The Definitive Guide to Rivets: Types of Rivets and Riveting Processes
 Dec 14,2022
Dec 14,2022

Rivet is not only a tool or a material, it can play a pivotal role in many industries.
For example, various industries such as housing construction and machine manufacturing need rivets to fasten some parts, so the rivets should be fastened as they do, which is related to the quality and development of each industry using rivets, work efficiency and use safety.
Rivets have high reliability, high connection strength, long life, and easy operation and use. They can be used for the connection of aluminum alloys, structural steels, and composite materials. They are often used in riveting and maintenance of closed parts of aircraft.
What is a Rivet?
A rivet is a mechanical fastener, a rod-shaped part with a cap at one end, after penetrating the connected component, the other end is pressed out at the outer end of the rod, and the component is pressed and fixed.
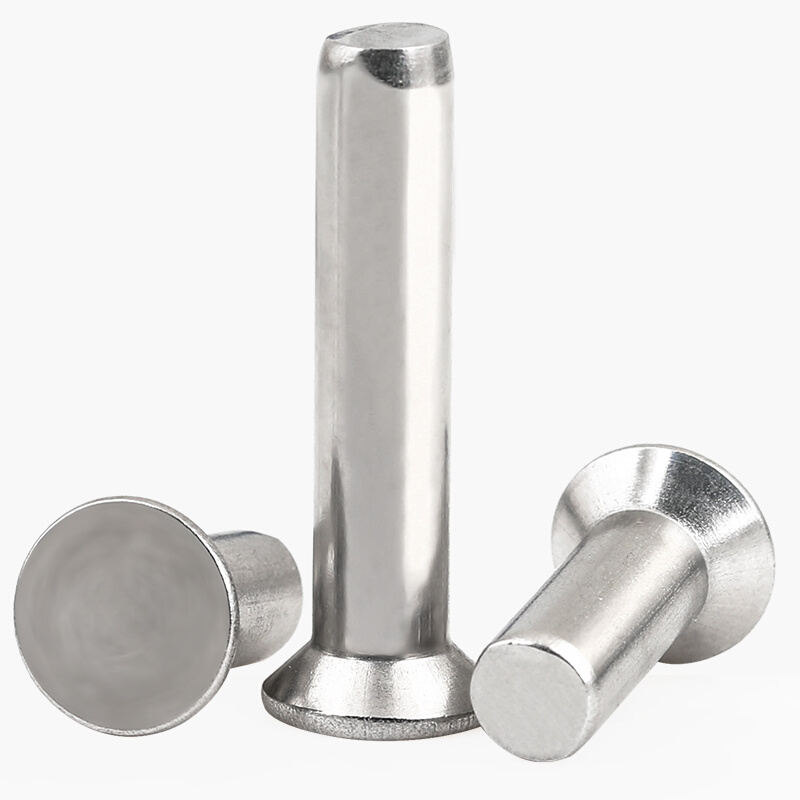

Today, Tuofa CNC Machining introduces the development history, process concept, type, application scenarios and selection strategies of rivets.
The Development History of Rivets
The earliest rivets were small pegs made of wood or bone, and the earliest metal deformations may be the ancestors of rivets.
They are the oldest method of joining metals known to man, dating back as far back as the original use of malleable metals.
In the Bronze Age, the Egyptians used rivets to fasten the six wooden sectors on the outer line of the slotted wheel. After the Greeks successfully cast large statues in bronze, they used rivets to fasten the parts together.
Hollow rivets In 1916, H.V White of the British aircraft manufacturing company obtained the patent for blind rivets that can be riveted on one side for the first time. Since then, blind rivets have been widely used in mechanical connections of aerospace, office machines, and electronic products.
It is unclear exactly when the hollow rivet was invented, but horse harnesses using hollow rivets were invented in the 9th or 10th century AD.
Do you know what is the most famous steel structure building in the world? There is no doubt about the answer - the Eiffel Tower in Paris, France! This steel tower building covering an area of about 10,000 square meters was built as a symbol of the World Expo in 1889. It was also the tallest building in the world at that time. It took two years, two months and three days to build. The body of the tower is built with a hollow steel frame, using a total of 7,300 tons of steel, 12,000 metal parts, and 2.5 million rivets. At that time, the most controversial point was to abandon traditional steel bars and cement, and use building materials such as steel frame materials and rivets. Can it stand for a long time?
