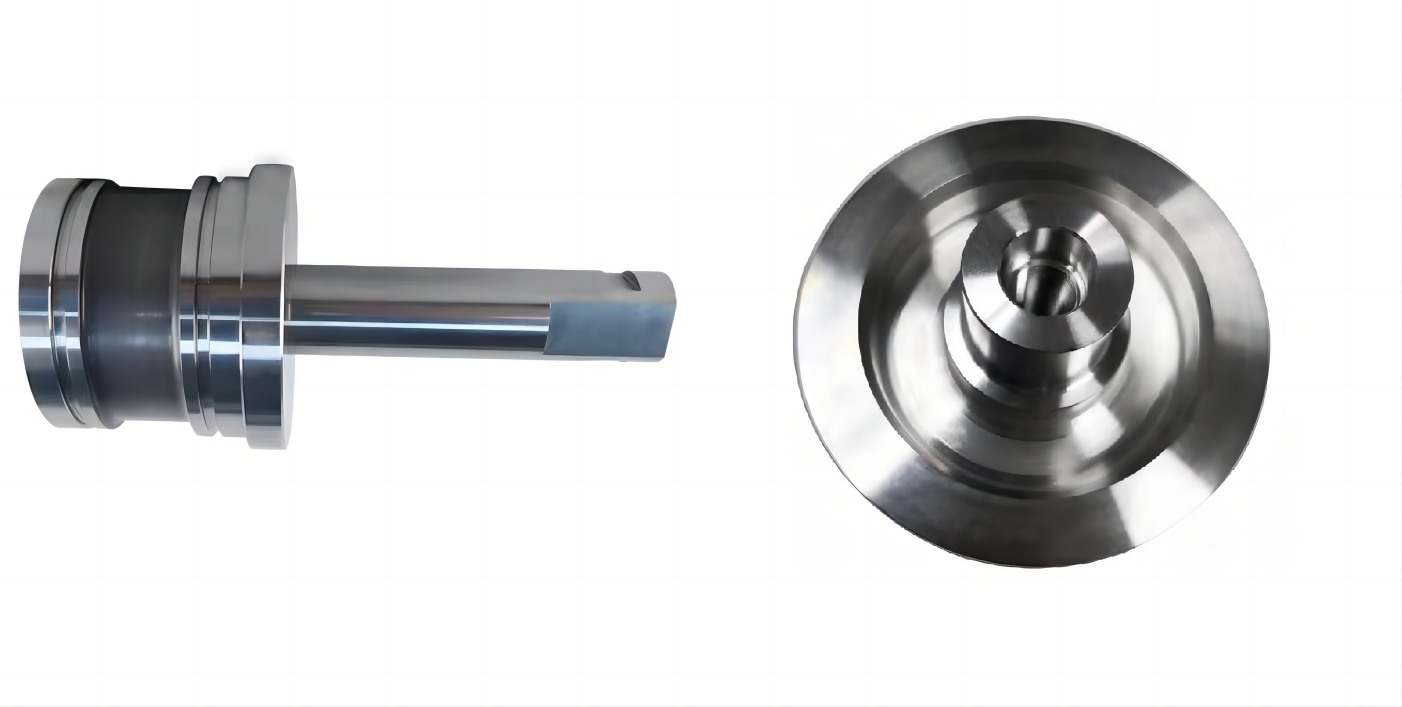

Fig 1: 420 Stainless steels parts
What is 420 Stainless Steel?
It is a type of steel that belongs to 400 series of stainless steel with carbon being the main constituent element in its composition. UNS S42000 is another name for 420 stainless steel and is a high C version of 410 stainless steel. Being a martensitic stainless steel, it contains promising properties like good strength and hardness.
For further information:
How good is 420 stainless steel?
It provides good strength as well as hardness due to its martensitic nature. Secondly, this material is well known for its enhanced corrosion resistance due to the presence of chromium in its composition (similar to 410). One of its unique properties is that when this material is fully hardened, it has exceptional tensile strength and hardness which is far better that other grade of stainless steel making it a remarkable choice for various industrial tools demanding such properties.
Is 420 stainless steel magnetic?
Yes, this stainless-steel grade is magnetic in nature. As compared to other types of steel, this material shows reasonable magnetic properties both in annealed as well as hardened condition but challenging to magnetize when gone through oil quenching. Moreover, the microstructure (composition affect) has a great impact on 420 stainless steel magnetic behavior.
Different forms of 420 stainless steel
- Sheet and Plate: Flat-rolled products available in various thicknesses and widths.
- Coil: Continuous strips wound into coils
- Bar: Round, square, hexagonal, and flat.
- Wire: Available in different diameters and grades.
- Tube and Pipe: Hollow cylindrical products.
- Forgings: Formed by applying pressure and heat to shape the metal into desired forms.
