41 Questions for CNC Machinist- Necessary Knowledge
 Nov 25,2022
Nov 25,2022

After the third scientific and technological revolution, human beings are moving towards intelligence and informationization in today's era, and we who are studying mechanical design, manufacturing and automation, how should we take advantage of this rapidly developing era in machining services and become What about a qualified and excellent CNC machinist?
Tuofa believes that a qualified CNC machinist should have a solid foundation. By explaining the necessary knowledge of CNC machinists, let us know that an excellent CNC machining is first of all a love of this industry, and then the accumulation of knowledge, including mathematics , engineering drawing, English, physics learning, professional skills and innovative ability to adapt to the development of manufacturing industry.
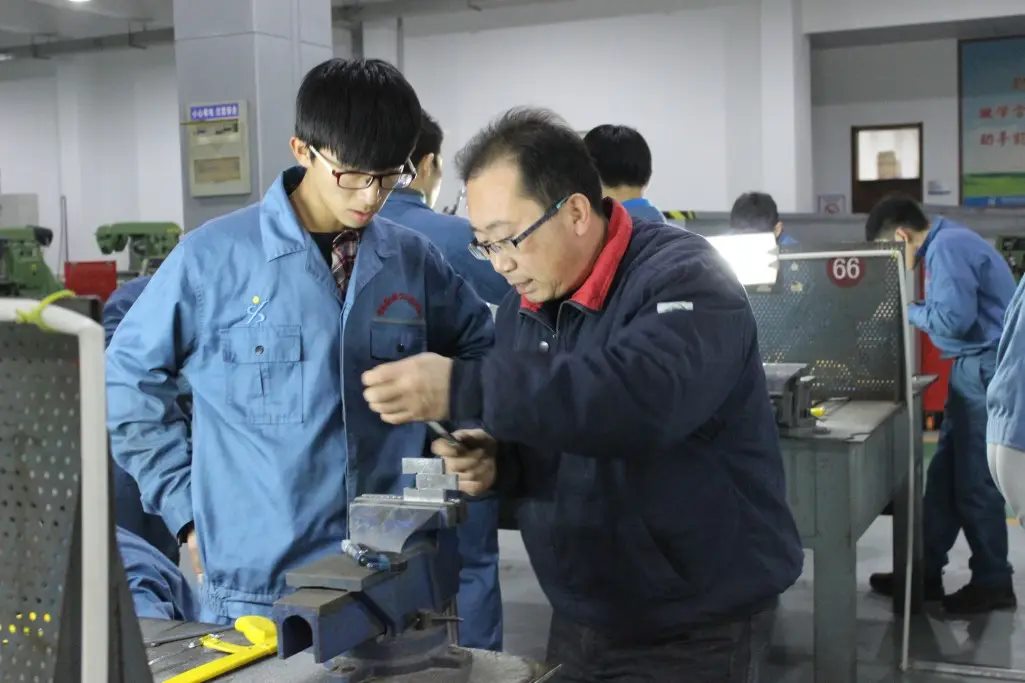

1. What are the three methods of work piece clamping?
1. Clamping in the fixture;
2. Alignment and clamping directly;
3. Line alignment and clamping.
2. What does the process system include?
Machine tool, work piece, fixture, tool
3. What are the components of the machining process?
Rough machining, semi-finishing, finishing, super-finishing.
4. How are benchmarks classified?
1. Design reference
2. Process reference: process, measurement, assembly, positioning: (original, additional): (rough reference, fine reference)
What does machining accuracy include?
- 1. Size accuracy
- 2. Shape accuracy
- 3. Position accuracy

5. What are the original errors in the processing process?
Principle error · Positioning error · Adjustment error · Tool error · Fixture error · Machine tool spindle rotation error · Machine tool guideway error · Machine tool transmission error · Forced deformation of process system · Thermal deformation of process system · Tool wear · Measurement error · Work piece residual stress Caused error
6. What is the effect of process system stiffness on machining accuracy (machine tool deformation, work piece deformation)?
