316 vs 18-8 Stainless Steel: Which is Better?
 Sep 26,2024
Sep 26,2024

18-8 and 316 alloys are the stainless-steel grades and well known for their corrosion resistance and good strength. There is a slight difference between 18-8 steel and 316 which is the presence of 2% of Molybdenum content in the chemical composition. This article will be covering the main aspects related 316 and 18-8 stainless steel to make you understand their properties.
What is 18-8 Stainless Steel?
The main alloying elements of 18-8 steel are 18% and 8% of Cr and Ni, respectively. 304 steel is another name of 18-8 steel. 18-8 stainless steel is austenitic stainless steel. Its applications are found in marine, surgical equipment’s and utensils due to the easy fabrication and high corrosion resistance.

18-8 Stainless Steel Equivalent
It is equivalent to 304 stainless steels.
| Country | Standard | Grade |
|---|---|---|
| United States | ASTM | 304 |
| United Kingdom | BS | 304S15 |
| Germany | DIN | 1.4301 |
| Japan | JIS | SUS304 |
| China | GB | 0Cr18Ni9 |
| France | NF | Z2CN18-10 |
| Italy | UNI | X5CrNi18-10 |
Does 18-8 Stainless Steel Rust?
No, 18-8 stainless steel contains 18% Chromium which increases its corrosion resistance in ordinary conditions. Chromium has ability to form chromium oxide which act as protective layer from further oxidation. Rust occurs due to the presence of chlorine.
What is 316 Stainless Steel?
Molybdenum is the main alloying element which creates the main difference between 18-8 and 316 stainless steels.
What are the Disadvantages of 316 Stainless Steel?
Corrosion resistance and stress corrosion cracking are the main disadvantages along with the high cost.