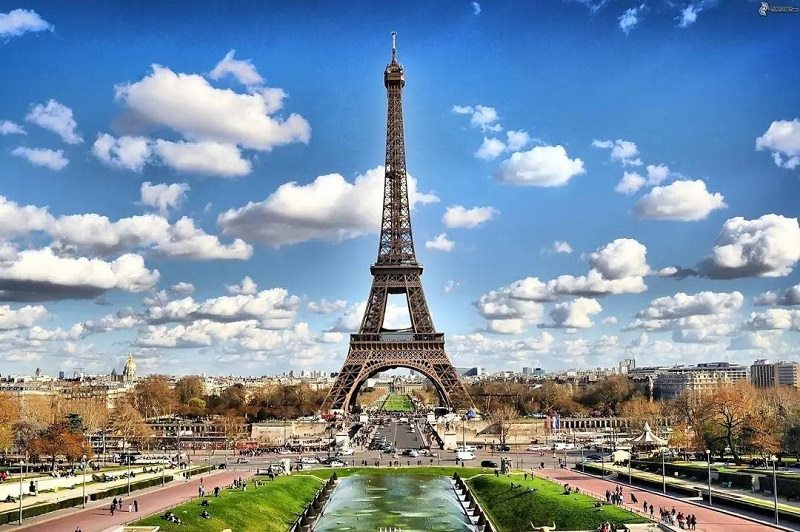

However, time has given us the best answer. The Eiffel Tower still stands today, showing the world its structural beauty and artistic beauty! All of this depends on the big role played by small rivets. The riveted iron tower has excellent insulation and fire performance, non-magnetic, heat insulation, light weight, high temperature resistance and corrosion resistance.
Rivets Role
The role of rivets: It is a method to replace screw connections, so that multiple parts can be connected together, which can not only be fastened, but also allow the parts to rotate (using step rivets). How to use:
1. It can be manually riveted, the efficiency is not high, and it is suitable for small batch production;
2. It can be riveted by machine, and human and machine can cooperate; the production efficiency is high, it is suitable for mass production, and semi-automatic operation is realized, which is 5-10 times the efficiency of manual riveting.
The use of rivets can greatly reduce production costs and shorten the production cycle. The cost performance is 1/4 of the cost of using screws, which is 3 times faster than screw connection. (You must both buy nuts and screws.) It increases the cost; even if you use an electric screwdriver or an air screwdriver to install the screws, it cannot be riveted faster than a riveter. Anyone who has used rivets knows that the structure that can use rivets will try to design rivets, because you can save unnecessary expenses. Improve the competitiveness of the company's products!
Rivets Correlation Analysis
Stamping force of rivet assembly die
When rivets are assembled and riveted, the customer generally defines the strength with the mold, which has nothing to do with the hardness of the rivet: for example, 80GF, 110GF, 200GF, and 260GF can be pressed down.

Riveting die punch size
When the rivet is assembled and riveted, the customer uses the die punch to drive the rivet into the hole of the galvanized sheet. Generally, the die punch is 0.01MM larger than the maximum outer diameter of the rivet, and the rivet is visually viewed on the galvanized sheet after riveting. There will be traces that the product will be recessed around, and the approximate size of the recess is about 0.01MM~0.02MM, which is the best embedding (controlled by the mold).
Thickness of galvanized sheet
Usually the thickness of the galvanized sheet is related to the rivet embossing/grooving step difference, the customer must define it according to the thickness of the galvanized sheet when designing the rivet embossing/grooving step difference, and the thickness of the galvanized sheet is generally set to 0.5MM~1 .OMM or so (subject to open mold).

Rivet torque value
Generally, the torque of M3 can reach more than 8kg, and the pulling force can reach more than 40kg; generally, the torque of M4 can reach more than 10kg, and the pulling force can reach more than 45kg; generally, the test after riveting is usually driven in with a force of 50kg; (average value of 50kg).
Rivet hardness issue
Usually, the heat treatment of rivets is not only to increase the hardness of the rivets, but the actual effect of heat treatment is to relieve the stress of the rivets and prevent the products from cracking after riveting. The rivet hardness requirements are set according to the customer's plate thickness. The thicker the plate thickness, the higher the rivet hardness requirements. On the contrary, the thinner the plate thickness, the lower the rivet hardness requirements.
