1018 vs 4140: What is the difference between?
 Nov 07,2023
Nov 07,2023

Steel is the most widely used material in the world because of its many types that provides applications in almost every field. So, how one can learn which type would be suitable for their application. For this purpose, we need to learn about different steel properties. The two most common and most applicable types of steel includes 1018 and 4140 Steel. They have a balanced set of properties according to respective applications and remain an efficient material for economical processes. In this article, we will study the material properties, applications, advantages and disadvantages of both and will help you to find the best material for your application.

1018 vs 4140 steel
What is 1018
1018 steel is a type or one of the grades of low carbon steel. It possesses properties such as good ductility and strength which makes it a popular material for general applications. The steel grade of 1018 in the United States corresponds to 20 steel in China. It is widely used because of characteristics such as:
- Machinability: Can be used to create complex parts.
- Weldability: Aids an efficient joint formation.
- Other characteristics such as malleability and workability aids its cold forming, which is a better option to avoid prolonged working and heat treatment of material.
Carbon Content
1018 steel contains a carbon content from 0.14% upto 0.20%.

Cold rolling of 1018 steel
Applications
It has certain applications involving sheet metal parts, gears, bolts, tie rods, brackets, motor shafts, etc.

Applications of 1018 steel
What is 4140 Alloy Steel
4140 steel is a type or one of the grades of medium carbon steel. Chromium, molybdenum, and manganese are present as an alloying element in 4140 alloy steel. [6]. The workability and machinability of 4140 steel is challenging due to these alloying components and greater carbon content.
Carbon Content
It exhibits carbon content ranging from 0.38% upto 0.43%.
Applications
It exhibits exceptional mechanical properties, impact resistance, fatigue strength that makes it commonly used in the aerospace, automobile, oil, and gas industries to manufacture landing gear components, connecting rods, crank shafts, steering components, drill collars, drill bits, etc. where resistance to high stress is required. It can be tempered to achieve desired ductility, toughness, and wear resistance.
The following video shows the material properties of 4140 steel,