- Powder: Usage in powder metallurgy
Applications and Uses
420 stainless steel finds many applications across numerous industries due to its fundamental properties. Below is the table illustrating applications along with their uses:
Table 1: Application and uses
|
Applications |
Uses |
420 Stainless Steel Picture |
|
Cutlery and Kitchenware |
Kitchen knives, scissors, flatware |
|
|
Surgical Instruments |
Forceps, scalpels, and surgical scissors |
|
|
Industrial Blades and Cutting Tools |
Used in various manufacturing processes. |
|
|
Aerospace Components |
Aircraft bearings, Gears, Valve components |
|
|
Pump and Valve Components |
Pump shafts, valve stems, and other components for fluid handling systems |
|
|
Automotive Parts |
Exhaust systems, suspension components, and trim parts |
|
|
Firearms and Defense |
Gun barrels, receivers, and firearm frames |
|
|
Oil and Gas Equipment |
Valves, pumps, and pipelines |
|
Industries and products that use 420:
Below are some of the industries and products that uses 420 stainless steels extensively:
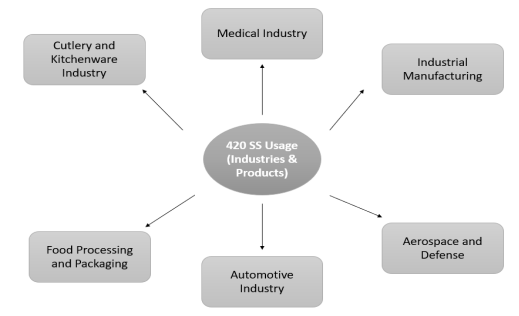
Fig 2: 420 Stainless steel industrial usage
Chemical composition:
Table 2: Chemical composition of 420 stainless steel
|
Element |
Percentage Composition |
|
C |
0.15 to 0.40 |
|
Cr |
12.0 to 14.0 |
|
Mn |
Less than 1.0 |
|
Si |
Less than 1.0 |
|
P |
Less than 0.04 |
|
S |
Less than 0.03 |
|
Fe |
Balanced |
Physical Properties
Table 3: Physical properties of 420 stainless steel
|
Property |
Value |
|
Density (g/cm³) |
7.74 |
|
Melting Point °C |
1480 to 1530 |
|
Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) |
24.9 |
|
Specific Heat Capacity (J/kg·K) |
460 |
|
Electrical Resistivity (nΩ·m) |
550 |
|
Magnetic Nature |
Ferromagnetic |
|
Modulus of Elasticity (GPa) |
200 |
|
Poisson's Ratio |
0.27 |
|
Hardness (Rockwell C) HRC |
50-55 |
Mechanical Properties
Table 4: Mechanical properties of 420 stainless steel
|
Property |
Value |
|
Tensile Strength (MPa) |
655 to 795 |
|
Yield Strength (MPa) |
415 to 690 |
|
Percentage Elongation |
15 - 25% |
|
Modulus of Elasticity (GPa) |
190 to210 |
|
Poisson's Ratio |
0.27 |
|
Hardness (Rockwell C) HRC |
50 to 55 |
Manufacturing Process
Below is the brief description showing the major steps involved during the manufacturing of 420 stainless steel:

Fig 3: Steps for manufacturing 420 stainless steel
Thermal Properties of 420 Stainless Steel
Table 5: Thermal properties of 420 stainless steels
|
Thermal Properties |
Value |
|
Melting Point (°C) |
1480 to1530 |
|
Specific Heat Capacity (J/kg·K) |
460 |
|
Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) |
24.9 |
|
Thermal Expansion (μm/m·K) |
10.4 |
How To Heat Treat 420 Stainless Steel
420 stainless steels when heat treated could be of so much value because this process leads to variety of enhanced properties depending on the application usage. Following are different heat treatment processes for this material:
Annealing
- Heating 420 stainless steel at temperature of around 800-900°C and ensure sufficient soaking time for uniform heating followed by slow cooling in the furnace.
- This process relieves internal stresses and improves machinability.
Quenching
- The 420 SS is heated to the austenitizing temperature, usually between 950-1050°C and then cooled rapidly in a suitable medium i.e., oil or water which results in martensitic transformation.
- It leads to a hard and brittle structure.
Tempering
- The quenched 420 SS steel is tempered to a lower temperature, usually between 150-400°C to relieve internal stresses for improving toughness and ductility.
- Tempering involves reheating the steel and holding it at that temperature for a specific time depending on the desired mechanical properties.
Machining 420 Stainless Steel
Machining is an important part while manufacturing or developing a particular component in an industry. Likewise, when a 420 stainless steel component is machined, it typically includes several operations like cutting shaping as well as drilling with precision and accuracy being the prime factors.
Several important factors need to be kept in consideration while machining stainless steel grade 420. Some of them are given below:
Tool Selection: Usually carbides and high speed steels tools are used for machining 420 SS.
