Types of Bearings Explained: Main Types, Applications & Housing
 Apr 14,2025
Apr 14,2025

Bearings are one the most important component of mechanical systems. From the smallest wrist watch to a giant forging press, bearings are everywhere. For mechanical engineers and designers, choosing the correct bearing type is crucial. Let's look find out what are the different types of bearings and where are they used.
What Are Bearings and Why Are They Important?
Bearings are essential components in mechanical systems which reduce friction, support load and may constraint motion in one or more directions. Bearings are found in almost all machinery in this era. Virtually every rotating component in machines like sprocket in bicycles, shafts in automobiles, etc. require bearings.
What Is the Main Purpose of Bearings?
Bearings are mainly used for reducing friction between moving parts. They also support loads and may constraint motion to only the desired direction. Reduction in friction boosts up efficiency by conserving energy. Motion becomes more precision and regulated. Speeds of rotation become more uniform.
How Do Bearings Reduce Friction in Machines?
Bearings convert the sliding motion into rotating motion. The rolling element, for example balls in ball bearings have a very smooth surface. The raceway is also smooth. Additionally, lubricants like oil or grease further reduce friction. In short, the coefficient of friction between surfaces in bearings is significantly lower than the coefficient of friction otherwise. The rotating motion further smoothens the movement.
Benefits of Using Bearings in Mechanical Systems
The benefits of using bearings are enormous. Some of these are listed below:
- Conserving energy: Low friction requires less energy for movement of parts
- Uniform speeds: Uniformity of surface characteristics across the whole breaing ensures uniform speeds
- Extended service life of machine:Good quality bearings minimize wear.
1. Ball Bearings: Types and Common Uses
Ball bearings are one of the most commonly used types of bearings. The rolling element is in the form of spherical, hard, smooth and incompressible balls. Ball bearings have sub-types like deep grove ball bearings, angular contact ball bearings, self-aligning ball bearings and thrust ball bearings.
Material Types
- Titanium Ball Bearings
Titanium is used in specialized applications as a ball bearing material. Titanium ball bearing is considered superior to steel ball bearing due to high strength-to- weight ratio, corrosion resistance and fatigue resistance. Titanium is relatively more expensive than steel. It is used in aerospace, medical devices and other such specialized applications where longevity and lighter weight are appreciated.
Deep Groove Ball Bearings

Bearing Housing:
1. Pillow Block Housing:Typically used for easy mounting and alignment on shafts in conveyors and fans.
2. Flanged Housing:
Advantages and Typical Applications
These bearings are good in bearing both radial and axial loads. These are rugged and their simple yet sleek design makes them suitable for all common applications where high speed, load bearing capacity and low friction are desired.
Angular Contact Ball Bearings
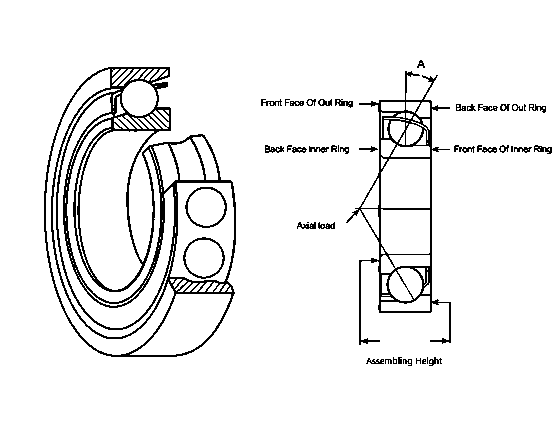
Bearing Housing:
- Flanged Housing
- Cartridge Housing
When to Use Angular Contact Bearings?
In angular ball bearings the inner and outer raceway are displaced relative to eacjh other in an angular range of 15o to 40o. It enables them to support both axial and radial loads in applications like machine tool spindles, centrifugal pumps, and precision gearboxes.
Self-Aligning Ball Bearings