1. The shape error of the work piece caused by the position change of the cutting force action point
2. The machining error caused by the change of the cutting force
3. The machining error caused by the clamping force and gravity
4. The influence of transmission force and inertial force on the machining accuracy.
7. What are the guiding errors and spindle rotation errors of machine tool guide rails?
1. The guide rail mainly includes the relative displacement error between the tool and the work piece in the error-sensitive direction caused by the guide rail.
2. Spindle radial circular run out, axial circular run out, and inclination swing.
8. What is the phenomenon of "error double reflection"?
What is error replication coefficient?
What measures can be taken to reduce error remapping?
Due to the change of process system error deformation, the error of the blank is reflected on the work piece. Measures: increase the number of tool passes, increase the stiffness of the process system, reduce the feed rate, and improve the precision of the blank.
9. Analysis of the transmission error of the transmission chain of the machine tool?
Measures to reduce the transmission error of the transmission chain?
Error analysis: it is measured by the angle error &Delta φ of the end element of the transmission chain
Measures: 1. The fewer the number of transmission chains, the shorter the transmission chain, the smaller the Δφ, and the higher the precision.
2. The smaller the transmission ratio i, especially the small transmission ratio at the first and last ends.
3. Because the end parts of the transmission parts The error has the greatest influence, so it should be as accurate as possible.
4. Use a correction device.
10. How to classify processing errors?
Which errors are constant errors?
Which errors belong to variable value system errors?
Which errors are random errors?
systematic error: (constant systematic error variable value systematic error) random error.
Constant value system error: custom machining error caused by machining principle error, manufacturing error of machine tools, tools, fixtures, force deformation of process system, etc.
Variable value system error: wear of props; thermal deformation error of tools, fixtures, machine tools, etc. before thermal balance
Random error: copying of blank error, positioning error, tightening error, error of multiple adjustments, deformation error caused by residual stress.
11. What are the ways to ensure and improve the machining accuracy?
1. Error prevention technology: Reasonable use of advanced technology and equipment to directly reduce the original error, transfer the original error, average the original error, average the original error.
2. Error compensation technology: online detection, automatic grinding of even parts, active control of the decisive error factors.
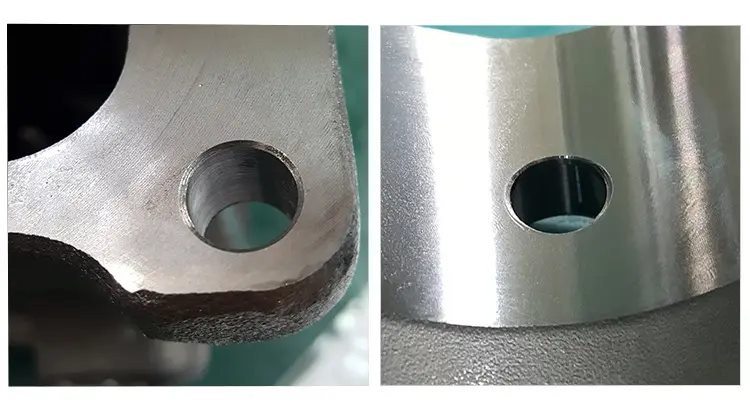

12. What is included in the geometry of the processed surface?
Geometric roughness, surface waviness, grain direction, surface defects.
13. What are the physical and chemical properties of the surface layer material?
- Cold work hardening of surface metal;
- Metallographic deformation of surface metal;
- Residual stress of surface metal.
14. Try to analyze the factors affecting the surface roughness of cutting process?
The roughness value is determined by: the height of the remaining cutting area;
The main factor: the radius of the tool nose, the leading deflection angle, the secondary deflection angle, and the feed rate. grinding quality.
15. Try to analyze the factors affecting the surface roughness of grinding?
- Geometric factors: Effect of grinding amount on surface roughness.
- Effect of grinding wheel particle size and grinding wheel dressing on surface roughness.
- Influence of physical factors: Plastic deformation of surface layer metal: Grinding amount, selection of grinding wheel.
16. Try to analyze the factors that affect the cold work hardening of the cutting surface?
Influence of cutting amount, influence of tool geometry, influence of processing material properties.