Cutting Speeds and Feeds: Based on the operation needed to be done,optimized cutting speed and feed rate must be determined along with the specimen( workpiece) geometry.
Coolant: Used for lubrication purpose promoting tool life and smooth process.
Chip control: Prevention of chip forming to prevent poor surface finish by selecting appropriate parameters of the operation.
Surface finish: Strong influence on cutting parameters for machining the workpiece.
Tool wear monitoring: To maintain dimensional as well as performance accuracy, monitoring of tool wear plays a pivotal role and for replacing the damaged tool on time before any serious damage.
Safety Precautions: All the mandatory protocols for safety must be followed while machining the 420 stainless steel to avoid accidents due to exposure of heat or metal chips.
Sheet metal fabrication
Sheet metal fabrication is a process that includes forming and shaping thin sheets of a particular material. This process comprises of several steps depending on the requirements and desired properties of this material [16]. Below are the mandatory steps involved in this process:
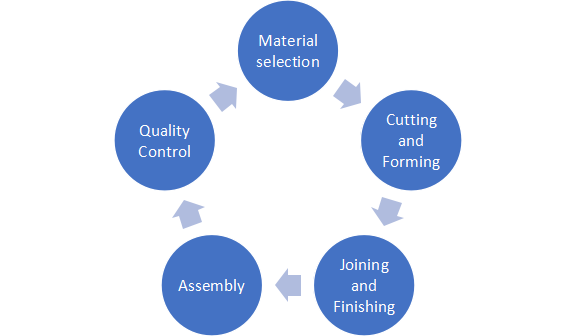
Fig 4: Steps for Sheet metal fabrication
The fulfillment of all the mentioned steps involved during sheet metal fabrication assures quality products of 420 stainless steel in different applications i.e., automative, medical, aerospace and many other industrial applications.
Surface Finishing
Surface finishing is a major step required while manufacturing a particular 420 stainless steel product as it plays a major role in enhancing the overall aesthetic look of the component and also promotes the overall properties of that particular part. Many methods are used besides grinding and polishing. Here are the most common one used for 420 SS surface finishing:
Passivation: removes free iron and other contaminants from the surface of stainless steel, creating a passive oxide layer that enhances corrosion resistance
Electropolishing: removes surface material from stainless steel parts, resulting in a smooth, shiny finish with improved corrosion resistance.
Plating and Coating: with a layer of another metal or protective material can enhance corrosion resistance, improve surface hardness, and provide decorative or functional properties
Quality and Standards Compliance
It is mandatory to follow certain standards and certification especially for 420 grade stainless steel surgical instruments and knife blades. These standards are mentioned below:
Fig 5: Quality standard and certification for surgical instruments& Knife blades
- ISO 7153-1:2016, Surgical instruments - Materials
- ISO 13485:2016, Medical devices - Quality management systems
- ISO 7740:1985, Instruments for surgery
- ISO 17664:2017, Processing of health care products
- ISO 14971:2007, Medical devices - Application of risk management to medical devices
- EU Medical Devices Directive 93/42/ECC, Class I
Following the above-mentioned standards are crucial as well as very important especially for the products like knife blades and surgical instruments because these standards meet required criteria whether its quality, performance or safety.
Comparison with Other Stainless Steels
420 stainless steel vs 304
Table 5: 420 stainless steel vs 304
|
Property |
420 Stainless Steel |
304 Stainless Steel |
|
Composition |
0.15% C, 12-14% Cr, small amounts of Mn, Si, and sometimes Mo or Ni. |
0.08% C, 18-20% Cr, and varying amounts of Ni, Mn, and sometimes Mo. |
|
Corrosion Resistance |
Moderate |
Excellent |
|
Hardness |
Generally harder and more durable |
Softer |
|
Applications |
knife blades, surgical instruments, and mechanical parts |
food processing, chemical processing, pharmaceuticals |
|
Magnetic Properties |
magnetic |
non-magnetic in its annealed state |
|
Cost |
less expensive |
more expensive |
316 vs 420 stainless steel
Table 6: 316 vs 420 stainless steel
|
Property |
316 Stainless Steel |
420 Stainless Steel |
|
Composition |
16-18% Cr, 10-14% Ni, 2-3% Mo, and minor amounts of other elements such as C, Mn, Si, and S. |
0.15% C, 12-14% Cr, small amounts of Mn, Si, and sometimes Mo or Ni. |
|
Corrosion Resistance |
Excellent |
Moderate |
|
Hardness |
lower. |
harder and more durable |
|
Applications |
marine applications, chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, |
knife blades, surgical instruments, and mechanical parts. |