Bearing Housing:
- Pillow Block Housing
- Self-Aligning HousingIdeal Applications for Self-Aligning BearingsSelf-aligning can automatically adjust misalignments between shafts and racings. As a result these bearings are specifically suitable in applications like agricultural machinery, textile machines and conveyors.
Thrust Ball Bearings
Bearing Housing:
- Thrust Bearing Housing
- Washer-Type Housing
Key Benefits of Thrust Bearings in Vertical Loads
Thrust ball bearings are specifically designed to support axial loads in one or both directions. They can bear loads along the shaft due to the specialty of their rolling elements. Thrust bearings are well-suited for applications like crane hooks, vertical shafts, machine tool tables, and elevator motors.
Roller Bearings: Types and Applications
Roller bearings are another common type of bearings which are usually used to support heavy radial loads. They have a larger area of contact. As opposed to ball bearings which have point contacts, roller bearings have line contact. It is due to the shape of the rolling element. There are specialized sub- types of roller bearings which are being discussed in this blog.
Cylindrical Roller Bearings

Bearing Housing:
- Plummer Block Housing
- Cartridge Housing
- End Cap Housing
Advantages for High-Speed and Heavy-Load Applications
Cylindrical roller bearings can withstand heavier load due to their design. The rolling elements have a large area of contact with the raceways. This increases its stiffness. Due to geometric uniformity of the rolling element, it reduces friction. These roller bearings offer high speeds. These are ideal for electric motors, machine tool spindles, compressors and gearboxes
Spherical Roller Bearings

Bearing Housing:
- Split Pillow Block Housing
- Self-Aligning Housing
- Adapter Sleeve Housing
Best Uses for Misalignment and Heavy Loads
Spherical roller bearings can auto-adjust to misalignments and shat deflections. They are self-aligning. Due to the design of the rolling element and raceways, spherical rolling bearing can support high radial and axial loads. It makes them ideal for applications like mining equipment, vibrating screens, and paper mill machinery.
Tapered Roller Bearings
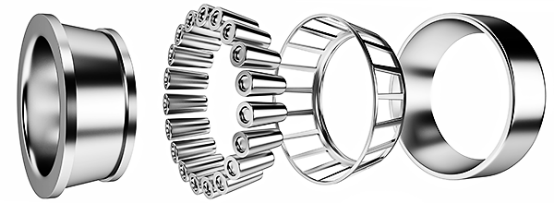
Bearing Housing:
- Flanged Housing
- Double Cup Housing
- Unitized Tapered Roller Housing
Why Automotive and Heavy Machinery Prefer Tapered Bearings
Tapered roller bearings have a conical geometry comprising of a cup and cone configuration. This allows it to withstand both radial and axial loads which are desired in heavy machinery and automotives.
Needle Roller Bearings