17. What is grinding tempering burn?
What is Grinding Quenching Burn? What is grinding annealing burn?
Tempering: If the temperature in the grinding zone does not exceed the phase transformation temperature of the quenched steel, but exceeds the transformation temperature of martensite, the martensite of the metal on the surface of the work piece will transform into a tempered structure with lower hardness.
Quenching: If the temperature in the grinding zone exceeds the phase transition temperature, coupled with the cooling effect of the coolant, the surface metal will appear a secondary quenched martensite structure, the hardness is higher than the original martensite; in its lower layer, due to cooling A tempered structure with a lower hardness than the original tempered martensite appears slowly.
Annealing: If the temperature in the grinding zone exceeds the phase transition temperature and there is no coolant in the grinding process, the annealed structure will appear on the surface metal, and the hardness of the surface metal will drop sharply.
18. Prevention and treatment of machining vibration
Eliminate or weaken the conditions for mechanical processing vibration; improve the dynamic characteristics of the process system, improve the stability of the process system, and adopt various vibration and vibration reduction devices.
19. Application of machining technology
Briefly describe the main differences and application occasions of machining process cards, process cards, and process cards
Process card: single-piece small batch production using common processing methods;
Machining process card: mid-batch production;
Process card: a large number of mass production types require strict and meticulous organization.
20. Principles for rough benchmark selection?
Fine benchmark selection principle?
Rough datum: 1. The principle of ensuring mutual position requirements; 2. The principle of ensuring a reasonable distribution of machining allowance on the machined surface; 3. The principle of facilitating work piece clamping; 4. The principle that rough benchmarks are generally not to be reused.
Fine datum: 1. Datum overlap principle; 2. Unified datum principle; 3. Mutual datum principle; 4. Self datum principle; 5. Easy clamping principle.
21. What are the principles of the process sequence?
- Process the reference plane first, and then process other surfaces;
- In half of the cases, process the surface first, and then process the hole;
- Process the main surface first, and then process the secondary surface;
- Arrange the rough machining process first, and then arrange Finishing process.
22. How to divide the processing stages?
What are the benefits of dividing processing stages?
Machining stage division: 1. Rough machining stage, semi-finishing stage, finishing stage, precision finishing stage
Dividing the processing stages can ensure sufficient time to eliminate thermal deformation and eliminate residual stress caused by rough processing, so that the subsequent processing accuracy can be improved. In addition, when the blank is found to be defective in the rough machining stage, it is not necessary to proceed to the next processing stage to avoid waste. In addition, the equipment can be used reasonably. Low-precision machine tools are used for rough machining and precision machine tools are specially used for finishing to maintain the precision level of precision machine tools. Reasonable arrangements for human resources, high-tech workers specialize in precision ultra-precision machining, which guarantees It is very important to improve the product quality and improve the technological level.
23. What are the factors affecting the process margin?
- Dimensional tolerance Ta of the previous process;
- Surface roughness Ry and surface defect depth Ha produced by the previous process;
- Spatial error left by the previous process.
24. What are the components of the working hours quota?
T quota=T single piece time+t quasi-final time/n number of pieces.
25. What are the technological ways to improve productivity?
- Shorten the basic time;
- Reduce the overlap between the auxiliary time and the basic time;
- Reduce the time for setting up work;
- Reduce the preparation and finalization time.
26. What are the main contents of the assembly process specification?
- Analyze the product drawing, divide the assembly unit, and determine the assembly method;
- Draw up the assembly sequence and divide the assembly process;
- Calculate the assembly time quota;
- Determine the assembly technical requirements, quality inspection methods and inspection tools for each process;
- Determine the delivery method of assembly parts and the required equipment and tools;
- Select and design the tools, fixtures and special equipment required in the assembly process.
27. What should be considered in the assembly process of the machine structure?
1. The machine structure should be able to be divided into independent assembly units;
2. Reduce the repair and machining during assembly;
3. The machine structure should be easy to assemble and disassemble.
28. What is generally included in the assembly accuracy?
1. Mutual position accuracy;
2. Mutual movement accuracy;
3. Mutual coordination accuracy.
29. What problems should be paid attention to when looking for the assembly size chain?
1. The assembly dimension chain should be simplified as necessary;
2. The assembly dimension chain is composed of "one piece and one link";
3. The "directivity" of the assembly dimension chain has assembly accuracy in different positions and directions in the same assembly structure According to the requirements, the assembly dimension chain should be supervised in different directions.