6 Types and Uses of Rivets
Commonly used are R-type rivets, fan rivets, blind rivets (core rivets), tree rivets, semi-round heads, flat heads, semi-hollow rivets, solid rivets, countersunk rivets, blind rivets, hollow rivets, which are usually used The riveted parts are connected by self-deformation. Generally, cold riveting is used for those smaller than 8 mm, and hot riveting is used for larger sizes. But there are exceptions. For example, the nameplate on some locks is riveted by the interference between the rivet and the hole of the lock body.
R type plastic rivets
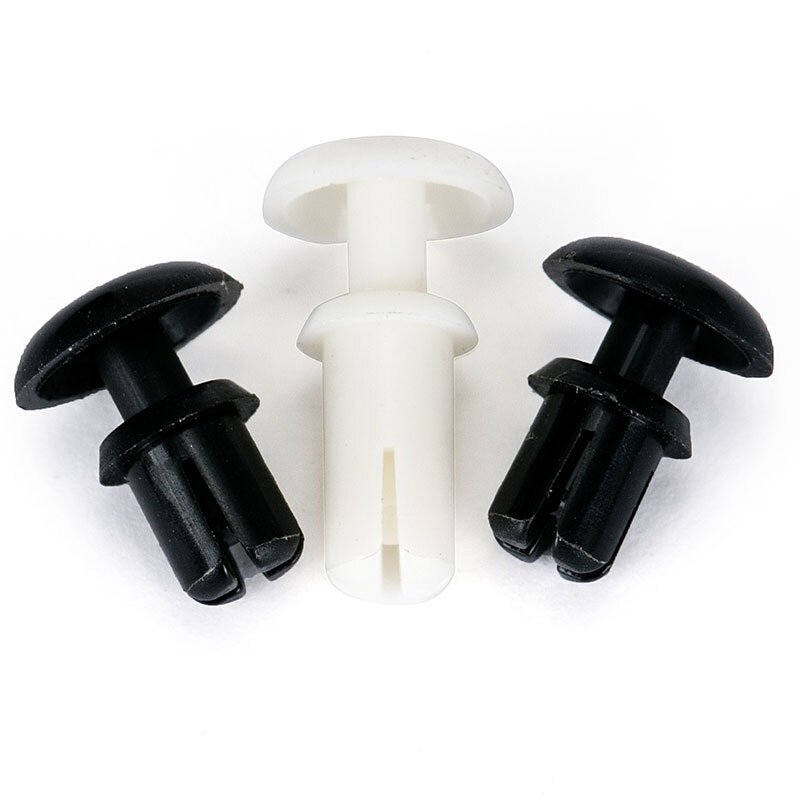

R-type plastic rivets are also called expansion rivets, which are composed of two parts: plastic nails and female buckles. It does not need to use installation tools when installing, place the installation base in the smooth hole, and then press the head, the specially designed feet expand and expand after being stressed, and are firmly locked on the installed surface. It is often used to connect plastic shells, lightweight boards, insulating materials, circuit boards, or any other thin, light-weight materials, beautiful and practical, and easy to use.
Fan rivets

The fan rivets are specially designed for manual installation. They can be pulled in through the holes of the panel or chassis. They are made of elastomer materials with good toughness, and can be installed quickly even in interference fit. The design is ingenious and has an elastic function, and it is not easy to slide out after being pulled in with the corresponding aperture. The fan rivet is mainly used for fixing between the fan of the electronic computer case, the heat sink and the chip, and has anti-vibration and noise reduction.