Bearing Housing:
- Drawn Cup Housing
- Caged Needle Housing
- Insert Housing
Applications Requiring Compact and Lightweight Bearings
The rolling element is in needle shape having a very small diameter to length ratio. This makes it sleek, compact and lightweight.
3. Plain Bearings (Friction Bearings): An Overview
Plain bearings are the simplest types of bearings. They do not comprise of rolling elements and raceways. Instead, they have sleeve in which a shaft rotates freely by sliding motion. Lubricants like oil and grease lowers the surface friction and facilitates in rotation of shaft.
Types of Plain Bearings Explained
Journal Bearings
These support rotating shafts and handle radial loads, often found in engines and heavy machinery.
Sleeve Bearings
These are simple, tube-shaped bearings used in low-speed, light-duty equipment like small motors and fans.
Flange Bearings
These are designed with a flange for secure mounting, commonly used where alignment and positioning are important.
|
Feature |
Journal Bearings |
Sleeve Bearings |
Flange Bearings |
|
Shape |
Cylindrical |
Tube-like |
Tube with flange |
|
Load Type |
Radial |
Light radial |
Radial + limited axial |
|
Housing |
Pillow block, split, solid |
Bored holes, integral housing |
Flanged or bolt-on housing |
|
Axial Support |
Needs extra component |
None |
Built-in via flange |
|
Use |
Engines, turbines |
Fans, small motors |
Conveyors, fixed assemblies |
Key Advantages and Limitations of Plain Bearings
Advantages:
- Low cost
- Compact
- Tolerance for misalignments
Limitations
- Excessive wear
- Low' precision
- High friction
- Low speeds
Common Applications in Industry
Plain bearings are commonly employed in industrial machinery, automotive and light consumer products.
4. Linear Bearings: Everything You Need to Know
Linear bearings are used to guide the movement of shaft a linear rather than a rotary path. They reduce friction along the path and also precisely aligns the mating components. Let's look more into their types.
How Do Linear Bearings Work?
Linear bearings capitalize on the use of lubricants and smooth rolling elements to lower friction along a linear path.
Types of Linear Bearings and Their Features
Ball Bushing Bearings
They have a smooth linear motion using ball recirculation. It's precise and low-friction.
Linear Roller Bearings
Linear Roller Bearings use rollers for higher load capacity and stiffness. They are ideal for heavy-duty setups.
Slide Bearings
Slide bearings operate on sliding contact, typically made from self-lubricating materials.
|
Type |
Housing |
Load |
Precision |
Friction |
Applications |
|
Ball Bushing |
Round flange, pillow block |
Moderate |
High |
Very Low |
CNCs and 3D printers |
|
Roller Bearing |
Square block |
Heavy |
Moderate |
Low |
Industrial machines and robotics |
|
Slide Bearing |
Compact block |
Light |
Low |
Moderate |
Furniture |
Best Applications for Linear Bearings
Linear bearings are best suited for applications that require low friction along a straight path. As an example, ball bushing bearings provide smooth, accurate and repeatable motion to the arms of 3D printers. Linear roller bearings can accommodate heavy loads suited for industrial machinery. Slide bearings are compact and support light applications like drawers.
5. Mounted Bearings: Types and Selection Tips
Mounted bearings are already pre-installed and thus they facilitate the installation without the need of additional brackets. These bearings have housings with them that can help in installation, alignment and replacement. Common types will be discussed here.
Understanding Mounted Bearings and Their Housing Types
Pillow Block Bearings
Pillow block bearings are mounted on a solid base and used to support a rotating shaft. They are commonly installed on flat surfaces making them suitable for a wide range of equipment.
Flanged Bearings
Flanged bearings have a mounting flange with bolt holes that allow them to be fixed to a surface. They are often used when the shaft passes through a wall.
Take-Up Bearings
Takeup bearings are designed to slide within a frame, allowing movement to adjust the tension of belts or chains. They are often used in conveyor systems.
Common Industrial Uses of Mounted Bearings
Mounted bearings are commonly used in locations fixing with minimal supports is required. Material handling systems, gearboxes, packaging lines, agricultural equipment and various other industrial fixtures use mounted bearings.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Mounted Bearings
- Load magnitude
- Direction of loading
- Space considerations
- Ease of access for maintenance
- Housing type
Specialized Bearings: Fluid and Magnetic Bearings
Specialized bearings use a fluid or magnetic force to support the radial loads. Instead of solid surfaces coming in direct contact with each other, a pressurized fluid or magnetic force supports that load. Thus, it becomes nearly frictionless. Wear and tear also become negligible.
Fluid Bearings Explained