30. What are the methods to ensure the assembly accuracy?
How are the various methods applied?
1. Interchange method;
2. Selection method;
3. Repair method;
4. Adjustment method.
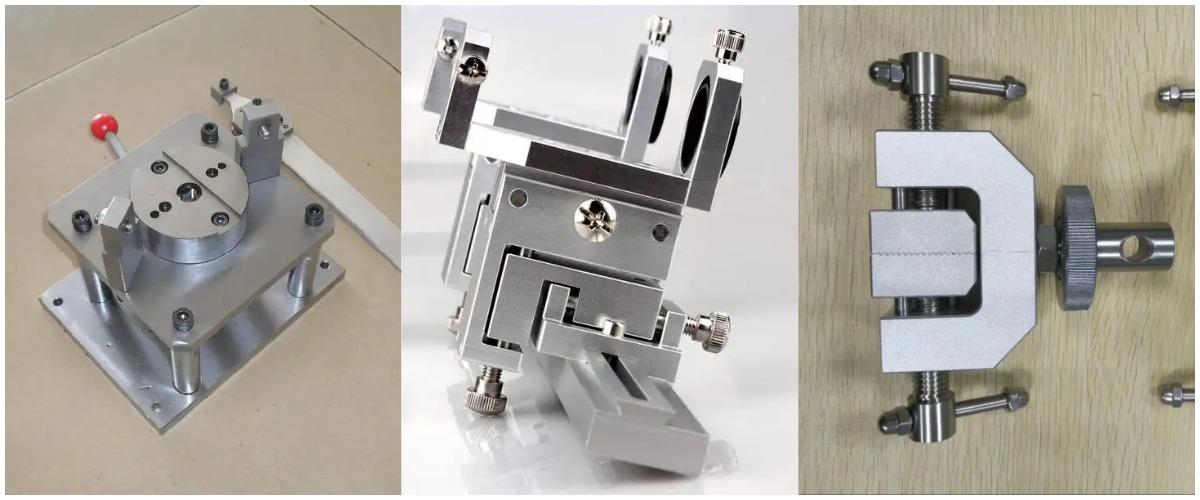

31. The composition and function of the machine tool fixture?
The machine tool fixture is a device for clamping the work piece on the machine tool. Its function is to make the work piece have a correct position relative to the machine tool and the tool, and keep this position unchanged during the processing. The components are: 1. Positioning element or device. 2. Tool guiding element or device. 3. Clamping element or device. 4. Connection element 5. Clamp body 6. Other elements or devices..
Main functions 1. Ensure processing quality 2. Improve production efficiency. 3. Expand the range of machine tool technology 4. Reduce labor intensity and ensure production safety.
32. According to the scope of use of fixtures, how are machine tool fixtures classified?
1. Universal fixture; 2. Special fixture; 3. Adjustable fixture and group fixture; 4. Combined fixture and random fixture.
The work piece is positioned on a plane.
33. What are the commonly used positioning components?
And analyze the elimination of degrees of freedom.
The work piece is positioned on a plane. Commonly used positioning elements are:
- Fixed support
- Adjustable support
- Self-positioning support
- Auxiliary support
The work piece is positioned with a cylindrical hole
34. What are the commonly used positioning components?
And analyze the elimination of degrees of freedom.
The work piece is positioned with a cylindrical hole. Commonly used positioning components include: 1. mandrel 2. positioning pin.
35. What are the commonly used positioning components for the positioning of the outer circular surface of the work piece?
And analyze the elimination of degrees of freedom.
Positioning on the outer circular surface of the work piece. Commonly used positioning elements are V-shaped blocks.