Machinery parts made of 4140 steel
What is the Difference Between 1018 and 4140 Stainless Steel
1018 Chemical composition
The precise constiturion of 1018 steel varies significantly depending on the manufacturer, although it generally falls within these limits.
Following table shows the chemical composition of 1080 steel:
|
Elements |
Content |
|
Carbon |
0.14-0.20 % |
|
Manganese |
Upto 0.90 % |
|
Sulfur |
Upto 0.05 % |
|
Phosphorous |
Upto 0.04 % |
|
Iron |
98.81-99.26 % |
AISI 1018 Steel properties
Following table shows the American Iron and Steel Institute 1080 steel properties:
|
Properties |
Value |
|
Density |
7.87 (g/cm3) |
|
UTS |
440 (MPa) |
|
Yield Strength YS |
370 (Mpa) |
|
Brinell’s hardness value |
126 |
|
Rockwell’s hardness value |
71 |
|
Vickers hardness value |
131 |
|
Knoop hardness value |
145 |
Note: Values of Rockwell, Vickers and Knoop hardness are converted from Brinell hardness value.
4140 Steel Properties
4140 is an alloy steel due to the presence of certain alloying elements like chromium, manganese, silicon, phosphorous, molybdenum and sulfur. It is often heat-treated to obtain desired properties.
Following table contains the constituent elements of 4140 steel:
|
Elements |
Content |
|
Chromium |
1.12 % |
|
Molybdenum |
0.18 % |
|
Manganese |
0.93 % |
|
Sulfur |
0.031 % |
|
Phosphorous |
0.025 % |
|
Silicon |
0.33 % |
|
Nickel |
0.17 % |
|
Carbon |
0.40 % |
4140 steel properties
Following table shows the American Iron and Steel Institute 4140 alloy steel properties:
|
Properties |
Value |
|
Density |
7.85 (g/cm3) |
|
UTS |
655 (MPa) |
|
Yield Strength YS |
415 (Mpa) |
|
Brinell Hardness |
197 |
|
Rockwell Hardness |
92 |
|
Vickers Hardness |
207 |
|
Knoop Hardness |
219 |
|
Thermal conductivity |
42.6 (W/mK) |
Note: Values such as Rockwell, Vickers and Knoop hardness are converted from Brinell hardness value.
1018 vs 4140: Material Properties
1018 steel machinability
- The fine-grained microstructure decreases the possibility of chipping or breaking and ensures consistency throughout the machining process.
- Because it is relatively soft and ductile, it facilitates cutting, drilling, turning, milling, and other processes.
- Because of minimal tool wear, cutting tool life increases, which lowers the overall cost of machining operations.
- When the machining process is done, a good surface finish is also achieved.
Following video shows machining process of 1018 steel,
4140 steel machinability
- Because 4140 steel is harder than 1018 steel, heat treatment is required to make it easier to machine. Typically, annealing is performed to remove stress within the material and to prepare it for machining processes.
- The proper cutting tool is required; often, high-speed steel or carbide tools are employed.
- Adjusting the cutting speed is also required to prevent tool wear and achieve a higher surface finish.
- To prevent tool breakage, chip breakers may be used to assure appropriate chip control.
- After machining, a post-heat treatment technique is performed to achieve the necessary mechanical properties.
Following video shows machining process of 4140 steel
Which is Better 1018 Steel or 4140
In order to determine which type of steel either 1018 or 4140 would be beneficial for your application, you need to consider that they both differ in their properties. If your application doesnot require high strength and high temperature, 1018 steel would be the one you should select as it would be more adaptable, easy to machine and cost-effective. And if there is high-end application where cost effectiveness is neither a priority, you should go for 4140 steel as it provide better strength properties, good wear and abrasion resistance and have ability to perform under high temperature.
Pros of 1018 steel
- Ductility: This property offers the ability to be formed into complex shapes through bending, as it shows proper signs before failure such as necking would occur.
- Machinability: The fine-grained microstructure makes it easier to drill, mill and grind without risk of breaking cutting tool and provides a good surface finish.
- Weldability: Since carbon is low, formation of heat affected zones would be minimum thus avoiding the risk of cracking during welding.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Considering all the properties of 1018 steel, it is clear that the whole process would be inexpensive as there is no requirement or necessity of heat treatment process and it ensures the greater life of cutting tools.
Cons of 1018 steel
Although there are several Pros of 1018 steel but when it comes to the applications requiring high tensile strength and other mechanical properties, it is not suitable because of following Cons:
- Low strength: It offers low strength when compared to other alloy steel which makes it of no use in high end applications.
- Low hardness: Since the carbon content is relatively low, this material cannot offer greater hardness thus providing low wear resistance.
- Less Corrosion resistance: Corrosion properties in steels are typically enhanced by the presence of alloying elements such as chromium and molybdenum. As they are not present in 1018 steel, that’s why it offers poor corrosion resistance and require coatings.
Pros of 4140 steel
- Good toughness: 4140 steel can absorb high amount of energy prior to fracture. This is because of its good toughness which provides applications which involves impact, dynamic loading or other mechanical properties.
- High strength: 4140 alloy steel is a stronger and more durable material because of its high tensile and yield strength which makes it a good candidate for the manufacturing of structural components.
- Wear resistance: Hardness is one of the characteristics which enhances wear properties of 4140 steel. That’s why it is often used for components where loss to friction or wear can be experienced.
- Heat- treatment: In order to alter the properties such as toughness and hardness, heat treatment processes are carried out. These heat treatment processes involves normalizing, annealing, hardening and tempering.
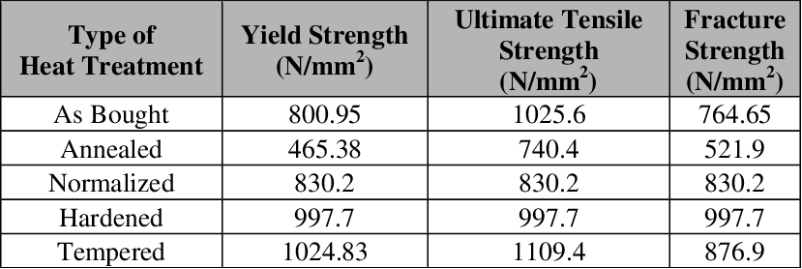
Heat treatment processes: 4140 steel
- Corrosion resistance: Due to the presence of alloying elements such as chromium and molybdenum, 4140 steel provides good corrosion reisitance. Although it might require protective coatings in corrosive environments.
Cons of 4140 steel
- Machinability: It is one of the issues and requires greater care. When machining it, specific precautions must be taken to reduce tool wear and maintain surface smoothness, especially when it is hardened.
- Cracking: When improperly heat-treated or quenched, 4140 steel is prone to cracking, which can be a severe disadvantage in some applications.
- Cost: 4140 steel is more expensive than low carbon steel and its processing involves more precise control. e.g. Specific cutting tools are required followed by accurate cutting speed otherwise it would result in breakage of cutting tools.
Learn More Stainless Steel Metal Grades
Different grades of Stainless Steel
We have different series of Stainless Steel grades, most common are:
- 200 series having chromium, nickel and manganese as alloying elements
- 300 series having chromium and nickel as alloying elements.
- 400 series
Similarly, we have 500 series and 600 series stainless steel grades having chromium and martensitic alloys respectively.
There are many Stainless Steel grades among these series, we discuss only few yet common grades.
Srainless Steel 304
It is widely used steel and constitutes around 50% of steel being used all over the world. It belongs to the 300 series and contains 18% chromium and 8% nickel [13]. It is being used in the form of sheets, plates, bars, and steel tubes. It has applications in fasteners and bolts, sanitary fittings, sinks, etc.