Hydrostatic Bearings
These bearings require an external pressure source like a pump to fill the gap with the fluid. They can operate well even with zero shaft speed.
Hydrodynamic Bearings
These bearings fill the gap with the fluid capitalizing on the shaft speed. Thus, a threshold speed of speed is required for smooth operation.
Magnetic Bearings and Their Unique Features
Active Magnetic Bearings:
In active magnetic bearings magnetic levitation is generated with electromagnets. An external power source provides the current to magnetize. A feedback control system helps to keep the shaft at the center by varying current.
Passive Magnetic Bearings
Passive magnetic bearings use permanent magnets for magnetic levitation. The magnetic field remains stable. But changes in loads might not always work well.
Housing For Specialized Bearings
Specialized bearings require custom housings, typically CNC-machined to ensure a precise fit and meet specific needs like load handling, misalignment, or fluid containment.
Bearings in Automotive Applications
A lot of different bearing types are found in automobiles. All rotating parts needs bearings for their efficient movement by reduction in friction, precise alignments and load endurance. Engines, transmission systems, wheels, steering system and suspension systems require bearings.
Types of Bearings Used in Cars
Wheel Bearings
Tapered roller bearings are commonly used bearing type. They support both the radial and axial loads that are generated by the movement of wheels.
Transmission Bearings
Gearboxes require needle roller bearings to the compact space in there. Tapered roller bearings are needed by the axles to support radial and axial loads.
Engine Bearings
Plain bearings and journal bearings of alloys that can withstand high temperature and resist creep are required in the engine.
|
System |
Bearing Types |
Function |
Benefit |
|
Engine |
Journal or Plain |
Support crankshat/camshaft |
Reduce friction and handle heat |
|
Transmission |
Needle, Ball and Tapered Roller |
Support gears |
Smooth shifting |
|
Wheels |
Deep Groove and Tapered Roller |
Enable rotation, bear weight |
Stability, safety |
|
Steering |
Ball and Thrust |
Assist steering motion |
Responsive control |
|
Suspension |
Spherical roller and Bushings |
Absorb shocks, allow movement |
Alignment |
How Automotive Bearings Impact Vehicle Performance
A good quality bearing will ensure smooth movement of parts. By reducing friction and providing a precise alignment, parts will wear less often. A lot of energy can be conserved. Thus, vehicles will give a better fuel mileage and less maintenance needs,
Signs of Bearing Wear in Automotive Systems
An automotive with worn out bearing will give unusual noise and its efficiency will be away from normal.
Precision Bearings CNC Machining
CNC machining plays a very vital role in ensuring product consistency, precision and automation. It is especially important for high value bearings.
How CNC Machining Work On Precision Bearings?
A perfectly designed computer aided design (CAD) is fed to the CAM software (computer aided manufacturing). Cam converts it in a set of instructions which are called G-Codes. The CNC then applies various functions like turning, milling, drilling etc as per the G-codes to manufacture the bearings.
Step-To-Step Machining Titanium Ball Bearings List
- Material prep
- Turning
- Heat treatment
- Raceway milling
- Hole drilling
- Grinding
- Inspection
- Assembly
- Final testing
Benefits of Custom Precision Bearings CNC Machining
CNC machining brings a lot of benefits for high value precision bearings. The bearings can be customized as per a well-thought-out CAD. Special alloys can be used that can support the desired application. Additional features can be added and cost is not very high for batch productions.
Conclusion
Bearings come in a lot of types, sizes and materials. For a given application the correct bearing specifications should be identified. A correct bearing would minimize friction, conserve energy, enhance efficiency and minimize maintenance needs.
FAQs
What's the Difference Between ZZ and Z Bearings?
ZZ bearing has a metal seal on both sides while a Z bearing has a metaal should on one side only.
How Do You Know if a Bearing Needs Replacement?
The movement of the part will show signs like unusual noise, disturbance in movement and more need of lubrication.
Which Bearing Type is Most Durable?
It depends solely on the application.
Can You Replace One Bearing Type with Another?
It is very difficult because a lot of adjustments would be needed in the design. It can be done but with a lot of effort.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 10 Types of Precision Shaft Machining Processes: All You Need to Know
10 Types of Precision Shaft Machining Processes: All You Need to Know 