|
Magnetic Properties |
non-magnetic, |
magnetic |
|
Cost |
more expensive |
less expensive |
440 vs 420 steel
Table 7: 440 vs 420 steel
|
Property |
440 Stainless Steel |
420 Stainless Steel |
|
Composition |
0.95-1.20% C, 16-18% Cr, 0.75% Mo, and minor amounts of Mn, Si, P, and S. |
0.15% C, 12-14% Cr, small amounts of Mn, Si, and sometimes Mo or Ni. |
|
Corrosion Resistance |
Less |
Moderate |
|
Hardness |
More |
Less |
|
Applications |
Bearings |
knife blades, surgical instruments, and mechanical parts. |
|
Magnetic Properties |
440 stainless steel is magnetic due to its martensitic structure. |
magnetic |
|
Cost |
more expensive |
less expensive |
3cr13 stainless steel vs 420
Table 8: 3cr13 stainless steel vs 420
|
Property |
3Cr13 Stainless Steel |
420 Stainless Steel |
|
Composition |
Contains chromium (12-14%), carbon (0.3%) with some Mn, Si, P |
0.15% C, 12-14% Cr, small amounts of Mn, Si, and sometimes Mo or Ni. |
|
Corrosion Resistance |
Moderate |
Moderate |
|
Strength |
Moderate strength |
Higher strength |
|
Hardness |
Varies, typically around 55 HRC |
Varies, typically around 50-55 HRC |
|
Machinability |
Good machinability |
Good machinability |
|
Weldability |
Fair weldability |
Fair to good weldability |
|
Applications |
knives, scissors, |
industrial blades, Cutting tools |
420 vs Other 400 Series Grades Chart
Table 9: 420 vs Other 400 Series Grades Chart
|
Property |
420 SS |
410 SS |
430 SS |
440C SS |
|
C (%) |
0.15-0.40 |
0.08-0.15 |
0.12 |
0.95-1.20 |
|
Cr (%) |
12-14 |
11.5-13.5 |
16-18 |
16-18 |
|
Hardness (Rockwell C) |
50-55 HRC |
40-50 HRC |
20-30 HRC |
58-62 HRC |
|
Corrosion Resistance |
Moderate |
Moderate |
Moderate |
Good |
|
Strength |
Higher |
Moderate |
Moderate |
High |
|
Magnetism |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Applications |
Knives, scissors, |
Automotive parts, |
Kitchen utensils, |
High-performance |
|
|
surgical instruments |
industrial equipment, |
sinks, appliances |
knives, bearings, |
Pros and Cons of 420 Stainless Steel
Here are the pros and cons of 420 stainless steel:
Advantages and Limitations
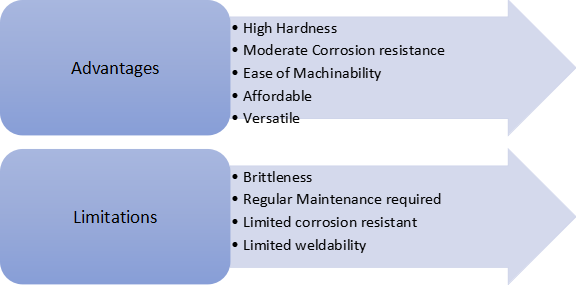
Fig 5: Advantages and Limitations of 420 stainless steel
Best Practices in the CNC Machining Stainless Steel
CNC machining services for 420 stainless steel offer developing and manufacturing solutions that are primarily based on precision and accuracy. Along with offering tolerance and flexibility, it also offers customizing the various prototypes regardless the production of 420 SS is on small scale or large scale meeting the customer requirements. In addition to this, it provides cost-effective solutions with dimensional accuracy ensuring high-quality components for numerous industrial applications.
Conclusion:
420 Stainless steels with a blend of different demanding properties like good hardness, machining ability along with a moderate resistant to corrosion proves its versatility among the materials that are in high demands especially for different industrial sectors and aerospace components. Secondly, the cost is much affordable which attracts the buyers in order to maintain the durability and performance at much cheaper rate. But it is good to consider both advantages as well as the limitations while considering this material for any application. Overall, the great usage of 420 stainless steel proves its reliability and sustainability in this modern engineering world.
FAQ
What is 420 stainless steel equivalents to?
X20Cr13 (1.4021), X30Cr13 (1.4028) and Japanese grade SUS420J2 are considered roughly equivalent to 420 stainless steels.
420 stainless steels for knives
Properties like high hardness, good corrosion resistance, and machinability along with affordability and performance promotes its usage in knives.
Is 420 steel rust-resistant?
440C stainless steel offer moderate rust resistant but only for mild environments and in order to maintain that level of resistance for extended period of time, regular preservation and storage techniques should be considered. Beside these conditions, it can get exposed to rust especially in aggressive environmental condition.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home







 Comparing 201 and 304 Stainless Steel: Properties, Uses, and Cost Analysis
Comparing 201 and 304 Stainless Steel: Properties, Uses, and Cost Analysis 