Expansion rivets
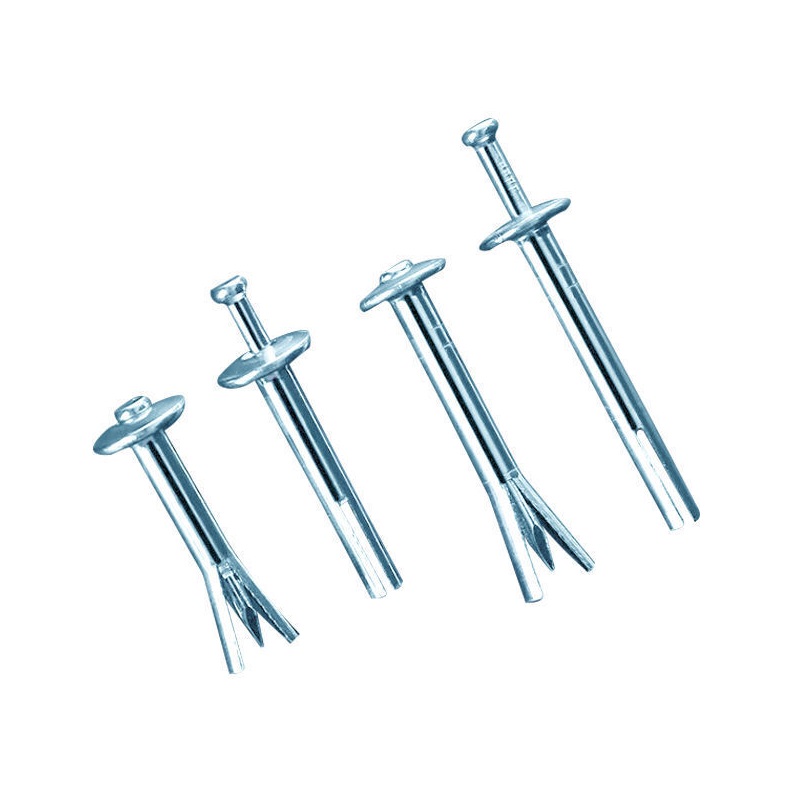
The core rivet is a new type of riveting fastener that is very convenient for riveting. The core rivet can show its unique advantages in a relatively small space or in an environment where there is no riveting gun or the riveting gun cannot be used. Two or several connected parts can be successfully riveted by hitting the nail core with a hammer or other utensils on one side. Core rivets can be divided into oblate head core rivets and countersunk core rivets according to the shape of the brim of the nail cap. According to the combination of materials, they can be divided into all aluminum core rivets, aluminum steel core rivets, and all stainless steel core rivets. Rivets, steel core rivets, aluminum stainless steel core rivets, plastic core rivets, etc. The core rivet does not have to be riveted with a manual riveter or a pneumatic riveter like a blind rivet. It has better riveting and convenience, and can be widely used in riveting of various connected parts.
Christmas tree rivets
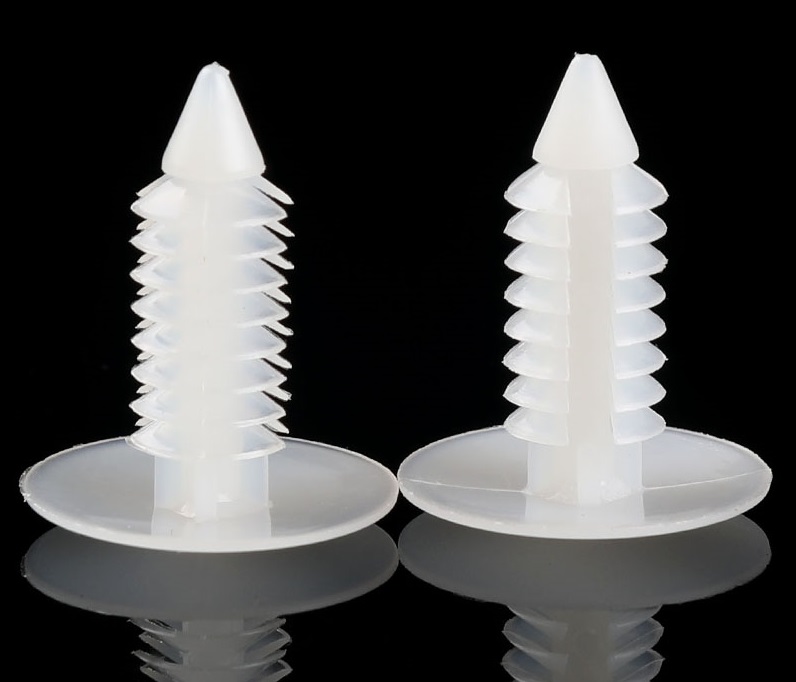

Christmas tree rivets are also called inverted-toothed plastic rivets, also known as Christmas tree-shaped plastic rivets. The tooth-shaped sheet has good elasticity and can be directly pressed and installed in the round hole of interference assembly. The tooth-shaped sheet can be installed according to the actual thickness. It can be fixed by self-adjustment. The design of the inverted tooth shape is that the rivet is firmly fixed on the installed surface after installation, and is not easy to be pulled out. It is suitable for fixing between soft materials such as foam, wood, rubber, and car interiors. Plastic tree rivets have excellent insulation, fire resistance, non-magnetism, heat insulation, light weight, high temperature resistance, high strength, and corrosion resistance, and are widely used in various industrial fields.
