Soft Machining: Meeting Accuracy and Practicality of Materials
 Jun 17,2024
Jun 17,2024

Machining is a process of creating designs from raw materials to final products in full scale production. Machining encompasses the whole process of creating, designing, developing prototype parts necessary for product development. It ensures the precision and efficiency and create a foundation of manufacturing of volume production by molding prototyping processes. There are various parts and machines are required for mass production like jigs, molds and fixtures. Effective machining extends the product’s life and improves the product quality. Depending on the rapid prototyping or mass production in product development, machining can be soft tooling or soft machining or hard machining. This article will explore soft machining and its important features.
Soft Machining Techniques: Precision and Care
Soft machining is a kind of machining process for prototyping process. It utilizes low cutting forces and speed on prototyping parts to remove excessive material. This technique is advantageous for prototyping parts and for the brittle materials which have difficult machining with conventional methods.
In soft machining, total cut depth in tight tolerance prototypes parts is obtained by multiple layers of cut. Every layer has different longitudinal overlap and lateral stepover. This decreases the force and stress in the prototyping process.
Milling: A Versatile Method for Intricate Designs
Milling is basically utilized in product development to remove excessive material from the workpiece. It helps in the process of creating prototyping parts from raw shape to a specific form. Thus, creating part with required dimensions and tight tolerance. This is an important step in rapid prototyping of parts used in industries like aviation, automobile and medical field which required tight tolerance in final product development.
Its cost effectiveness is considered as a most important parameter in full scale production where volume production or mass production is required. It also provides highly polished surface finish and can create complex 3D parts. It can produce mass production or volume production that is difficult to produce with other machining processes. CNC machining for milling can produce identical pars with tight tolerance repeatedly with mass production and volume production. Milling can be applied to all the types of material like metals, alloys, plastics, and polymer etc.
Conventional milling and climb milling process
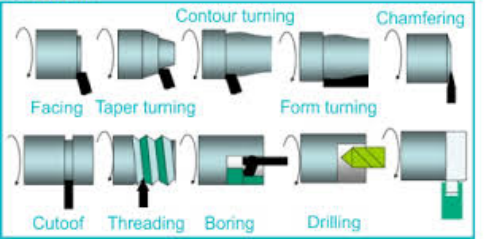
Turning: Shaping Cylindrical and Rotational Parts with Precision
Turning is the process of creating specific shape of a raw material by rotating the workpiece and moving the cutting tool in a linear direction. This creates a cylindrical shape. Normally lathe machines is used for turning process. Turning of prototype parts can be carried out automatically and manually. Manual turning requires continuous supervision. Automatic turning is an efficient process for mass production and volume production. By using CNC machining method, all the parameters like speed, cutting forces and production tooling, can be programmed from computer. CNC machining allows consistent and efficient process of creating workpiece shape with high accuracy and tight tolerance in full scale production. Single point tools in different shapes are utilized in turning soft tooling. Different angles are used in tuning to get desired shapes.
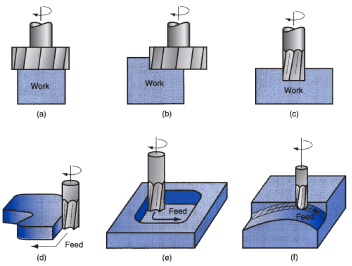
Drilling: Creating Holes with Accuracy and Control
Drilling is a process of creating round holes in workpiece. Drill press is used which can be applied on milling machine. As a waste material, chips are produced. Drill bits are designed in that way that chips fall away from the workpiece. And workpiece remain debris-free.
Drifts and leading-off is reduced by keeping the drill bit perpendicular in prototyping process. For tight tolerance, the center drill process is done before drilling. Other methods of drilling in soft machining are head rotation on manual machines and multiple axis on CNC machining.
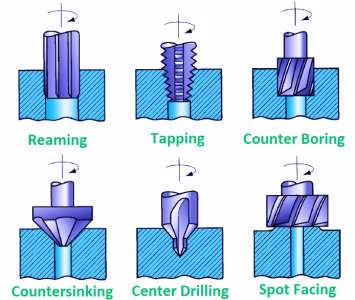
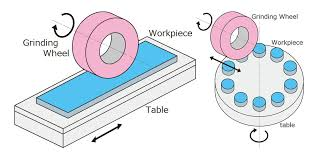
Grinding: Achieving Ultra-Fine Finishes and Tight Tolerances
Grinding is a process of creating final shape of workpiece by removing excessive material by abrasion. A rotating abrasive wheel is used to shape the material by grinding in full scale production. The soft machining process utilizes abrasive particles for material removal from prototype parts surface in a tight tolerance. when prototype parts come in contact of moving abrasive particles, the works as minuscule cutting tool. This shear off the all the small chip particle in rapid prototyping from workpiece.
