Why Implement Geometric Dimension and Tolerances Processes?
 Sep 06,2024
Sep 06,2024

Geometric Dimension and Tolerancing (GD&T) is important for making parts that fit together perfectly. It shows exact sizes and shapes, helping reduce mistakes in manufacturing. GD&T makes it easier to produce high-quality parts that work well together, lowering costs and saving time. It is especially useful in industries like aerospace, automotive, and custom machining.
4 Key Factors of Geometric Dimension and Tolerance in Manufacturing
Improved Communication
GD&T provides a standardized language that minimizes crimes and misconstructions between contrivers, masterminds, and manufacturers. By easily defining permissible variations in part figure, GD&T ensures that everyone involved in the product process is on the same runner.
Enhanced Functionality
GD&T focuses on the functional conditions of corridor, icing that they fit together and operate as intended. By controlling the figure of corridor with perfection, GD&T helps help issues like misalignment, poor fit, and mechanical failures.
Cost Reduction
Enforcing GD&T can lead to significant cost savings by reducing scrap, rework, and bond claims. By icing that corridor are manufactured to the correct specifications the first time, GD&T minimizes the need for expensive corrections.
Increased Efficiency
GD&T provides clear guidance for machinists and inspectors, streamlining the product process. By using GD&T symbols and tolerances, manufacturers can snappily understand the design intent and produce corridor that meet the needed norms with lesser effectiveness.
How Geometric Dimension and Tolerances Works
GD&T workshop by using a system of symbols and point control frames to define permissible variations in part figure. These rudiments work together to specify how much a part can diverge from its nominal confines and still serve rightly. GD&T symbols represent colorful geometric controls, similar as flatness, straightness, and circularity, while point control frames contain the specific tolerances information for each point. These symbols and frames are placed on engineering delineations or 3D models to communicate the design intent easily and constantly.
Common GD&T Symbols and Their Meanings
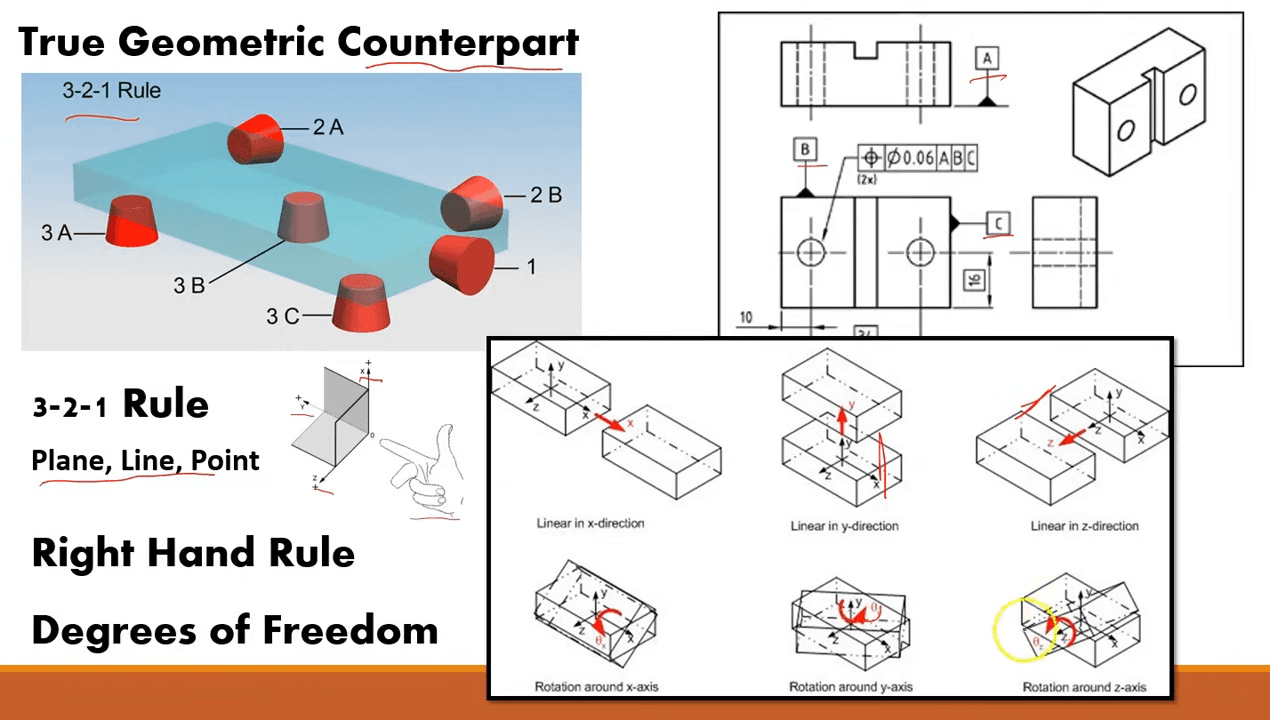
In GD&T, symbols play a pivotal part in communicating geometric Tolerances on engineering drawings. Each symbol represents a specific type of geometric control, and understanding these symbols is essential for interpreting and applying GD&T effectively. Some of the most common GD&T symbols include
Straightness
The straightness symbol is used to control the permissible divagation of a point, similar as a line or an axis, from a impeccably straight line. This symbol ensures that the point remains within a specified Tolerances zone, which is critical for corridor that must fit or move easily in their assembly.