Blind rivet
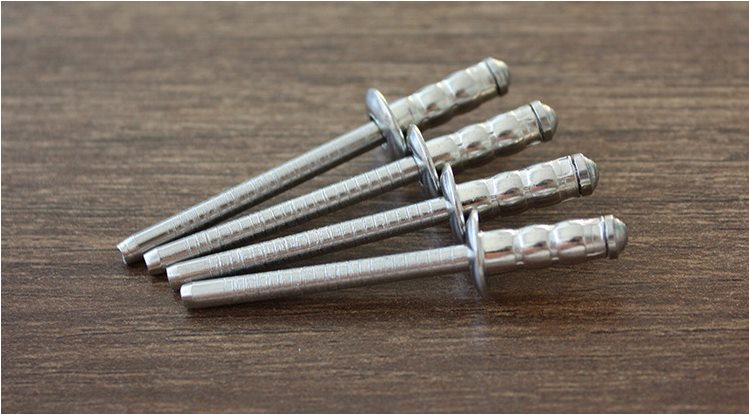

Blind rivet are a kind of rivets used for single-sided riveting, but they must be riveted with a special tool - riveting gun (manual, electric, pneumatic). This type of rivet is especially suitable for riveting occasions where it is inconvenient to use ordinary rivets (riveting must be done from both sides), so it is widely used in construction, automobiles, ships, aircraft, machines, electrical appliances, furniture and other products.
The types of blind rivets can be roughly divided into open type, closed type, double-drum type, and single-drum type series. The following is a brief description of each model.
Countersunk head type blind rivets: For the riveting of riveted parts that require a smooth and beautiful surface after riveting.
Double-drum blind rivets: When riveting, the mandrel pulls the end of the rivet body into a double-drum shape, clamps the two structural parts to be riveted, and reduces the pressure on the surface of the structural parts. Uses: Mainly used for riveting various thin structural parts in various vehicles, ships, construction, machinery, electronics and other industries.
Large brim blind rivets: Compared with ordinary blind rivets, the diameter of the aluminum cap of this rivet is significantly larger. When the rivet is riveted with the connecting piece, it has a larger contact area and a stronger supporting surface to enhance the torque. Strength, can withstand higher radial tension. Applicable industries: suitable for fastening soft and fragile surface materials and large holes, increasing the brim diameter for special protection applications for soft materials.
Closed blind rivets: specially designed to cover the mandrel head after riveting, very suitable for various applications with waterproof requirements. With high shear force, anti-vibration, anti-high pressure.
All aluminum blind rivets: all-aluminum blind rivet The rivet body is also made of high-quality aluminum wire, which is beautiful and durable after riveting and will never rust: Compared with ordinary blind rivets, the riveting strength of the rivet is lower, and it is suitable for joints with softer materials . Split Stainless Steel Rivet: This rivet is a high tensile demand, corrosion resistant choice. Round head rivets are mainly used in riveting occasions subject to large lateral loads, and are the most widely used. Flat cone head rivets are corrosion-resistant due to their large nail heads, and are often used in highly corroded riveting occasions such as ship hulls and boiler water tanks.
Flat head rivets
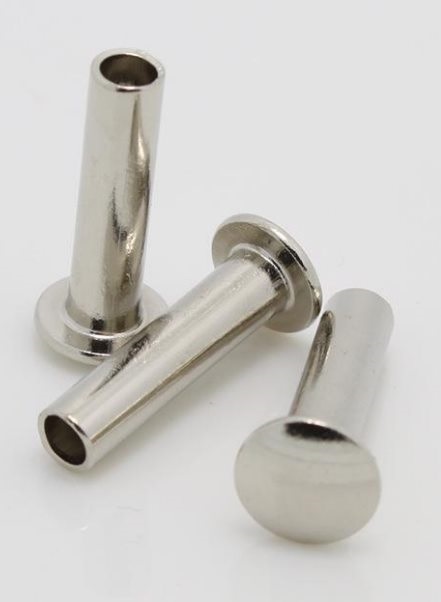

Flat head, countersunk head, semi-sunk head, 1200 countersunk head, and semi-sunk head rivets are mainly used for riveting occasions where the surface needs to be smooth and the load is not large. Flat head rivets are used for riveting occasions subjected to general loads. Flat head and round head rivets are mainly used for riveting occasions of non-metallic materials such as metal sheets or leather, canvas, and wood. Large flat head rivets are mainly used for riveting occasions of non-metallic materials. Semi-tubular rivets are mainly used in riveting occasions where the load is not large. Tubular rivets are used for unloaded riveting of non-metallic materials. Nameplate rivets are mainly used for riveting nameplates on machines and equipment.