36. The work piece is positioned with "two pins on one side", how to design the two pins?
1. Determine the size and tolerance of the center distance between the two pins.
2. Determine the diameter of the cylindrical pin and its tolerance.
3. Determine the width, diameter and tolerance of the diamond pin.
37. What are the two aspects of positioning error?
What are the methods to calculate the positioning error?
Positioning error in two aspects. 1. The positioning error caused by inaccurate manufacturing of positioning components on the work piece positioning surface or fixture is called reference position error. 2. The positioning error caused by the non-coincidence of the process reference and positioning reference of the work piece is called reference inaccuracy. coincidence error.
38. Basic requirements for the design of work piece clamping devices.
1. During the clamping process, it should be able to maintain the correct position obtained when the work piece is positioned.
2. The clamping force is appropriate. The clamping mechanism should ensure that the workpiece does not loosen or vibrate during processing, and at the same time avoid improper deformation and surface damage of the work piece. The clamping mechanism should generally have a self-locking effect.
3. The clamping device should be easy to operate, labor-saving and safe.
4. The complexity and automation of the clamping device should be compatible with the production batch and production method. The structural design should be simple, compact and use standardized components as much as possible.
39. What are the three elements to determine the clamping force?
What are the principles of clamping force direction and action point selection?
Size & direction & action point
The selection of the clamping force direction should generally follow the following principles:
1. The direction of the clamping force should be conducive to the accurate positioning of the workpiece without destroying the positioning. For this reason, the main clamping force is generally required to be vertical to the positioning surface;
2. The direction of the clamping force should be as consistent as possible with the direction of the greater rigidity of the workpiece to reduce the clamping deformation of the workpiece;
3. The direction of the clamping force should be consistent with the direction of the cutting force and the gravity of the workpiece as far as possible, so as to reduce the required clamping force.
General principles for selection of clamping force point:
1. The action point of the clamping force should be directly in the support surface formed by the support element to ensure that the position of the workpiece has been obtained unchanged
2. The point of action of the clamping force should be at a place with better rigidity to reduce the clamping deformation of the workpiece. 3. The point of action of the clamping force should be as close as possible to the processing surface to reduce the turning moment of the workpiece caused by the cutting force.
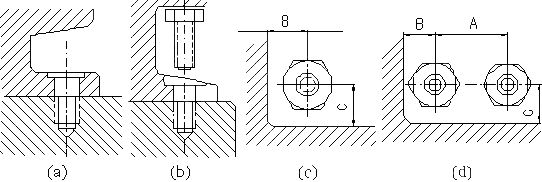
40. What are the commonly used clamping mechanisms?
Focus on analyzing and mastering the wedge clamping mechanism.
- Wedge clamping structure;
- Spiral clamping structure;
- Eccentric clamping structure;
- Hinge clamping structure;
- Centering clamping structure;
- Linkage clamping structure.
41. How to classify according to the structural characteristics of drilling jigs?
How to classify according to the structural characteristics of the drill sleeve?
What are the types of connection between the drill template and the clamp?
According to the structural characteristics of the drilling jig:
1. Fixed jig; 2. Rotary jig; 3. Flip jig 4. Cover jig; 5. Sliding column jig
Classification of drilling jig structure characteristics:
1. Fixed jig; 2. Replaceable jig; 3. Quick-change jig; 4. Special jig.
The connection method between the drilling template and the clamping body:
Fixed, hinged, separated, suspended.
The Future of CNC Machinist
CNC machinists should have the ability of "independent innovation" and "flexibility". In a rapidly changing market, the more knowledge CNC machinists have, the stronger their comprehension and creativity, and the richer their experience, the more capable they are of coping with the future, and the more beneficial it is to improve the technological development capabilities of modern enterprises and contribute to the development of enterprises. bigger.
If you need an outsourcing company, contact us today to get a quote. Tuofa CNC machining engineers and machinists have the ability to help you better complete the project, CNC machining is what we do. We are experts, and we will bring our knowledge and experience to you in CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication, and 3D printing services. Want more? Keep learning with our free Tuofa blog.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 Complete Stainless Steel Welding Process, The Mechanic Must Know It!
Complete Stainless Steel Welding Process, The Mechanic Must Know It! 