There is a misconception about grinding in full scale production. That is a rubbing process by an abrasive grinding wheel is used to material. However, it has the same cutting action as milling, tuning and drilling has in product development.
Materials Suitable for Soft Machining: Delicate Yet Diverse
Manual soft machining or CNC machining both are capable to machine any type of material in mass production and volume production with tight tolerance. These materials are plastics, alloys, composites and non-ferrous metals.
Plastics: A Realm of Versatility and Formability
Soft machining of plastics is an important field of application in CNC machining. Plastics can undergo soft machining with own specifications, properties. plastics have poor thermal conductivity. Therefore, it is important to remove generated heat from the chips during plastics machining.
Plastics prototypes parts are cast or drawn. Soft machining like grinding, milling, turning and drilling all can be employed to plastics. But sharp cutting tools with highly smooth surface are required to machining plastics. This can separate plastic quickly and move it away without any effort. This results in smooth surface finish of prototype parts in product development.
Types of plastics for soft processing
The types of plastics that can be processed are:
- Thermosetting plastics: epoxy and formaldehyde resins, polyurethane, silicon rubber.
- Thermoplastic: Polyethylene, polypropylene, PVC, PTFE, PVDF, Polyesters, polyamides
- Elastomers: rubbers, latex
- Fibers: GF, CF, AFU
- Foams: soft and hard foams of PE, and PU
Composites: Blending Strength and Lightweight Properties
Soft machining of composites is shaping and finishing the prototypes parts by cutting, milling, tuning, drilling and other processes. Composite machining requires special tools and methods because they are hard and layer-structured materials. Composite machining helps in shaping with tight tolerance with maintaining the integrity of material in prototyping process. Soft machining helps the rods and tubes fit accurately in rapid prototyping and make a perfect bond.
Non-Ferrous Metals: Achieving Precision and Aesthetics
Non-ferrous metals are excellent machinable material due to absence of iron. They have easy cutting, drilling, turning and grinding. They have fine finishes, and their cost effectiveness is high. The high electrical and thermal conductance is ideal for machining of protype parts. Surface finish processes like anodizing also gives better results after machining of nonferrous metals. The lightweight metals reduced overall weight of prototyping process and in product development.
Soft Machining Tools
Soft tools are used in the process of creating temporary molds used in production methods. Soft tooling made of easy materials are used in rapid prototyping and initial manufacturing stage like prototyping processes. It is before the durable and expensive hard tooling in the volume production of product development. Soft tooling has higher cost effectiveness in production tooling. One more advantage of soft tooling is the flexibility in the material requirements. It adds convenience and versatility in production tooling. Soft tooling is beneficial for rapid prototyping before mass production and volume production.
Soft tooling examples
The soft tooling use in the process of creating prototype parts are as:
- Silicon mods: these are utilized in creating prototype parts and for low volume production and mass production because it is affordable and has easy fabrication.
- Carbon fiber: these molds provide cost effectiveness and durability. These are suitable for short run production and rapid prototyping of delicate parts.
- Glass fiber: this option is also a great advantage towards cost effectiveness for large parts and prototypes parts. But it requires additional finishing treatment for smooth surface.
- Aluminum molds: this is an expensive option in soft tooling. It offers high durability and a better heat transfer rate in volume production and mass production.
Applications of Soft Machining: A Spectrum of Industries and Products
Soft machining is ideal for creating complex parts which requires high accuracy and tight tolerance in different fields which are explained below:
Aerospace: Precision and Performance for Demanding Environments
The notable application of soft machining whether manual or CNC machining includes manufacturing of cabin components, wing ribs and fuselage parts. CNC machining is also used in building actuators, motion control sensors, engine housing, landing gear parts and disc and filter bodies.
Medical: Delicate Precision for Life-Saving Devices
The applications of soft machining in medial fields are many because of its high accuracy, tight tolerance and flexibility and versatility. These include rapid prototyping parts of medical instruments, manufacturing of orthopedic implants for hip and knee replacement. It’s also utilized in manufacturing surgical instruments and endoscopic tools, and for manufacturing parts for diagnostic equipment.