Rivet Exception Problem
The situation that causes the rivet to fail to rivet:
If the outer diameter of the rivet base is too large, the rivet cannot be put into the galvanized sheet during riveting;
Conditions that affect the torsional force of the rivet:
1. The outer diameter of the rivet base is too small, which will cause the rivet to loosen after riveting.
2. There is no abnormality in the rivet, but the customer did not rivet the rivet into the galvanized sheet optimally during riveting, resulting in loosening of the rivet after riveting.
3. If the section difference of the rivet groove is too small, the galvanized sheet cannot be squeezed into the groove well during riveting.
4. The torsional tension of the rivet is mainly due to the difference between the embossed section of the rivet and the section of the groove. At the same time, the relevant size must also match the thickness of the customer's galvanized sheet.
5. The thread of the rivet is the key dimension of the rivet. If there is a phenomenon of tooth tightness, the customer will damage the thread of the rivet and cause slippage because the screw cannot be driven in after riveting.
6. The rivet has NOGO phenomenon. After riveting, the screw cannot match the rivet thread, which will lead to slipping.

In case of rivet breakage
1. If there is no abnormality in the rivet, if the height of the customer's punch is uneven (weary), a longer punch may cause the possibility of breaking.
2. The depth of the rivet slot is too deep, the hardness is too hard, and it is easy to break after riveting.
The main considerations for the selection of rivets
The material of the connected parts-metal or non-metal, the hardness and brittleness of the material, etc.;
Plate thickness - the selected rivets ensure that the plate thickness is within its clamping range;
Connection strength ¾ determines the tensile force and shear force required for the connection point of the rivet;
Hole size--The manufacturer specifies the matching hole size for the rivet nut, and you can refer to the manufacturer's design information;
The coating thickness of the plate should be considered to avoid the hole becoming smaller after coating and not suitable for installation;
Corrosion resistance of materials--The choice of material type and coating for rivets should be based on the required corrosion resistance. Try to choose rivets with the same material as the connecting piece. Different materials may lead to galvanic corrosion;
Special requirements, such as flat head, countersunk head, double drum type, or lantern type;
Watertightness and airtightness requirements - watertightness and airtightness requirements for riveting area.
|
Try Tuofa Now! Tuofa Engineer Support Team - Real human quotes are more accurate than software quotes |
Get a free quote |
3 Misconceptions About Rivets
Misconception 1: All rivets are same
A more accurate statement should be: All blind rivets are installed in the same way. However, in terms of the configuration of fasteners, there are many options for the head style and material type.
The head style is a very important parameter for any type of fastener, and it is also very important for blind rivets. You can't use convex rivets to fix the skin on the outer surface of the aircraft, no matter Both aesthetically and aerodynamically, this application requires the choice of a countersunk head.
The choice of material depends to a large extent on the protection against corrosion. Usually, the rivet material should match the material to be assembled to prevent electrochemical corrosion between dissimilar metals. Of course, it can also be achieved by coating or Plating to prevent the release of such problems. In some cases, different materials can be selected for the core rod and sleeve to suit different application requirements.
Misconception 2: Rivets are removable fasteners
Rivets can indeed be disassembled, but from the perspective of structural connection, they are permanently installed fasteners, that is, they should be at least equal to the service life of the aircraft after being installed correctly. But for blind rivets: From the point of view of the installation method of rivet locking, the blind rivet can only be disassembled by destroying the joint between the lock ring in the sleeve and the mandrel, so this disassembly is essentially a destructive method. Disassembly, and the disassembled parts cannot be used anyway. From this point of view, it is completely different from the bolt and nut that can be loosened. Therefore, it can be said that blind rivets are permanent installation fasteners.