Flatness
The flatness symbol controls the permissible variation in a face's flatness, icing that all points on the face taradiddle within two resemblant planes. This is particularly important for icing proper sealing or contact between lovemaking shells.
Circularity( Roundness)
The circularity symbol is used to control the roundness of a point, similar as a hole or a shaft. This symbol ensures that the point remains within a specified Tolerances zone, which is pivotal for corridor that rotate or fit within a indirect assembly.
Cylindricity
Cylindricity combines both straightness and circularity, controlling the permissible variation in the form of a spherical feature. This symbol is used when both the roundness and straightness of a point are critical for its function.
Profile of a face
The profile of a face symbol controls the permissible variation in the shape of a face, icing that it conforms to a specified profile within a Tolerances zone. This is generally used for complex, twisted shells where maintaining the precise shape is essential for the part's function.
Profile of a Line
Analogous to the profile of a face, the profile of a line symbol controls the permissible variation in the shape of a line, icing that it follows a specified profile within a Tolerances zone. This is frequently used for controlling the form of edges or boundaries on a part.
Angularity
The angularity symbol is used to control the angle of a point relative to a datum. This symbol ensures that the point is within a specified Tolerances zone at the needed angle, which is essential for corridor that must align at specific angles in an assembly.
Perpendicularity
The perpendicularity symbol controls the 90- degree relationship between two features, similar as a face and an axis. This is critical for icing that corridor fit together at right angles, which is common in mechanical assemblies.
Community
The community symbol controls the permissible variation in the resemblant relationship between two features, icing that they remain within a specified Tolerances zone. This is important for corridor that must move or fit together easily in resemblant alignment.
Position
The position symbol is one of the most protean and extensively used in GD&T. It controls the permissible variation in the position of a point relative to a detail, icing that the point is within a specified Tolerances zone. This is particularly important for icing the correct assembly of corridor with multiple features.
Concentricity
The concentricity symbol controls the permissible variation in the centerline of a point relative to a detail axis. This is used for features that must be centered relative to other features, similar as a shaft within a bearing.
Harmony
The harmony symbol controls the permissible variation in the harmony of a point relative to a detail plane. This is important for corridor that must be balanced or centered in their assembly.
Each of these symbols plays a critical part in defining the permissible variations in a part's figure, icing that the part will serve as intended indeed if there are minor diversions in its manufacturing process.
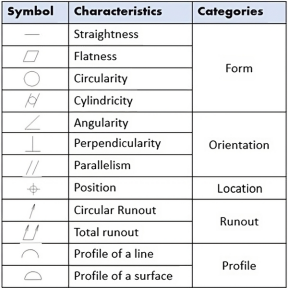
Figure 3: GD&T Symbols and Their Meanings.
Tolerancing in CNC Machining
Role of Tolerances in CNC Machining
Tolerances are pivotal in CNC machining for achieving the asked delicacy and perfection in cultivated corridor. CNC machines operate with high perfection, and GD&T helps insure that the corridor produced meet the design intent and function rightly. By specifying precise tolerances, GD&T reduces the liability of blights and ensures that corridor fit together as intended.
ISO 2768-f vs. ISO 2768-m
ISO 2768 is a extensively used standard in CNC machining for defining general tolerances. The standard is divided into different grades, with ISO 2768- f( forfeiture) and ISO 2768- m( medium) being the most common. Fine tolerances are used for corridor taking high perfection, while medium tolerances are suitable for lower critical operations. Choosing the applicable tolerances grade depends on the part's conditions and the machining process's capabilities.
GD&T Tolerancing Guidelines
When applying GD&T to CNC crafted corridor, it's essential to consider the capabilities and limitations of the machining processes. Factors similar as machine delicacy, tool wear and tear, and material parcels can affect the attainable tolerances. opting the applicable tolerances norms, similar as ISO 2768- f or ISO 2768- m, is pivotal for icing that the corridor meet the design specifications without compromising manufacturability.