Electronics: Miniaturization and Performance for Cutting-Edge Devices
The major example of soft machining in electronics is the metal alloy casing of APPLE products. These are made by CNC machining and CNC router. It is also used in products like PCBs, housings, jigs, semiconductors devices like wafer plates, gas distribution channels, wafer carriers and solder flex stencils.
Consumer Goods: Aesthetics and Functionality for Everyday Products
Soft machining is used in niche manufacturing such as making jewelry, musical instruments, furniture, in consumer electronics and semiconductors. These are like making pianos, engravings, carving, tuning knobs, fret slots and other musical instruments. In metal frames, glass cutting, polishing and engraving for furniture.
Soft Machining: A Winning Combination for Delicate Materials
Minimal Material Removal and Reduced Stress
Material removal methods are utilized to build incomplete casting conform to design specifications. This allows generic casting to be changed into a unique finish product. soft machining has this benefit along with the reduced stresses. These are induced while machining because of thermal mechanical and chemical factors and can cause fatigue failure.
High Precision and Tight Tolerances
Tight tolerance is acceptable with narrow variation of 0.005in. Soft machining can produce parts with high accuracy and tight tolerance and their actual dimensions of prototypes part may or may not deviate more than 3inches.
Smooth Finishes and Reduced Burrs
Soft machining regrading surface finish has the best results, it produces smoothest finish which can be due to many factors. These are material elasticity, mold release features, vibration damping and less tool marks unlike in hard tooling.
Versatility for a Wide Range of Materials and Geometries
Soft machining is remarkable in handling complex parts. It has flexibility in the process which can create delicate shapes with higher accuracy and tight tolerance. Soft machining can create 3d parts with high fidelity to the patterns. It also has fast turnaround and cost effectiveness.
Challenges and Considerations in Soft Machining: Ensuring Success for Delicate Materials
Tool Selection and Optimization
Sot tooling is less durable. It can wear out and deform faster when high pressure and temperature condition are used. This can shorten the tool life and frequent replacement that can increase the production cost. Therefore, tool optimization and selection are important factors in soft machining.
Process Planning and Optimization
Soft machining process has longer cycle times. The flexibility in the process may require addition time for demold, cooling or setting that can affect the efficiency of the project.
Fixturing and Work-holding
Soft tooling and materials may have an issue of working and fixtures. This occurs due to insufficient clamping force and pressure applied to the workpiece. This results in movement, slippage and deformation of the workpiece.
Cooling and Lubrication
Efficient cooling and lubrication can result in longer production tooling life and shortened machining cycle. It increases the performance of the product development process and improves surface quality.
Monitoring and Control
Reliable monitoring and control provide real-time insight to the process. This can lead to long-term improvement in the overall production development process. The monitoring of machines and process reduces the chance of abnormalities and allows secure high productivity.in soft machining process, this can be challenging due to higher flexibility in process and longer cycle of process.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Soft Machining
The advantages of soft machining are as:
- Fast turnaround: this process is easy to shape and modify the prototypes parts. It also allows rapid design iteration and adjustments in product development.
- Cost effectiveness: it can be carried out at a low to medium volume production rate. The materials used in soft machining are more affordable than hard process and suitable for low budget projects.
- Complex and delicate geometries: it has higher flexibility in dealing with intricate designs and can form geometries with tight tolerance very accurately. It can also create 3d parts with
The disadvantages of soft machining are as:
- Low volume production and mass production: it is suitable for low to medium production volume and cannot withstand high volume demands on a large scale.
- Limited tool life: soft tooling is less durable and requires frequent replacement and repair. This can also increase the production cost sometimes.
Conclusion: Soft Machining – An Indispensable Tool for Delicate Materials
Soft tooling is carried out for design validation, product testing and low volume production. It is suitable for prototyping processes or to test design before mass production. It is preferred for creating intricate designs that can be time consuming and can be challenging by hard tooling. The advantages of soft machining are the cost effectiveness, high surface finish, fast turnaround, design and process flexibility and for manufacturing complex geometries. However, it has some limitations due to low production volume and not suitable for large scale production.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 Distinction Between A2 and A4 Stainless Steel: A Comprehensive Guide
Distinction Between A2 and A4 Stainless Steel: A Comprehensive Guide 