Misunderstanding 3: Blind rivets are used only when solid rivets cannot be installed
To be honest, this concept has been proven accurate for a long time before, when you need to use solid rivets to connect and can't install from both sides of the materials being joined, using blind rivets to complete the installation from one side is the best choice. The best solution. The biggest advantage of solid rivets is that they are cheap, but from an application point of view, if the thickness of the connecting plate is relatively thick or the joint is used for tensile applications, the tensile strength of the solid rivet is higher than its shear strength. Low, and the thicker the connecting plate, the more difficult it is to install; in addition, from the installation point of view, the noise of installing solid rivets is unacceptable.
The installation of blind rivets is faster than that of solid rivets, and the whole installation process is smooth and almost noiseless. When you need to improve assembly efficiency, you can consider simply choosing blind rivets installed on one side directly. The number of applications is large. The price will naturally be more reasonable, after all, the price of fasteners still largely depends on the purchase quantity.
What is riveting?
The rivet connection is to use a metal cylinder or metal tube slightly smaller in diameter than the prefabricated hole, pass through the part to be riveted, and tap or pressurize the two ends of the rivet to deform and thicken the metal column and form a rivet head at both ends. The part cannot come out of the rivet.
Punch rivet connections and rotary rivet connections generally require double-sided operations.
Blind rivets make single-sided operation a simpler and easier process. The working principle of blind rivets is realized by pulling the core head with a force from the inside to the outside with the help of a rivet gun.
Riveting is a very wide range. Non-professionals will think that the riveting process is the simplest. In the impression that the rivet itself is a casting, and riveting only needs to punch holes in the object to make the connection. However, the riveting equipment used in riveting needs to ensure that the pressure is adjusted appropriately, the riveting speed and riveting time are adjusted appropriately, and the riveting height is also adjusted to be just right according to the requirements. In order to complete a perfect riveting, to ensure that the riveted parts are just right. So riveting is not easy.
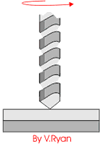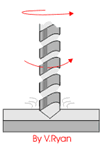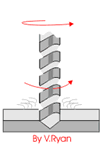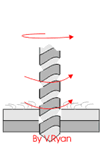
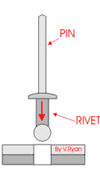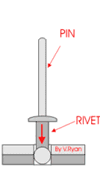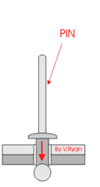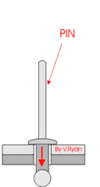
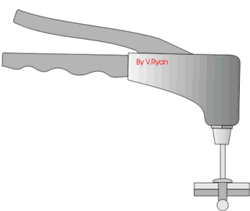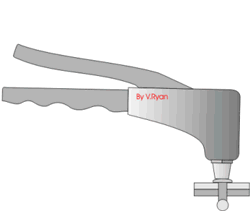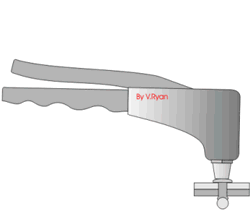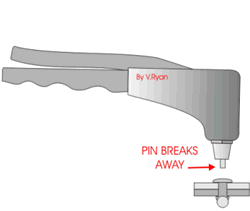
3 Processes and Characteristics of Riveting
Rivet connection: There are pull riveting, punch riveting, spin riveting, etc.
The main characteristics of rivet connection are: fast speed, anti-loosening, and not easy to disassemble.
Pull riveting
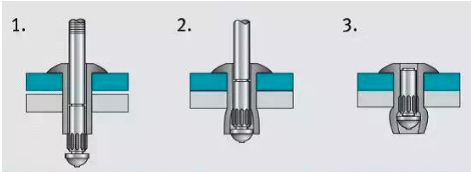
Pull riveting is a riveting method that uses manual or compressed air as power to deform special rivets and rivet riveted parts. It is a kind of cold riveting.
The main materials and tools used in riveting are blind rivets and pneumatic (or manual) riveting guns.
The feature of blind riveting is that it does not require top nail operation, and it is very convenient for components with complex structures that cannot be top nailed on the reverse side. However, because the rivet is made of aluminum, it is only used for light-load occasions.
Punch riveting
Punch riveting is also called pressure riveting process, through plastic deformation of rivets or parts after being stressed to link parts together.