Tolerance Stack Analysis
Tolerances mound analysis is a critical conception in GD&T, particularly when dealing with assemblies. It involves calculating the accretive effect of individual tolerances on the overall assembly. Proper tolerances mound analysis ensures that the final assembly meets the needed specifications and functions rightly.
Prototype and Manufacture Parts Rapidly With CNC Machining
GD&T plays a vital part in rapid-fire prototyping and manufacturing, especially in CNC machining. By using GD&T in CNC machining, masterminds and manufacturers can snappily and directly produce prototypes and final corridor that meet strict design specifications. This perfection is critical in diligence where indeed minor diversions can lead to significant issues in part functionality or assembly.
With CNC machining, the process of rephrasing GD&T specifications from design to product is streamlined, allowing for rapid-fire replication and refinement of prototypes. This effectiveness not only accelerates the development cycle but also ensures that the final corridor cleave nearly to the original design intent, minimizing the need for expensive adaptations or rework.
Also, the capability to fleetly prototype using GD&T allows masterminds to assess the fit, form, and function of corridor in real- world scripts. By doing so, implicit issues can be linked and resolved beforehand in the development process, reducing the threat of failures in product. The combination of GD&T with CNC machining therefore provides a important toolset for masterminds looking to bring high- quality products to request snappily and efficiently.
Applications of GD&T in Various Industries
Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing( GD&T) is extensively used across colorful diligence due to its perfection, clarity, and effectiveness in icing part functionality. Its operation extends beyond traditional manufacturing, chancing applicability in diligence where perfection is critical, similar as aerospace, automotive, medical bias, and electronics.
Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace assiduity, where safety and performance are consummate, GD&T is essential for icing that all corridor fit together impeccably and serve reliably under extreme conditions. Components in aircraft and spacecraft are subject to rigorous examinations, and GD&T provides the necessary frame for controlling the critical confines and Tolerances that impact performance and safety.
Automotive Industry
The automotive assiduity also relies heavily on GD&T to ensure that corridor are exchangeable, fit together rightly, and function as intended. GD & T helps in controlling the Tolerances of critical factors similar as machine corridor, transmissions, and body panels, icing that vehicles meet performance and safety norms.
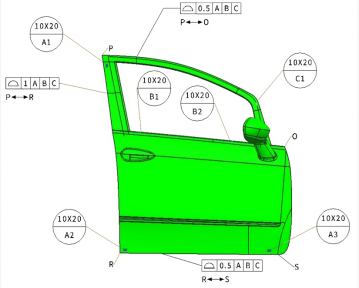
Figure 4 GD&T in automotive industry
Medical bias
In the medical device assiduity, perfection is pivotal for icing the safety and effectiveness of bias used in patient care. GD & T is used to control the figure of factors similar as implants, surgical instruments, and individual outfit, icing that they meet the strict conditions for delicacy and trustability.
Electronics Industry
The electronics assiduity also benefits from the operation of GD&T, particularly in the manufacturing of factors similar as published circuit boards( PCBs) and microelectronics. GD & T helps in controlling the Tolerances of features that are critical for the proper functioning of electronic bias, similar as connector legs, solder pads, and element placements.
Consumer Products
Indeed in consumer products, where aesthetics and ergonomics are frequently important, GD&T plays a part in icing that corridor fit together rightly and serve as intended. From ménage appliances to consumer electronics, GD&T helps in maintaining the quality and trustability of products that people use every day.
GD&T in a part design (Example)
Conclusion
Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) is necessary tool in ultramodern engineering and manufacturing, furnishing a standardized language for defining and communicating the permissible variations in part geometry. By icing that corridor meet their design intent and function rightly in their final operation, GD&T plays a critical part in maintaining quality, thickness, and trustability in manufacturing.
This companion has handed a comprehensive overview of GD&T, covering its principles, symbols, rules, and operations in colorful industries. Whether you're a seasoned mastermind or new to the field, understanding and applying GD&T is essential for icing the success of your designs and the quality of the products you produce.
By learning the principles of GD&T, you can improve the clarity of your engineering delineations, reduce the liability of crimes in manufacturing, and ensure that your corridor meets the loftiest norms of perfection and performance. In a world where perfection and trustability are decreasingly important, GD&T offers the tools you need to succeed in engineering and manufacturing.
 Tel/WeChat:
Tel/WeChat:  Email:
Email: 
 Home
Home
 Aluminum Bronze Machining: Properties, Challenges
Aluminum Bronze Machining: Properties, Challenges 