What are the Advantages of 316 Stainless Steel?
316 Stainless Steel has many advantages like strength formability and ease of maintenance, but it is known for its enhanced standard corrosion resistance in harsh conditions like chloride-rich conditions which makes It useful for marine applications.
Does 316 Stainless Steel Rust?
No, it does not rust. Every material faces corrosion issues, which creates a difference between them in the speed of rusting. When 316 stainless steel remains in seawater for a long time, it starts to rust on its surface but much slower than 18-8 stainless steel.
Difference Between 18-8 and 316 Stainless Steel
The only difference between 18-8 and 316 grades is the chemical composition i.e. Mo element. The Mo element causes increased corrosion resistance than 18-8 stainless steel. And second is the cost difference between them, 316 is more expensive than 18-8 stainless steel.
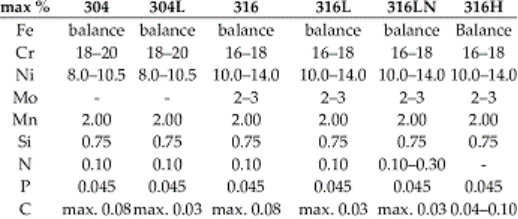
Differences in Chemical Composition
18-8 depicts the presence of 18wt% chromium and 8wt% Nickel, respectively. Other alloying elements are 20wt% of Manganese, 0.75 wt.% of Silicon and little concentration of C, S, P, and N.
While 316 Stainless Steel contains Cr (16-18%), Ni (10-14%), Mo (2%), Si (0.75%), C (0.08%) and trace amounts of S, P and Ni. For further information, read grade 316 stainless steel.
18-8 vs 316 Mechanical Properties
Choose between 18-8 and 316 stainless steel? Learn about their hardness, toughness, and corrosion resistance to make an informed decision.
18-8 vs 316 Stainless Steel Strength
18-8 is weaker than 316 stainless steels. It is used where load bearing and corrosion resistance are required aerospace wire baskets and carts.
Hardness
No appreciable difference is recorded in the hardness of 316 and 18-8 whish is 217 HB and 210-220, respectively. But in very close comparison, 316 is harder than 18-8 grade due to Mo. Check out the Marine Bolt Supply for a more detailed comparison.
Yield strength
Both grades have the same yield strength of 30 Ksi at 0.2% on the stress-strain curve.
Elongation
18-8 Stainless Steel offers 40-60% elongation at the break while 316 offers 40-50% elongation at break which means 18-8 grades are relatively more ductile than 316 grade.
Impact strength
18-8 stainless steel grade has an impact strength of 120-180 J at room temperature while 316 grade offers an impact strength of 100-160 J at room temperature.
Fatigue strength
316 and 18-8 stainless have 210-230 MPa and 240 MPa fatigue strength at room temperature in open air for 10 million cycles, respectively. Fatigue strength is highly affected by temperature, corrosive environment and surface roughness.
Toughness
Both grades have excellent toughness but 18-8 stainless steel shows higher charpy impact toughness (120-180 J) than 316 (100-160 J).
Tensile Strength
The ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of 18-8 grade is in the range of 515 – 720 MPa while 316 grade has a UTS of 485 – 700 MPa. The ultimate strength of the 316 is higher than the 18-8 steels.
Load-Bearing and Structural Integrity
316 SS has 567 MPa tensile strength whereas 18-8 grade has 515 MPa of tensile strength, respectively. Such tensile strength makes both grades applicable under stress conditions and structural applications.
Machinability
Mo makes 316 grade difficult to machine. 18-8 stainless steel is softer and preferable for manufacturing processes which require a lot of forming etc.
Weldability
The same is the case with weldability as machinability for 316 stainless steel due to Mo. Since it is harder than 18-8 grade, that’s why it is difficult to weld.
Price and Cost-Effectiveness
Ultimately it depends on the primary required properties. If the primary properties include corrosion resistance and load bearing, then the 316 is suitable but the cost will be higher. And in conditions like in kitchen or storage pipes etc. 18-8 grade is very cost-effective.
Try Tuofa Now!
Send drawings to info@tuofa-cncmachining.com
Tuofa Engineer Support Team
Real human quotes are more accurate than software quotes
Applications of 18-8 and 316 Stainless Steels
Both are famous for their use in corrosive environments, but the difference in their application is given below:
Food Processing and Medical Use of 18-8 Stainless Steel

18-8 grade is mainly used in food processing and medical use because of its ease of cleaning and non-reactivity. Following picture shows the food container made of 18-8 grade:
Marine and Industrial Applications of 316 Stainless Steel
316 grade of stainless steel is used in marine applications as marine water is rich with chlorine.
Fasteners
18-8 and 316 both grades are used in the manufacturing of fasteners but 316 is used to make those fasteners which are used in harsh conditions like sea water which contains salt in it.
Watch the following YouTube videos for a more detailed review:
18-8 vs 316 stainless steel bolts and 316 vs 18-8 stainless steel screws
316 is usually used for the bolts and screws have to face high corrosion resistance or high load bearing properties.
Which is Better 316 or 18-8 Stainless Steel?
18-8 stainless steel possess good corrosion resistance and is cost effective. But when corrosion resistance and load-bearing properties are required, 316 grade is more suitable but the cost will be higher.
FAQ
Is 18-8 the Same as 304 Stainless Steel?
No, they are not the same. 18-8 differs in composition mainly from 316. 316 grade contains 2% Mo which increases both strength and corrosion resistance.
Is 18-8 Stainless Steel Magnetic?
316 and 18-8 both are non-magnetic because of their austenitic microstructure but at high temperatures, these grades may show some magnetic behavior but still it's negligible.
How to Prevent Rust in 18-8 and 316 Stainless Steels

Daily cleansing processes and protective coatings in the prevention of corrosion. For more knowledge about the prevention of corrosion, visit Marsh Fasteners.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home

 Difference Between 303 and 304 Stainless: Which is Better?
Difference Between 303 and 304 Stainless: Which is Better? 