Whether it is rivet deformation or material deformation, the riveting process is a cold heading process.
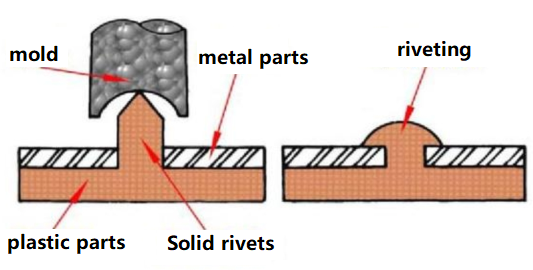
The punching riveting process is stressed quickly and the riveting efficiency is high. The connecting materials on the riveting point are inlaid with each other, and the bottom has neither edges nor burrs, which avoids stress concentration and can withstand high dynamic loads.
And there is no heat input during the connection process, and the material surface coating at the connection point will not be damaged. At the same time, welding spatter and welding deformation are avoided, and the connection of multi-layer materials, different plate thicknesses, and different materials can be realized.
Spin riveting
Spin riveting is a riveting method in which the rivet is partially pressurized by the rivet rod and continuously swings around the center until the rivet is formed. According to the cold rolling track of this riveting method, it can be divided into pendulum rolling riveting method and radial riveting method.
The pendulum rolling riveting method is easier to understand. The riveting head only swings and rolls along the circumferential direction. The radial riveting method is more complicated. Its trajectory of the riveting head is plum-shaped, and the riveting head passes through the center point of the rivet every time, that is, the riveting head not only moves in the circumferential direction, but also swings and rolls along the radial direction.
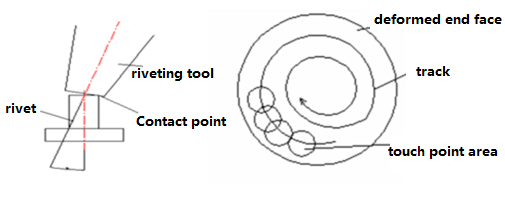
As far as the comparison of the two riveting methods is concerned, the quality of the riveted parts on the radial riveting surface is better, the efficiency is slightly higher, and the riveting is more stable, and the riveting parts do not need to be clamped, even if the center of the rivet is slightly offset from the center of the spindle, it can be smoothly Complete the riveting work.
The pendulum riveting machine must accurately position the workpiece, and it is best to clamp the rivet.
However, the radial riveting machine is generally not used in non-special occasions due to its complex structure, high cost and inconvenient maintenance. On the contrary, the pendulum roller riveting machine has simple structure, low cost, convenient maintenance and good reliability, and can meet the riveting requirements of more than 90% parts.
| Let's Start A New Project Today |
| Get a Free Quote |
Conclusion
Reasonable use of rivets can make parts or products have more excellent mechanical properties: the value of the pre-tightening force (clamping force) of rivet connections of the same specification is more than 10% greater than that of high-strength bolts, which can effectively improve the slip load of friction-type joint connections. The connection is more secure.
The stability of the rivet can have good axial force consistency: through the axial force stability test, the fluctuation range of the axial force of the rivet connection can be controlled within 5%.
Better anti-loosening performance: After the riveting is completed, there is no gap between the collar and the rivet ring groove, which effectively prevents loosening and improves the anti-loosening performance of the structural connection.
Excellent fatigue performance: Through the gentle arc design of the tooth profile, the stress at the root of the tooth profile can be effectively reduced by about 30%, and the fatigue life of the ring groove rivet can be significantly improved.
Tuofa CNC Machining is the largest and most powerful fastener, sheet metal, and 3D printing product production top enterprise in Shenzhen, China, integrating scientific research, development, manufacturing and sales, providing the necessary CNC machining metal or plastic rivets. Our professional mechanics and engineers have rich experience to provide the best service with the fastest lead time to get the expected results of global customers.
Contact info@tuofa-cncmachining After uploading part design files, our engineers will analyze the drawings and provide you with instant quotations (manual quotations are more accurate and reliable). Whenever your fabrication project requires the finest metal rivets, www.tuofa-cncmachining.com offers the perfect solution.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 Plastic Welding Knowledge: 5 Ways & 7 Processes & 4 Mistakes
Plastic Welding Knowledge: 5 Ways & 7 Processes & 4 Mistakes 