Applications of 304 stainless steel
Stainless Steel 316
Second widely used type of steel in general applications is stainless steel 316. Since 304 grade shows corrosion in marine environment, 316 Stainless steel shows resistance to corrosion in same environment as it contains around 4% of molybdenum. It has applications in boat hardware, medical implants, Oil and Gas industry and laboratory equipment.
Stainless Steel 430
It belongs to 400 series of Stainless Steel and are known as ferritic stainless steel containing around 11% chromium. Due to its higher carbon content, it offers good strength and offers good corrosion resistance in mild environments. It has applications in making outdoor grills, exhaust system due to resistance to high temperature and toolboxes.
Mild Carbon Steel grades
Mild carbon steel grades that are commonly used include:
ASTM A36
Among the most prominent mild carbon steel grades is A36. It is widely utilized in structural and building applications due to its strong wear, including high tensile strength. A36 steel is also commonly used to make steel bars and sheets.
AISI 1010
Mild carbon steel 1010 has a low carbon content of 0.10%. AISI 1010 is well-known for its formability and weldability, and it is frequently used in variety of applications that do not require significant strength or hardness. It has applications in automotive parts and machinery components.
What is considered mild steel?
Mild steels are steels with carbon contents ranging from 0.05% to 0.25%. As the carbon content is low, mild steel have ductility and they can be cold formed to desired shapes and also there machining is quite easy.
Types of Mild Steel
Hot Rolled
Mild steel that is known as hot rolled is made by heating a metal billet or sheet to a high temperature and then rolling it into the desired form or thickness. This treatment makes the steel more malleable and easier to form. Hot-rolled mild steel is widely utilized in building, structural applications, and manufacturing.
Cold Rolled
It includes compressing and shaping the steel at room temperature. This method produces a smoother and more precise. Cold-rolled mild steel is frequently used in applications requiring accurate dimensions and a smooth surface, such as automobile components and appliances.
FAQs
Can 1018 steel be hardened?
Ans. AISI 1018 steel is nearly impossible to harden through heat-treatment processes because of its low carbon content. However, it may be hardened by surface hardening processes such as carburizing to improve wear resistance.
Can you weld 4140 steel?
Ans. Yes 4140 steel can be welded but first you need to perform annealing or normalizing to reduce the risk of cracking.
Can 1018 steel be heat treated?
Ans. 1018 steel having carbon content around 0.18% is known as low-carbon steel. Since the carbon content is low, it is not recommended to undergo heat treatment to increase hardness. For this purpose, surface hardening can be done to improve material properties.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 What is a Blind Hole in CNC Machining | Easy Guide
What is a Blind Hole in CNC Machining | Easy Guide 







